Charting the American Landscape: A Journey Through Historical Maps of the United States
Related Articles: Charting the American Landscape: A Journey Through Historical Maps of the United States
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Charting the American Landscape: A Journey Through Historical Maps of the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the American Landscape: A Journey Through Historical Maps of the United States

The United States, a nation forged from diverse landscapes and shifting borders, has a rich cartographic history. Maps, far more than mere representations of geographical features, serve as powerful tools for understanding the evolution of the nation’s physical, social, and political fabric. From early colonial explorations to the modern era, historical maps offer a unique window into the past, revealing the stories of settlement, conflict, and the enduring quest for identity.
Early Explorations and the Birth of a Nation:
The earliest maps of the United States were created by European explorers navigating unfamiliar shores. These maps, often crude and inaccurate, were driven by a desire to chart new territories, claim lands, and establish trade routes. The voyages of Christopher Columbus, John Cabot, and Jacques Cartier, among others, resulted in the first depictions of the North American coastline. These maps, while rudimentary, laid the groundwork for future cartographic endeavors and contributed to the growing European understanding of the New World.
As European colonization intensified, the need for more detailed and accurate maps increased. Cartographers, often working under the patronage of colonial governments, produced maps that reflected the expanding reach of European power. These maps depicted not only physical features but also settlements, fortifications, and trade routes, offering valuable insights into the early development of the American colonies.
The Revolution and the Shaping of a Nation:
The American Revolution, a period of intense upheaval and transformation, witnessed the emergence of a new nation and a renewed focus on cartography. The need for accurate maps to guide military campaigns, facilitate communication, and solidify territorial claims became paramount. Revolutionary cartographers, such as William Faden and Simeon DeWitt, produced maps that captured the shifting battle lines, strategic locations, and evolving boundaries of the newly independent nation.
The maps produced during this period played a vital role in shaping the narrative of the Revolution, solidifying American identity, and establishing a visual representation of the newly formed republic. These maps, often imbued with patriotic symbolism, served as powerful propaganda tools, galvanizing public support and fostering a sense of national unity.
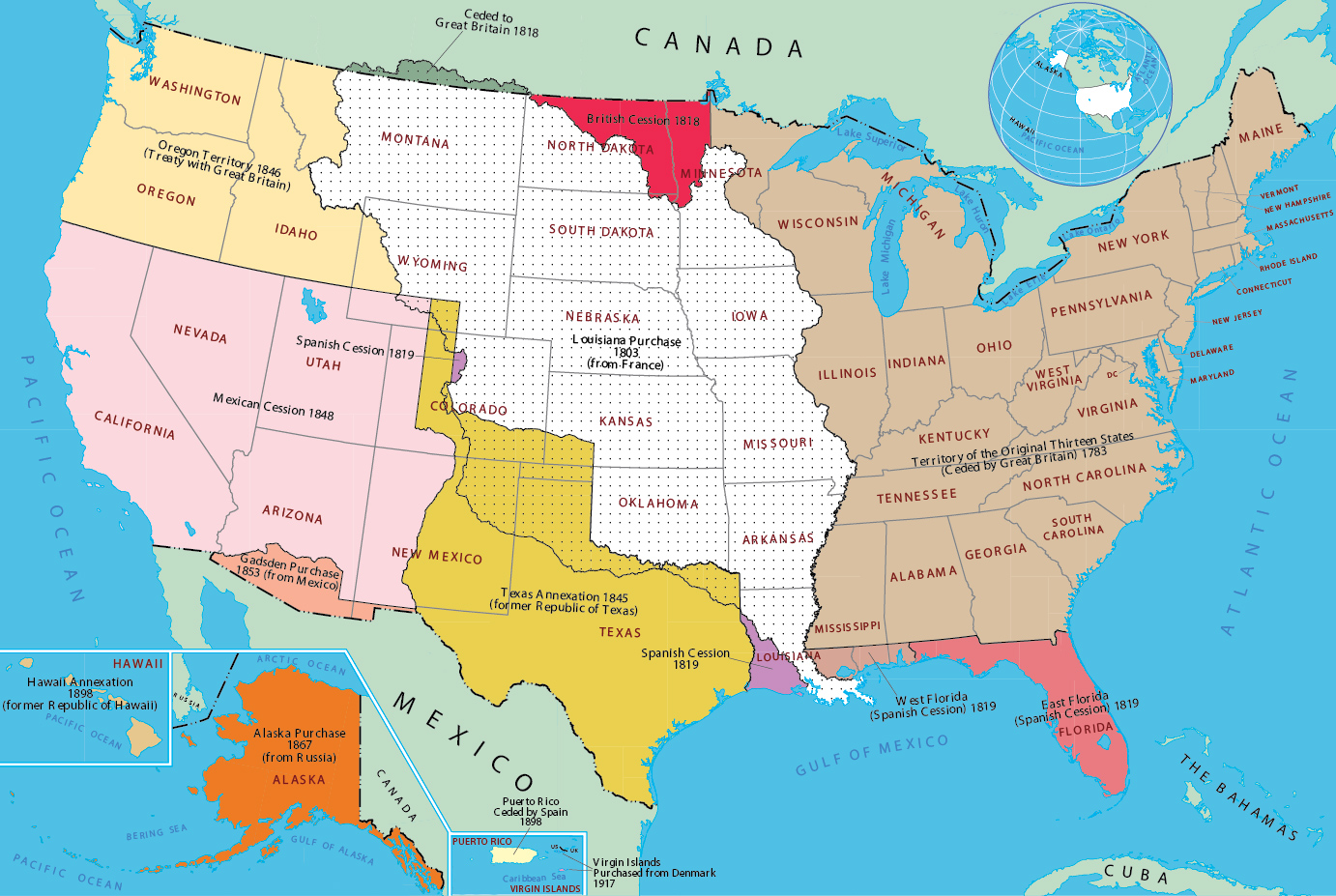
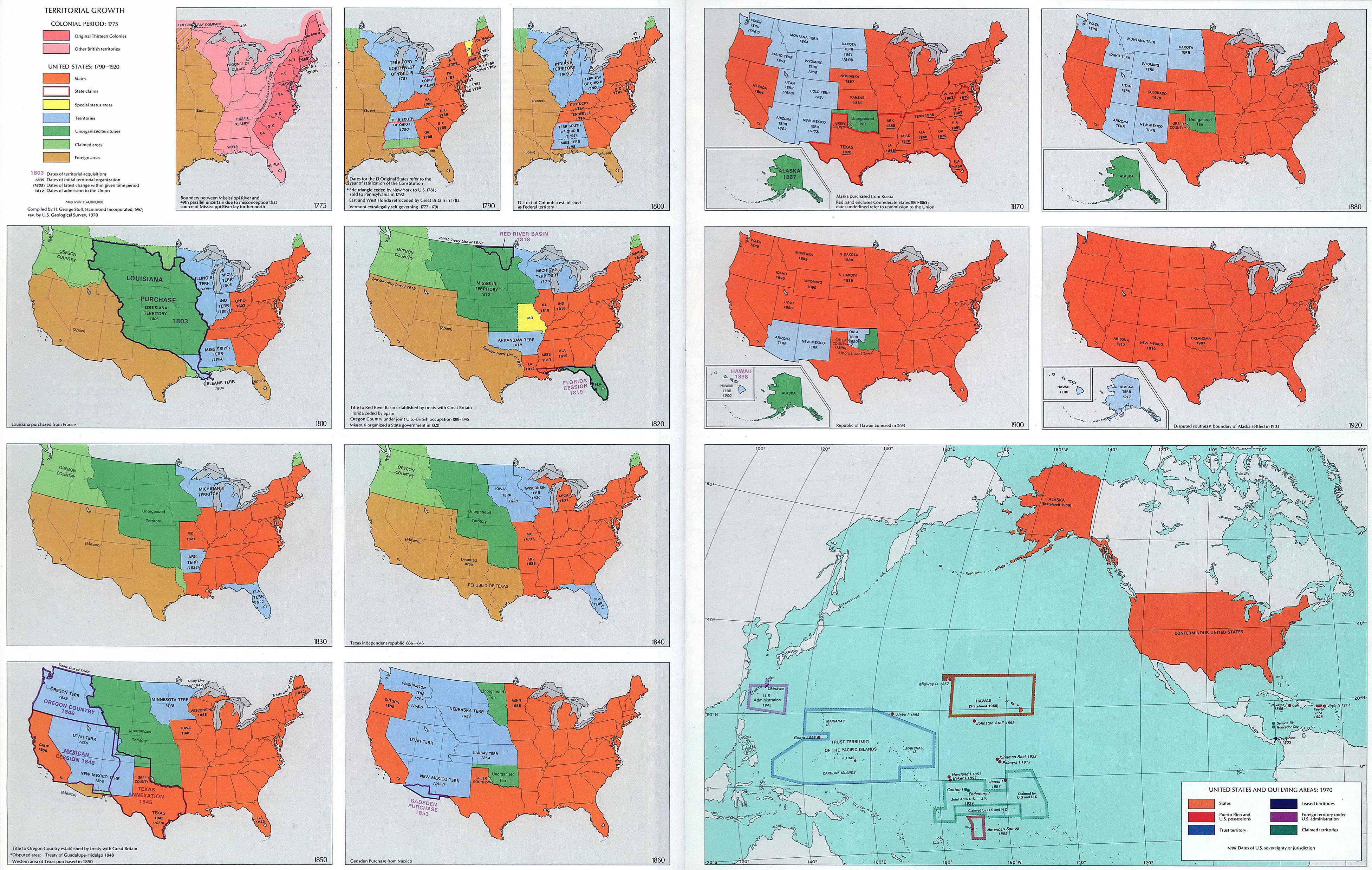
Westward Expansion and the Manifest Destiny:
The 19th century witnessed a dramatic expansion of the United States across the North American continent. The westward movement, fueled by the ideology of Manifest Destiny, led to the exploration and settlement of vast territories, from the Great Plains to the Pacific Coast. This expansion was closely intertwined with cartographic advancements, as surveyors, explorers, and cartographers played a pivotal role in mapping the vast and often treacherous landscapes.
