A Journey Through Africa’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: A Journey Through Africa’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Africa’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Journey Through Africa’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Journey Through Africa’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Majestic Spine of Africa: A Glimpse into the Continent’s Geological Past
- 3.2 A Tapestry of Biodiversity: The Ecological Significance of Africa’s Mountains
- 3.3 The Cultural Tapestry: Humans and Mountains in Africa
- 3.4 Navigating the Peaks: Understanding the Challenges and Opportunities
- 3.5 FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Africa’s Mountain Ranges
- 3.6 Tips for Exploring Africa’s Mountain Ranges
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Legacy of Mountains, A Future of Sustainability
- 4 Closure
A Journey Through Africa’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
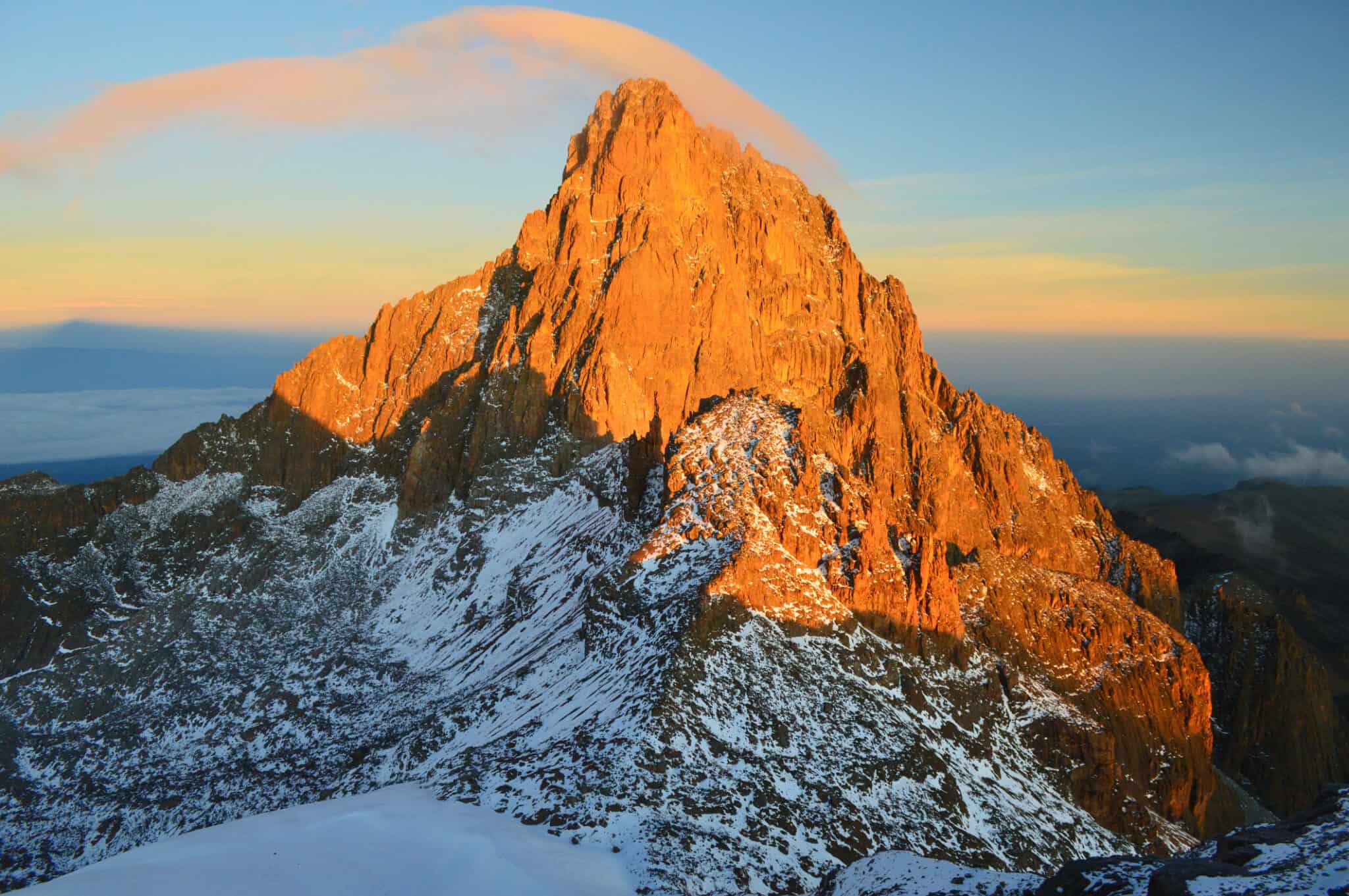

Africa, the second-largest continent, is renowned for its vast plains, diverse ecosystems, and vibrant cultures. However, beneath its sprawling savannas and arid deserts lies a hidden treasure: a network of majestic mountain ranges that shape the continent’s geography and influence its climate, biodiversity, and human history.
