A Thousand Years of Transformation: Mapping the Evolution of Europe from 1000 to 2000
Related Articles: A Thousand Years of Transformation: Mapping the Evolution of Europe from 1000 to 2000
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Thousand Years of Transformation: Mapping the Evolution of Europe from 1000 to 2000. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Thousand Years of Transformation: Mapping the Evolution of Europe from 1000 to 2000

The map of Europe has undergone a dramatic transformation over the past millennium, reflecting a complex interplay of political, social, economic, and cultural forces. Examining this evolution provides a unique lens through which to understand the continent’s history, its present-day realities, and its potential future.
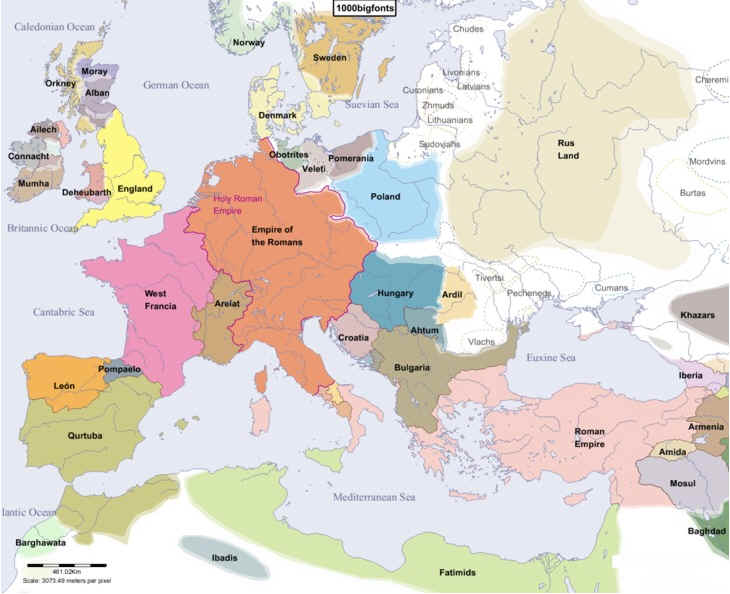
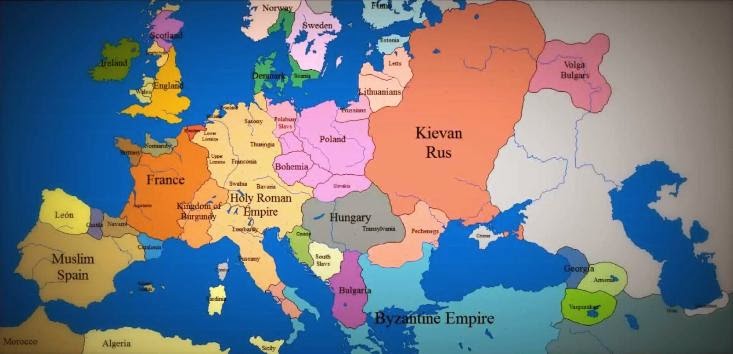
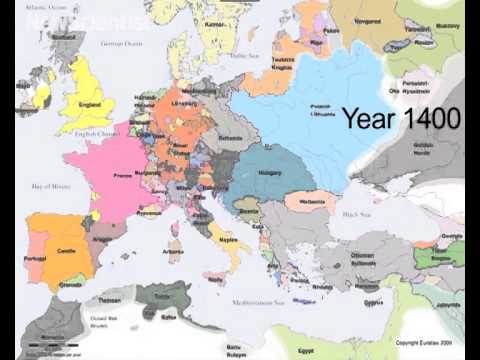
The Europe of 1000 AD: A Tapestry of Kingdoms and Empires
The year 1000 AD witnessed a fragmented Europe, characterized by a multitude of kingdoms and empires. The Holy Roman Empire, a sprawling entity encompassing much of central Europe, coexisted with powerful kingdoms like France, England, and the Scandinavian kingdoms. The Byzantine Empire, a remnant of the Roman legacy, held sway over the eastern Mediterranean.
