A Global Tapestry of Green: Exploring the Grasslands of the World
Related Articles: A Global Tapestry of Green: Exploring the Grasslands of the World
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Global Tapestry of Green: Exploring the Grasslands of the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Global Tapestry of Green: Exploring the Grasslands of the World

Grasslands, vast expanses of land dominated by grasses and other herbaceous plants, are among the most widespread and diverse biomes on Earth. From the rolling hills of the American prairies to the vast steppes of Eurasia, these ecosystems play a vital role in supporting a rich tapestry of life and providing essential services to humankind. Understanding the distribution, characteristics, and significance of grasslands is crucial for appreciating their ecological value and ensuring their sustainable management.
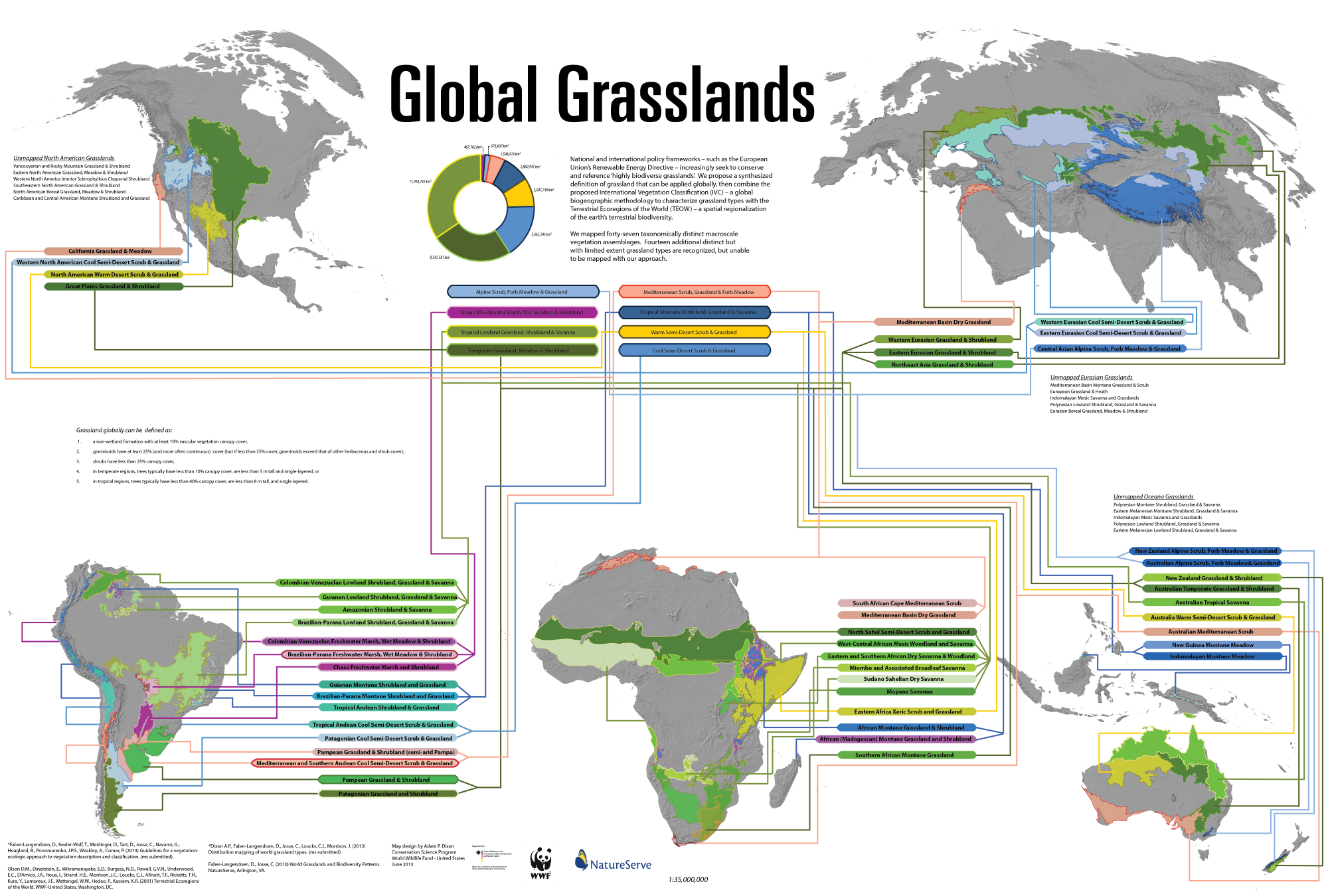
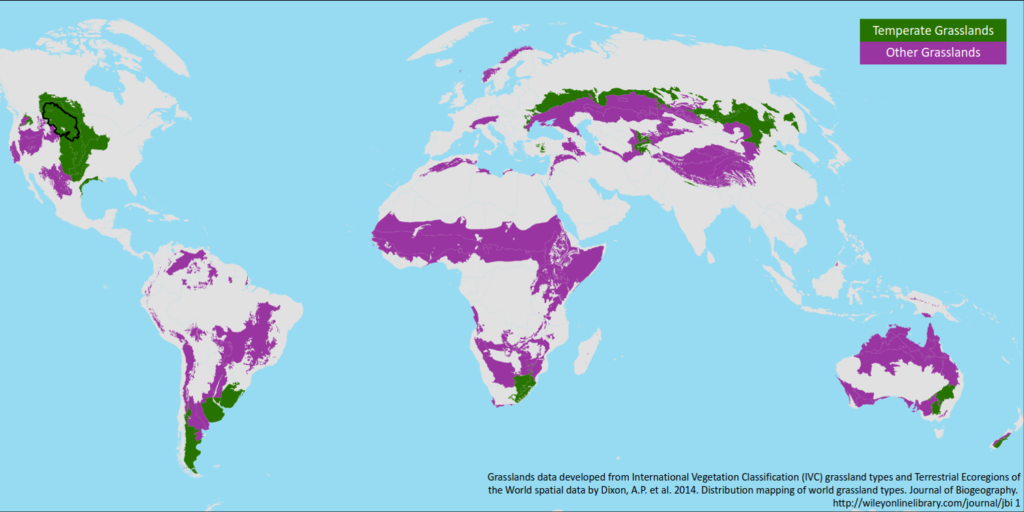
A Global Map of Grasslands:
Grasslands occupy a significant portion of the Earth’s land surface, found across a wide range of latitudes and climates. Their distribution is primarily determined by rainfall, temperature, and soil conditions. While they are often referred to as "prairies," "savannas," or "steppes," these terms are often used interchangeably and may denote specific variations within the broader category of grasslands.
Types of Grasslands:
- Temperate Grasslands: These grasslands are found in mid-latitude regions with moderate rainfall and distinct seasons. Examples include the North American prairies, the Eurasian steppes, and the Pampas of South America.
- Tropical Grasslands (Savannas): Characterized by warm temperatures, distinct wet and dry seasons, and scattered trees, savannas are found in Africa, South America, and Australia.
- Mediterranean Grasslands: Occurring in regions with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, these grasslands are found in areas around the Mediterranean Sea, California, and parts of Australia.
- Mountain Grasslands: Found at higher altitudes, these grasslands are often characterized by cold temperatures and harsh conditions.
Key Characteristics of Grasslands:
- Dominance of Grasses: Grasslands are defined by the presence of grasses as the dominant plant life.
- Low Tree Density: While some grasslands may have scattered trees, they are typically characterized by open spaces with low tree density.
- Seasonal Variation: Grasslands exhibit significant variation in plant growth and biomass throughout the year, influenced by rainfall and temperature.
- Adaptable Flora and Fauna: The plants and animals inhabiting grasslands have evolved unique adaptations to survive the harsh conditions, including drought, fire, and grazing pressure.
