A New Dimension in Cartography: The Rise of 3D Printed Maps
Related Articles: A New Dimension in Cartography: The Rise of 3D Printed Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A New Dimension in Cartography: The Rise of 3D Printed Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A New Dimension in Cartography: The Rise of 3D Printed Maps
The world of maps has undergone a dramatic transformation with the advent of 3D printing technology. Gone are the days of flat, two-dimensional representations confined to paper or screens. Now, maps can take on a tangible, three-dimensional form, offering an entirely new perspective on the world. This shift has profound implications for various fields, including education, design, and even urban planning.
Understanding 3D Printed Maps
3D printed maps utilize additive manufacturing processes to build physical models of geographical data. This involves layering materials, typically plastics, resins, or even metal, based on digital map data. The result is a detailed, tactile representation of the terrain, showcasing mountains, valleys, rivers, and other features with remarkable accuracy.
Benefits of 3D Printed Maps
The emergence of 3D printed maps brings a host of benefits, revolutionizing how we interact with and understand geographical information:
1. Enhanced Visual Understanding:
3D printed maps provide a more intuitive and immersive understanding of geography. The three-dimensional representation allows individuals to grasp the scale, shape, and relative positions of features with greater clarity than traditional maps. This is particularly beneficial for educational purposes, allowing students to visualize complex geographical concepts.
2. Tactile Exploration:
The physical nature of 3D printed maps allows for tactile exploration. Students, researchers, and even the visually impaired can physically touch and interact with the terrain, gaining a deeper understanding of the landscape. This tactile engagement enhances learning and exploration, making maps more accessible to diverse audiences.
3. Customization and Personalization:
3D printing offers unparalleled flexibility for customization. Users can tailor maps to their specific needs, focusing on particular regions, highlighting specific features, or even incorporating personalized elements. This opens up possibilities for creating unique and engaging maps for various purposes.
4. Accessibility and Affordability:
The accessibility of 3D printing technology has made it possible to create high-quality maps at relatively low costs. This democratizes map creation, allowing individuals and organizations with limited budgets to access and utilize these powerful tools.
5. Applications Beyond Traditional Cartography:
The applications of 3D printed maps extend beyond traditional cartography. They can be used in urban planning to visualize proposed developments, in architecture to model buildings and landscapes, and even in archaeology to recreate historical sites. This versatility makes them valuable tools across diverse industries.
Applications of 3D Printed Maps
The potential applications of 3D printed maps are vast and continue to expand:
1. Education:
3D printed maps are transforming classrooms, providing students with engaging and interactive learning tools. They allow for hands-on exploration of geography, promoting deeper understanding and fostering a sense of curiosity about the world.
2. Design and Architecture:
Architects and designers utilize 3D printed maps to visualize and model proposed projects. These detailed models provide a more comprehensive understanding of the site, allowing for better planning and design decisions.
3. Urban Planning:
Urban planners leverage 3D printed maps to visualize city landscapes and simulate the impact of proposed infrastructure projects. This facilitates informed decision-making regarding urban development and ensures sustainable growth.
4. Archaeology and History:
Archaeologists use 3D printed maps to reconstruct ancient sites and landscapes, providing valuable insights into past civilizations. These models offer a tangible representation of historical environments, bringing history to life.
5. Tourism and Recreation:
3D printed maps are becoming increasingly popular among tourists and outdoor enthusiasts. They provide detailed representations of hiking trails, national parks, and other recreational areas, enhancing the experience and ensuring safety.
Challenges and Future Directions
While 3D printed maps offer numerous advantages, several challenges remain:
1. Material Limitations:
The materials used in 3D printing currently limit the scale and detail achievable for larger maps. Further advancements in materials science are necessary to overcome these limitations.
2. Data Accuracy and Availability:
The accuracy of 3D printed maps depends on the quality and availability of digital map data. Ensuring data accuracy and accessibility is crucial for producing reliable models.
3. Cost and Time Considerations:
While 3D printing has become more affordable, the cost of producing high-quality, large-scale maps can still be significant. Additionally, the printing process can be time-consuming, requiring careful planning and optimization.
4. Sustainability and Environmental Impact:
The environmental impact of 3D printing, particularly in terms of energy consumption and material waste, requires careful consideration. Sustainable practices and responsible material choices are crucial for minimizing the ecological footprint.