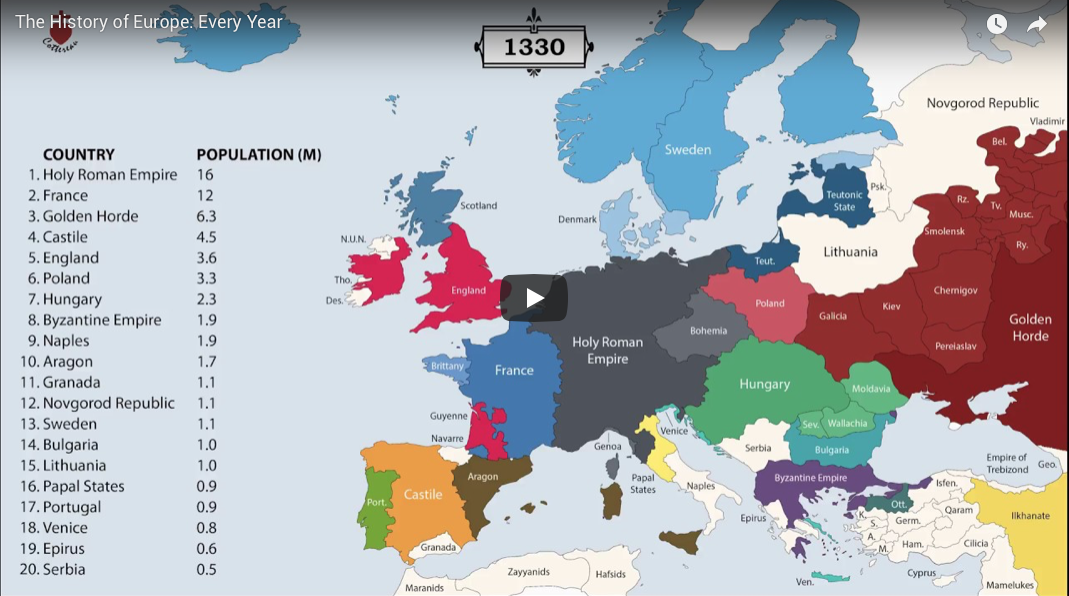
Political and Territorial Shifts: 1000 to 1500
The period between 1000 and 1500 was marked by significant political upheavals and territorial shifts. The Holy Roman Empire, despite its vastness, faced internal fragmentation and constant challenges from neighboring powers. The rise of powerful monarchies in England, France, and Spain gradually consolidated power, leading to the formation of more centralized states. The Crusades, a series of religious wars launched by European Christians against Muslim forces in the Levant, had a profound impact on the political landscape, shaping alliances and rivalries.
The Renaissance and Reformation: A Cultural and Religious Transformation
The Renaissance, a period of intellectual and artistic flourishing, originated in Italy in the 14th century and gradually spread across Europe. This cultural awakening led to a renewed interest in classical learning, scientific inquiry, and artistic expression. The Reformation, a religious movement initiated by Martin Luther in the early 16th century, challenged the authority of the Catholic Church and resulted in the emergence of Protestantism. These movements, while distinct, shared a common thread of questioning established norms and seeking new interpretations of the world.
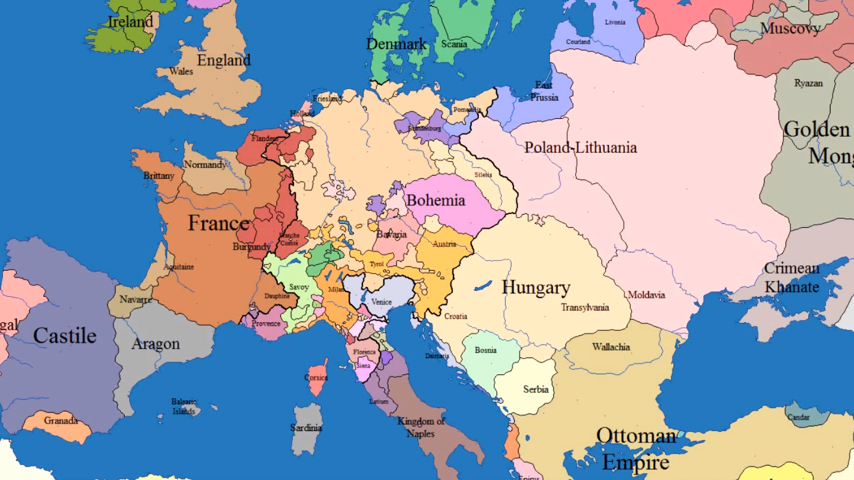
The Age of Exploration and Expansion: 1500 to 1800
The 16th and 17th centuries witnessed a period of unprecedented exploration and expansion driven by European powers. The quest for new trade routes and access to resources led to the discovery and colonization of vast territories in the Americas, Africa, and Asia. This era saw the rise of powerful maritime empires, such as Spain, Portugal, the Netherlands, and England, which established global trading networks and exerted significant influence across the world.