Ecological Importance of Grasslands:
Grasslands are critical for maintaining biodiversity and supporting a wide range of ecological processes. Their importance can be summarized as follows:
- Habitat for Diverse Wildlife: Grasslands provide habitat for a vast array of animals, including large herbivores like bison, zebras, and kangaroos, as well as smaller mammals, birds, reptiles, and insects.
- Carbon Sequestration: Grasslands act as significant carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in their soils and plant biomass.
- Soil Health: The deep root systems of grasses help to improve soil structure, enhance water infiltration, and prevent erosion.
- Water Cycle Regulation: Grasslands play a crucial role in regulating the water cycle by influencing evapotranspiration and groundwater recharge.
- Nutrient Cycling: Grasslands are vital for nutrient cycling, breaking down organic matter and releasing essential nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Human Impact on Grasslands:
Human activities have significantly impacted grasslands worldwide, leading to habitat loss, fragmentation, and degradation. Key threats include:
- Agriculture: Conversion of grasslands to agricultural land for crop production and livestock grazing has been a major driver of habitat loss.
- Urbanization and Development: Expansion of urban areas and infrastructure projects have fragmented grasslands and reduced their overall extent.
- Overgrazing: Excessive grazing by livestock can damage grasslands, leading to soil erosion, plant loss, and reduced biodiversity.
- Invasive Species: Introduction of non-native plant and animal species can disrupt grassland ecosystems and threaten native species.
- Climate Change: Climate change is altering rainfall patterns, increasing the frequency and intensity of droughts, and impacting the productivity and resilience of grasslands.
Conservation and Management of Grasslands:
Protecting and managing grasslands is essential for maintaining their ecological services and ensuring the survival of the diverse species they support. Conservation efforts focus on:
- Habitat Restoration: Restoring degraded grasslands through techniques like re-seeding, controlled burning, and invasive species removal.
- Sustainable Land Management: Promoting sustainable grazing practices, reducing livestock density, and implementing rotational grazing systems.
- Protected Areas: Establishing protected areas to safeguard intact grassland ecosystems and provide refuge for wildlife.
- Policy and Legislation: Developing and implementing policies and legislation to regulate land use, protect grasslands from conversion, and promote sustainable management practices.
FAQs about Grasslands:
Q: What is the difference between a prairie and a savanna?
A: Prairies are temperate grasslands with a higher density of grasses and fewer trees compared to savannas. Savannas are tropical grasslands characterized by scattered trees and a distinct wet and dry season.
Q: Why are grasslands important for biodiversity?
A: Grasslands support a diverse array of plant and animal life, providing habitat for a wide range of species, including large herbivores, predators, birds, reptiles, and insects.
Q: What are the main threats to grasslands?
A: Grasslands face threats from agriculture, urbanization, overgrazing, invasive species, and climate change.
Q: How can we help conserve grasslands?
A: We can help conserve grasslands by supporting sustainable land management practices, supporting protected areas, and advocating for policies that protect grasslands from conversion and degradation.
Tips for Understanding Grasslands:
- Visit a grassland: Experience the beauty and diversity of grasslands firsthand by visiting a local park or nature reserve.
- Learn about local grassland ecosystems: Research the specific grasslands in your region, their unique characteristics, and the threats they face.
- Support organizations working to conserve grasslands: Donate to or volunteer with organizations dedicated to protecting grasslands and their biodiversity.
- Practice sustainable land use: If you own or manage land, consider adopting sustainable practices that minimize impacts on grasslands.
Conclusion:
Grasslands are essential ecosystems that play a vital role in supporting biodiversity, regulating climate, and providing essential services to humankind. Understanding their distribution, characteristics, and importance is crucial for promoting their conservation and ensuring their long-term sustainability. By adopting sustainable land management practices, supporting protected areas, and advocating for policies that protect grasslands, we can help preserve these vital ecosystems for future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Global Tapestry of Green: Exploring the Grasslands of the World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!