This article delves into the intricacies of Africa’s mountain ranges, providing a comprehensive overview of their geographical distribution, geological origins, ecological significance, and cultural influence. We will explore the unique characteristics of each range, highlighting their distinctive features and the role they play in the continent’s tapestry.
The Majestic Spine of Africa: A Glimpse into the Continent’s Geological Past
Africa’s mountain ranges are not merely scenic landmarks; they are testaments to the continent’s dynamic geological history. The formation of these ranges is intricately linked to the tectonic plates that have shaped Earth’s surface over millions of years.
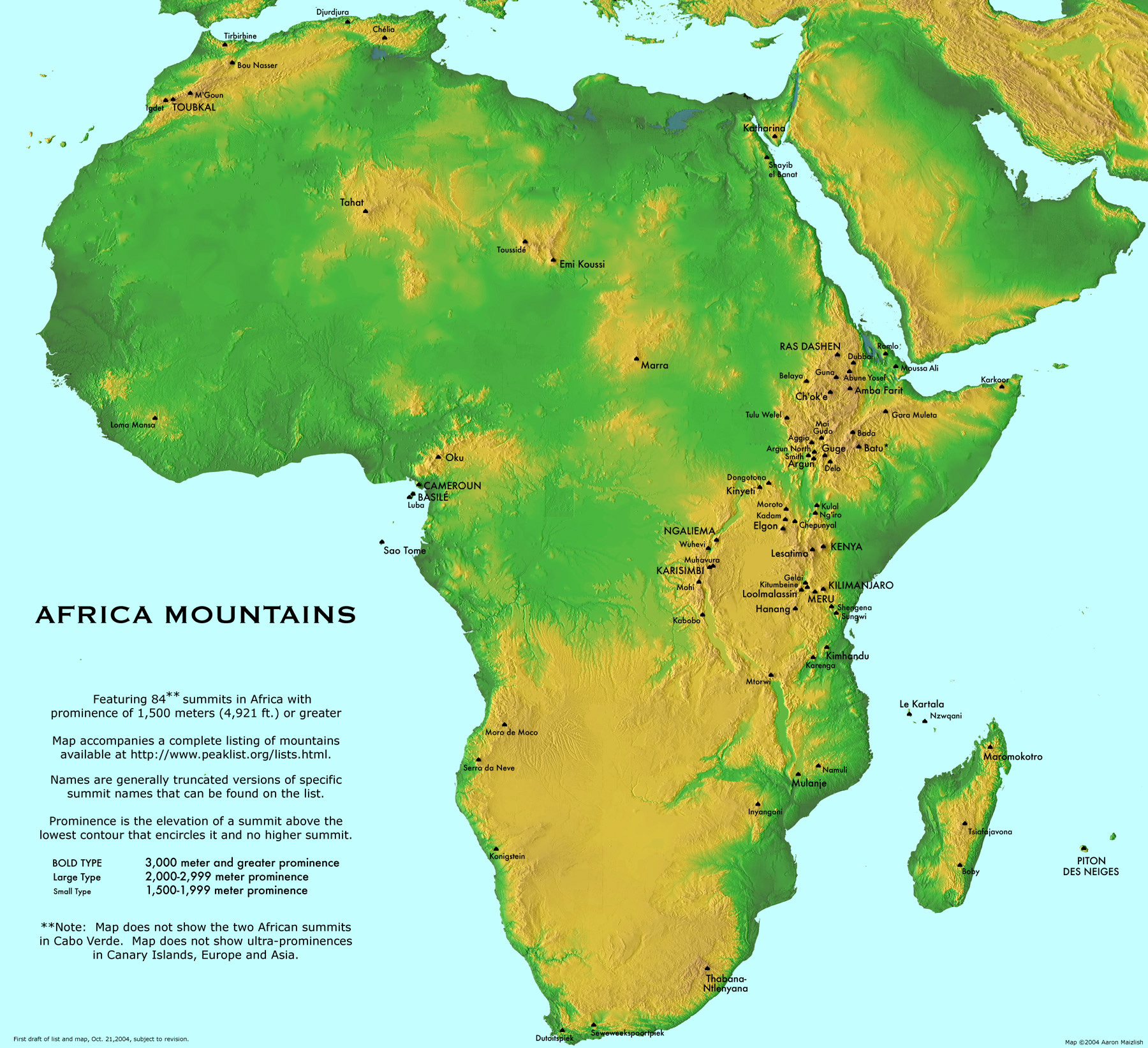
The Atlas Mountains: These majestic mountains, located in North Africa, are the result of the collision between the African and Eurasian tectonic plates. This collision, which began millions of years ago, created the Atlas Mountain range, stretching across Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. The Atlas Mountains are a significant geological feature, influencing the climate of North Africa and providing a natural barrier between the Mediterranean Sea and the Sahara Desert.
The Ethiopian Highlands: This vast plateau, located in the Horn of Africa, is a result of volcanic activity and tectonic uplift. The Ethiopian Highlands are home to numerous volcanic peaks, including the iconic Mount Ras Dashen, the highest mountain in Ethiopia. The highlands play a crucial role in regulating rainfall patterns and providing a unique habitat for diverse flora and fauna.
The East African Rift Valley: This geological wonder is a consequence of the separation of the African plate, creating a vast rift valley stretching from the Red Sea to Mozambique. The East African Rift Valley is home to some of the most iconic mountain ranges in Africa, including the Ruwenzori Mountains, the Virunga Mountains, and the Kilimanjaro Massif. These mountains, formed by volcanic activity and tectonic uplift, are characterized by their dramatic peaks, glaciers, and unique ecosystems.