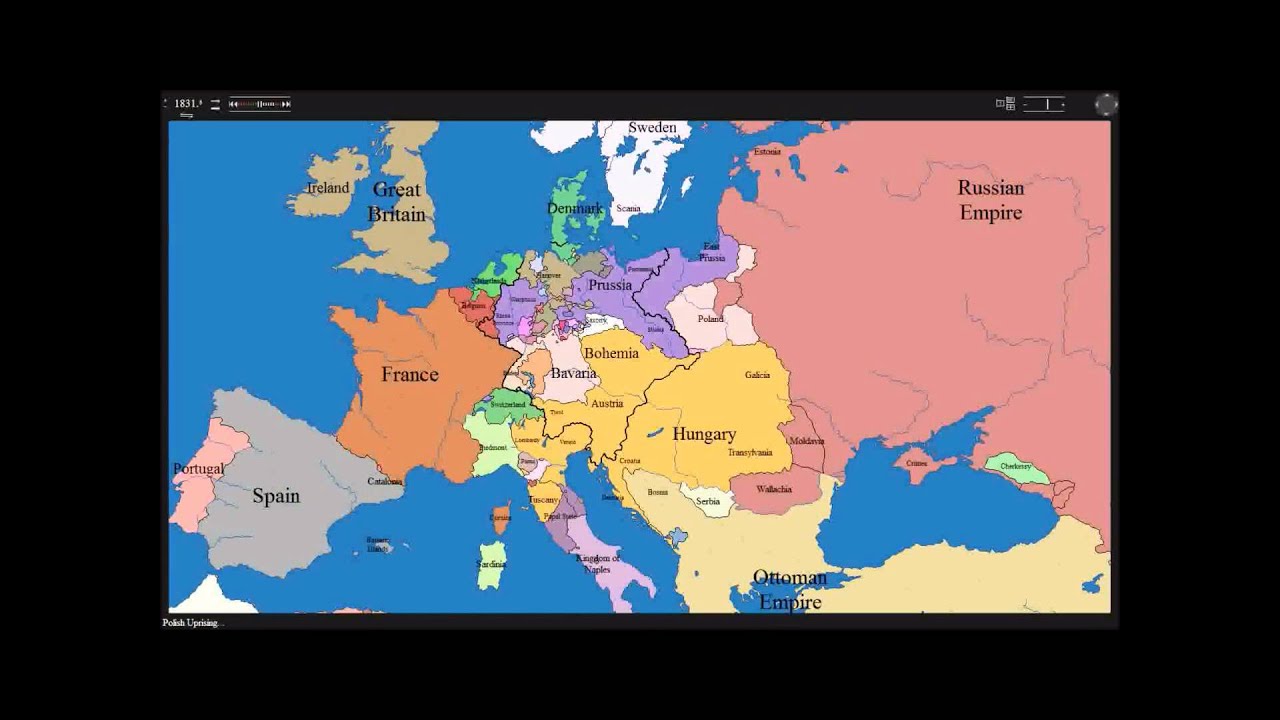
The Rise of Nationalism and Revolutions: 1800 to 1900
The 19th century witnessed the rise of nationalism, a powerful ideology that emphasized the shared identity and interests of people within a nation. This sentiment fueled revolutions and movements for independence across Europe, leading to the formation of new nation-states. The French Revolution, a pivotal event in the history of Europe, challenged the existing political order and inspired similar movements for democratic reforms and individual rights. The Industrial Revolution, which began in Great Britain in the late 18th century, transformed European economies and societies, leading to unprecedented urbanization and technological advancements.
