A Journey Through Time and Space: Understanding the Germany-Poland Border
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time and Space: Understanding the Germany-Poland Border
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time and Space: Understanding the Germany-Poland Border. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time and Space: Understanding the Germany-Poland Border

The border between Germany and Poland is more than just a line on a map. It represents a complex history, a shared cultural heritage, and a constantly evolving relationship. Understanding this border requires delving into the past, examining the present, and considering the future.
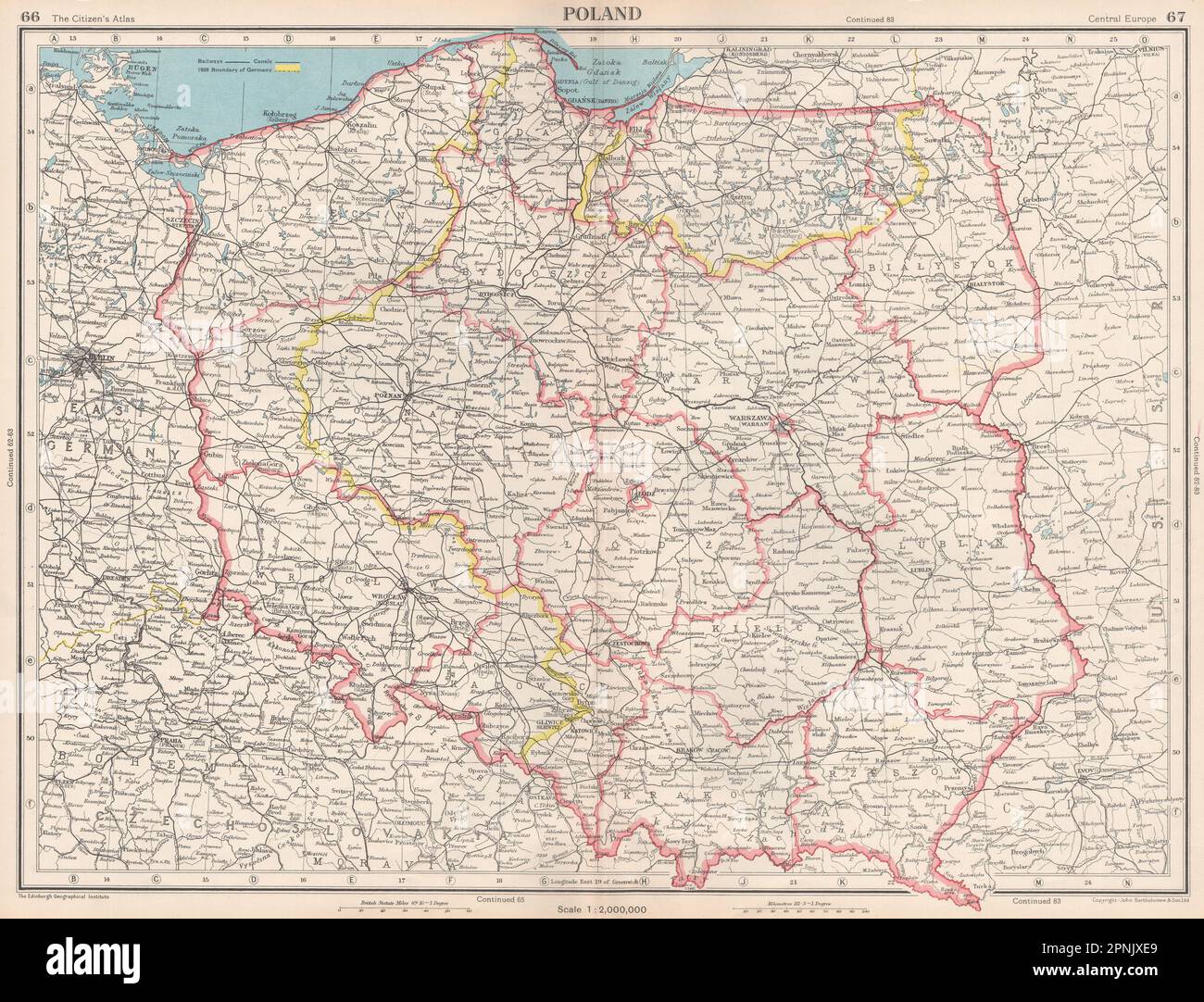
A History of Shifting Borders:
The history of the Germany-Poland border is a tumultuous one, shaped by wars, political shifts, and the aspirations of both nations.