5. Ethical Considerations:
As with any emerging technology, ethical considerations arise regarding the use of 3D printed maps. These include concerns about data privacy, the potential for misuse, and the need for responsible and transparent practices.
FAQs
1. What are the different materials used in 3D printed maps?
Common materials include plastics (PLA, ABS), resins (photopolymer), and metals (bronze, silver). The choice of material depends on the desired level of detail, durability, and budget.
2. What is the resolution of 3D printed maps?
The resolution of 3D printed maps is determined by the printing technology and the chosen material. Advanced printers can achieve resolutions of up to 100 microns, allowing for highly detailed models.
3. How are 3D printed maps created?
3D printed maps are created by converting digital map data into a printable format (STL or OBJ). The data is then sliced into layers, which are sequentially built by the 3D printer using a chosen material.
4. Are 3D printed maps accurate?
The accuracy of 3D printed maps depends on the quality and accuracy of the source data. High-resolution, accurate data will result in highly accurate models.
5. What are the limitations of 3D printed maps?
Current limitations include material limitations, data availability, cost, and printing time. However, ongoing research and development are addressing these challenges.
Tips for Utilizing 3D Printed Maps
1. Choose the right material for your needs. Consider factors like durability, cost, and desired level of detail.
2. Ensure accurate and high-resolution data. Use reliable sources for map data to ensure accurate representation.
3. Plan and optimize the printing process. Factor in printing time, material usage, and cost to ensure efficient production.
4. Explore customization options. Tailor the map to your specific needs, highlighting key features or incorporating personalized elements.
5. Engage with the map. Encourage tactile exploration and interaction to enhance understanding and engagement.
Conclusion
3D printed maps are revolutionizing the way we interact with and understand geographical information. Their ability to provide tangible, immersive representations of the world is transforming education, design, urban planning, and other fields. As technology continues to advance, 3D printed maps are poised to play an increasingly significant role in shaping our understanding of the world around us. The future of cartography is undoubtedly three-dimensional, offering a wealth of opportunities for exploration, innovation, and a deeper connection with the world we inhabit.
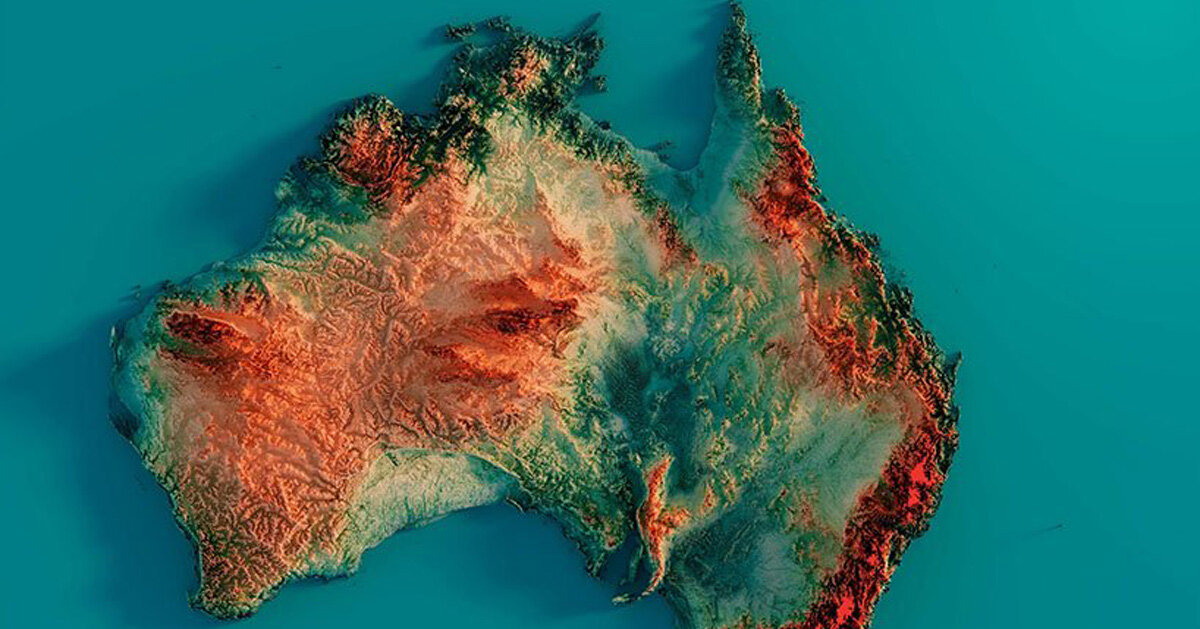
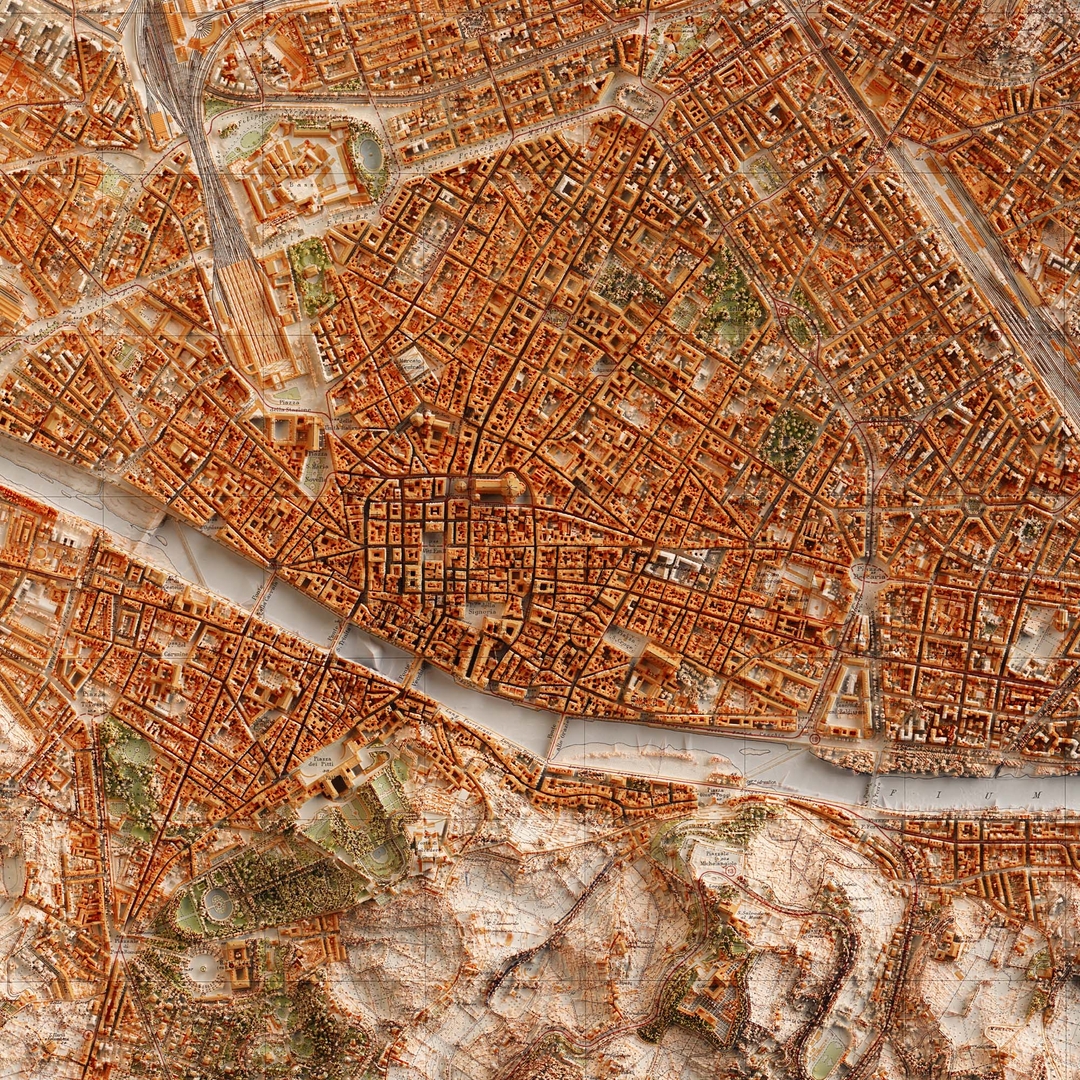







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A New Dimension in Cartography: The Rise of 3D Printed Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!