The 20th Century: Wars, Revolutions, and the Cold War
The 20th century was marked by two devastating world wars, the rise of totalitarian regimes, and the Cold War, a period of ideological and geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union. The First World War, which began in 1914, resulted in the collapse of empires, the redrawing of national boundaries, and the rise of new political ideologies. The Second World War, which began in 1939, witnessed the rise of Nazi Germany and its quest for domination, leading to the Holocaust, a systematic genocide of European Jews. The Cold War, which began in the aftermath of World War II, divided Europe into Eastern and Western blocs, characterized by ideological rivalry and proxy wars.
The Post-Cold War Era: Integration and Challenges
The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 marked the end of the Cold War and ushered in a new era of political and economic integration in Europe. The European Union (EU), established in 1993, has become a major economic and political power, promoting free trade, economic cooperation, and democratic values among its member states. However, the EU faces challenges in maintaining unity in the face of economic disparities, immigration pressures, and the rise of populist movements.
Understanding the Importance of the Map of Europe
The map of Europe is not merely a static representation of geographical boundaries but a dynamic reflection of the continent’s history, its present-day realities, and its potential future. Understanding the evolution of the map provides insights into:
- The complex interplay of political, social, economic, and cultural forces that have shaped Europe.
- The rise and fall of empires, the formation of nation-states, and the changing power dynamics within the continent.
- The impact of major historical events, such as wars, revolutions, and technological advancements, on the European landscape.
- The challenges and opportunities facing Europe in the 21st century, including economic integration, immigration, and the rise of populism.
FAQs
Q: What were the most significant political changes in Europe between 1000 and 2000?
A: The most significant political changes include the rise of powerful monarchies, the formation of nation-states, the collapse of empires, the rise of nationalism, and the emergence of the European Union.
Q: How did the Renaissance and Reformation impact the map of Europe?
A: While not directly altering political boundaries, these movements fostered intellectual and religious change, laying the groundwork for later political and social transformations. The Renaissance emphasized individual expression and challenged established hierarchies, while the Reformation led to religious divisions and the formation of new Protestant denominations.
Q: What were the consequences of European exploration and colonization?
A: European exploration and colonization led to the establishment of vast colonial empires, the exploitation of resources, and the displacement of indigenous populations. It also had a profound impact on the global distribution of wealth and power, shaping the economic and political landscape of the world.
Q: How did the Cold War impact the map of Europe?
A: The Cold War divided Europe into Eastern and Western blocs, with the Soviet Union controlling Eastern Europe and the United States supporting Western Europe. The ideological rivalry between the two superpowers led to proxy wars, military build-ups, and a period of intense geopolitical tension.
Q: What are the key challenges facing the European Union today?
A: The EU faces challenges in maintaining unity in the face of economic disparities, immigration pressures, the rise of populist movements, and the growing influence of external powers.
Tips for Studying the Map of Europe
- Use historical maps as a visual tool to understand the evolution of boundaries and political entities.
- Research key historical events and their impact on the map of Europe.
- Consider the social, economic, and cultural factors that have influenced the map of Europe.
- Explore the role of major powers, such as France, Germany, and the United Kingdom, in shaping the continent’s political landscape.
- Analyze the impact of globalization and technological advancements on the map of Europe.
Conclusion
The map of Europe is a testament to the continent’s rich and complex history. From the fragmented kingdoms of the Middle Ages to the integrated Europe of today, the map has undergone a remarkable transformation, reflecting the interplay of political, social, economic, and cultural forces. Understanding this evolution is essential for comprehending the present-day realities of Europe and its potential future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Thousand Years of Transformation: Mapping the Evolution of Europe from 1000 to 2000. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!