- The Middle Ages: The region was a patchwork of kingdoms and duchies, with no clear-cut border. The influence of the Holy Roman Empire and the Kingdom of Poland fluctuated over centuries.
- The Rise of Prussia: The 18th and 19th centuries saw the rise of Prussia, a powerful German state that annexed significant Polish territories. This led to a shift in the border, with Prussia controlling much of the land that would later become part of Germany.
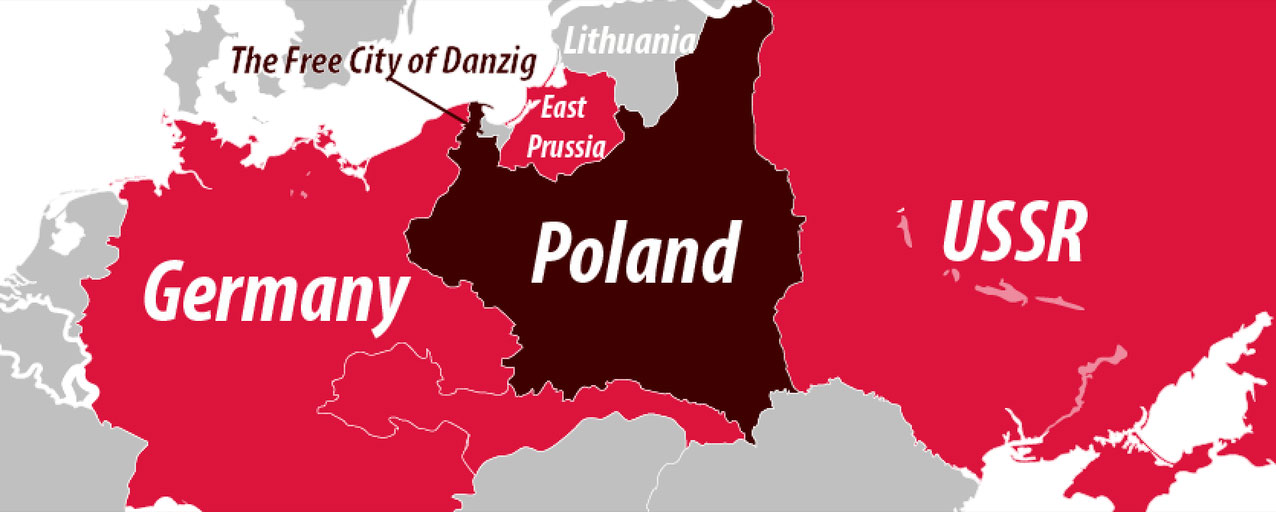
- World War I and the Treaty of Versailles: After the First World War, the Treaty of Versailles aimed to redraw the map of Europe. This resulted in the creation of the "Polish Corridor," a strip of land separating East Prussia from the rest of Germany. This move was intended to provide Poland with access to the Baltic Sea, but it also sowed the seeds of future conflict.
- World War II and the Potsdam Conference: The Second World War saw the Nazi regime’s annexation of large swathes of Poland. After the war, the Potsdam Conference established a new border, shifting it westward and leaving significant Polish territories under German control. The expulsion of German populations from these areas and the resettlement of Poles from the east created a complex demographic shift.
- The Cold War and the Iron Curtain: The post-war era saw the establishment of the Iron Curtain, separating Eastern Europe from the West. This solidified the border between Germany and Poland, which became a key element of the Cold War division.
- The Fall of the Berlin Wall and German Reunification: The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 and the subsequent reunification of Germany in 1990 marked a significant turning point. The border between Germany and Poland became a symbol of the end of the Cold War and the beginning of a new era in Europe.