The Drakensberg Mountains: Located in Southern Africa, the Drakensberg Mountains are a result of volcanic activity and erosion. They are known for their sheer cliffs, dramatic rock formations, and breathtaking views. The Drakensberg Mountains are a significant cultural landmark, with ancient rock art sites dating back thousands of years.
A Tapestry of Biodiversity: The Ecological Significance of Africa’s Mountains
Africa’s mountain ranges are not only geological marvels but also vital ecological sanctuaries. They provide diverse habitats for a wide range of flora and fauna, many of which are endemic to these unique environments.
High Altitude Ecosystems: The high altitudes of Africa’s mountains create unique microclimates, characterized by cold temperatures, strong winds, and limited sunlight. These conditions have led to the evolution of specialized plant and animal communities, adapted to survive in these harsh environments. For example, the alpine meadows of Mount Kilimanjaro are home to unique species of wildflowers, while the high-altitude forests of the Ruwenzori Mountains are home to the elusive mountain gorilla.
Water Towers of Africa: Africa’s mountain ranges are vital water sources, providing essential water resources for millions of people living in surrounding areas. The mountains act as "water towers," capturing rainfall and releasing it gradually through rivers and streams. This crucial role makes them essential for agriculture, hydropower, and drinking water supply.
Biodiversity Hotspots: Many of Africa’s mountain ranges are recognized as biodiversity hotspots, areas with a high concentration of endemic species. These areas are particularly vulnerable to habitat loss and climate change, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts to protect these unique ecosystems.
The Cultural Tapestry: Humans and Mountains in Africa
Africa’s mountain ranges have played a significant role in shaping the continent’s cultural landscape. They have served as natural barriers, influencing the movement of people and the development of distinct cultures.
Ancient Cultures and Traditions: The mountains have provided refuge for indigenous communities, fostering the development of unique traditions and beliefs. The San people of Southern Africa, for example, have a deep spiritual connection to the Drakensberg Mountains, reflected in their ancient rock art and oral traditions.
Mountain Communities: The slopes of Africa’s mountains are home to numerous communities, adapted to the unique challenges of living at high altitudes. These communities have developed sustainable practices, utilizing local resources and adapting to the harsh environment.
Tourism and Development: In recent years, Africa’s mountain ranges have become increasingly popular tourist destinations, attracting visitors from around the world. This influx of tourism has brought economic opportunities to local communities, but it also poses challenges related to conservation and sustainable development.
Navigating the Peaks: Understanding the Challenges and Opportunities
While Africa’s mountain ranges offer immense beauty and ecological value, they also face significant challenges, primarily related to climate change, human activities, and conservation.
Climate Change Impacts: Climate change is impacting Africa’s mountain ecosystems, leading to changes in rainfall patterns, glacial retreat, and increased temperatures. These changes threaten the delicate balance of these unique environments, impacting biodiversity and water resources.
Human Activities: Human activities, such as deforestation, mining, and agriculture, can have detrimental effects on mountain ecosystems. These activities can lead to soil erosion, habitat loss, and pollution, undermining the ecological integrity of these fragile environments.
Conservation Efforts: Recognizing the importance of preserving Africa’s mountain ranges, numerous conservation efforts are underway. These efforts involve establishing protected areas, promoting sustainable practices, and raising awareness about the importance of these ecosystems.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Africa’s Mountain Ranges
Q: What is the highest mountain in Africa?
A: Mount Kilimanjaro, located in Tanzania, is the highest mountain in Africa, with a summit elevation of 5,885 meters (19,308 feet).
Q: What are the most popular mountain ranges for trekking in Africa?
A: Some of the most popular mountain ranges for trekking in Africa include the Atlas Mountains, the Ruwenzori Mountains, the Virunga Mountains, and the Kilimanjaro Massif.
Q: What are the main threats to Africa’s mountain ecosystems?
A: The main threats to Africa’s mountain ecosystems include climate change, deforestation, mining, and agriculture.
Q: What are some examples of endemic species found in Africa’s mountains?
A: Some examples of endemic species found in Africa’s mountains include the mountain gorilla, the Ethiopian wolf, and the giant lobelia.
Q: What are the benefits of preserving Africa’s mountain ranges?
A: Preserving Africa’s mountain ranges is crucial for protecting biodiversity, regulating water resources, and maintaining the cultural heritage of local communities.
Tips for Exploring Africa’s Mountain Ranges
Plan Ahead: Research your chosen mountain range, understand the necessary permits and regulations, and prepare for the altitude and weather conditions.
Respect Local Cultures: Be mindful of local customs and traditions, and obtain permission before entering sacred sites or taking photographs.
Leave No Trace: Pack out all your trash and minimize your impact on the environment.
Stay Safe: Travel with experienced guides, be aware of potential hazards, and prioritize safety at all times.
Support Local Communities: Consider staying in locally owned accommodations and patronizing local businesses to support sustainable tourism.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Mountains, A Future of Sustainability
Africa’s mountain ranges stand as a testament to the continent’s geological history, ecological diversity, and cultural richness. They are vital for the well-being of millions of people and home to unique and irreplaceable ecosystems. As we navigate the challenges of climate change and human activities, it is crucial to prioritize the conservation and sustainable management of these majestic landscapes. By understanding the importance of these mountain ranges and embracing responsible tourism, we can ensure that their beauty and ecological value continue to inspire generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Africa’s Mountainous Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!