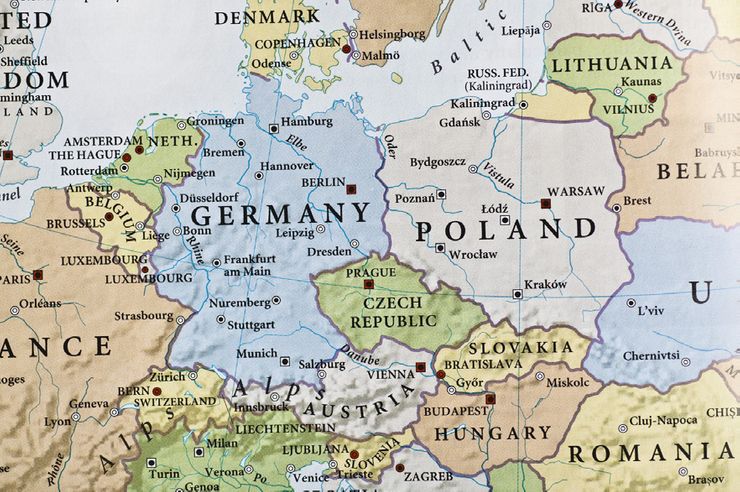
The Modern Border: A Bridge Between Two Nations:
Today, the Germany-Poland border is a symbol of cooperation and integration. Both countries are members of the European Union and NATO, and they share common goals and interests. The border has become a space for cultural exchange, economic collaboration, and political dialogue.
- Economic Cooperation: The border region has seen significant economic growth in recent decades, with numerous cross-border businesses and investments. The European Union’s funding programs have further fostered economic integration.
- Cultural Exchange: The border region is rich in cultural heritage, with a blend of German and Polish influences. Museums, theaters, and cultural events often feature cross-border collaborations.
- Political Dialogue: Both countries regularly engage in high-level political dialogue, addressing issues of mutual concern. The close cooperation on border security and migration management is a testament to the strong relationship between the two nations.
Looking Towards the Future:
The Germany-Poland border continues to evolve, shaped by new challenges and opportunities.
- Climate Change: Both countries are facing the challenges of climate change, requiring collaboration on environmental protection and sustainable development.
- Digitalization and Innovation: The border region is a hub for innovation and technological development, with both countries investing heavily in digital infrastructure and research.
- Security and Defense: The shared membership in NATO and the ongoing security challenges in Europe require close cooperation on defense and security matters.
FAQs About the Germany-Poland Border:
- What is the length of the Germany-Poland border? The current border between Germany and Poland is approximately 451 kilometers long.
- What are the main border crossings between Germany and Poland? Some of the main border crossings include Frankfurt (Oder) – Słubice, Görlitz – Zgorzelec, and Świnoujście – Ahlbeck.
- What is the history of the "Polish Corridor"? The "Polish Corridor" was a strip of land separating East Prussia from the rest of Germany, created after World War I. It aimed to provide Poland with access to the Baltic Sea but led to tensions and ultimately to the Second World War.
- How has the border impacted the cultural identity of the region? The border region has a unique cultural identity, shaped by the interaction of German and Polish influences. This is reflected in the local dialects, traditions, and architecture.
- What are the challenges and opportunities for the future of the border region? The challenges include climate change, economic disparities, and security threats. The opportunities lie in fostering economic cooperation, cultural exchange, and political dialogue.
Tips for Understanding the Germany-Poland Border:
- Visit the border region: Explore the historical sites, museums, and cultural events that highlight the shared history and cultural heritage of the region.
- Learn about the history of the border: Read books, watch documentaries, and visit historical archives to gain a deeper understanding of the complex history of the region.
- Engage with local communities: Talk to people who live in the border region to hear their perspectives on the history, culture, and challenges of the area.
- Follow the news and current events: Stay informed about the political, economic, and cultural developments that are shaping the relationship between Germany and Poland.
Conclusion:
The Germany-Poland border is a testament to the complex and dynamic nature of international relations. It is a story of conflict and cooperation, of shared history and cultural exchange, and of ongoing challenges and opportunities. Understanding this border requires a nuanced and historical perspective, recognizing the importance of dialogue, cooperation, and mutual respect in building a peaceful and prosperous future for both nations.

![Border changes in history of Poland [900 x 742] : r/MapPorn](https://i.redd.it/imuz02vvbk611.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time and Space: Understanding the Germany-Poland Border. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!