The maps produced during this period reflected the evolving understanding of the American West. They depicted the routes of westward expansion, the locations of Native American tribes, the distribution of resources, and the growth of settlements. These maps served as essential tools for government agencies, private companies, and individuals seeking to navigate the frontier and capitalize on the economic opportunities presented by westward expansion.
The Civil War and the Struggle for Unity:
The American Civil War, a conflict that divided the nation along ideological and geographical lines, also had a profound impact on cartography. The need for accurate maps to guide military operations, understand battlefields, and navigate the complex terrain became paramount.
Cartographers on both sides of the conflict produced maps that depicted the evolving battle lines, strategic locations, and logistical routes. These maps, often created under duress and with limited resources, played a vital role in shaping the course of the war. The maps produced during this period offer invaluable insights into the strategic thinking, logistical challenges, and human costs of the Civil War.
The Rise of Modern Cartography:
The late 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed significant advancements in cartographic techniques and technologies. The development of new surveying instruments, printing processes, and data collection methods led to the production of more accurate, detailed, and comprehensive maps. The rise of scientific cartography, driven by the desire to understand and represent the natural world, led to the creation of thematic maps depicting geological formations, climate patterns, and population distributions.
The development of the automobile and the rise of tourism further fueled the demand for accurate and user-friendly maps. Road maps, city plans, and travel guides became increasingly ubiquitous, revolutionizing the way people navigated and understood their surroundings.
The Digital Age and the Future of Mapping:
The advent of digital technology has revolutionized the field of cartography. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and online mapping platforms have transformed the way maps are created, accessed, and used. Digital maps offer unprecedented levels of detail, interactivity, and accessibility, enabling users to explore data, analyze trends, and gain new insights into the world around them.
While digital maps have become the dominant form of cartography, historical maps remain invaluable resources for understanding the past. They offer a unique window into the evolution of the American landscape, the changing perceptions of space and place, and the enduring quest for knowledge and understanding.
FAQs:
1. What is the significance of historical maps of the United States?
Historical maps of the United States provide crucial insights into the nation’s development, revealing the evolution of its physical landscape, the changing boundaries of its territories, and the impact of historical events on its geography. They offer a unique perspective on the nation’s history, shedding light on the struggles, triumphs, and transformations that shaped its identity.
2. How did historical maps influence the development of the United States?
Historical maps played a vital role in guiding exploration, settlement, and expansion across the North American continent. They facilitated navigation, communication, and resource management, enabling the development of infrastructure, the establishment of settlements, and the exploitation of natural resources.
3. What are some notable historical maps of the United States?
Notable historical maps of the United States include:
- The Vinland Map: A 15th-century map that depicts the North American coastline, including a possible representation of a Viking settlement in North America.
- The Lewis and Clark Map: A map created by the explorers Meriwether Lewis and William Clark during their expedition to the Pacific Ocean, offering valuable insights into the geography of the American West.
- The John Smith Map: A map of the Chesapeake Bay region created by the English explorer John Smith in the early 17th century, providing a detailed depiction of the coastline and indigenous settlements.
- The Benjamin Franklin Map: A map of the American colonies created by Benjamin Franklin in the 18th century, showcasing the interconnectedness of the colonies and their potential for unity.
- The William Faden Map: A map of the American Revolution created by the English cartographer William Faden, depicting the shifting battle lines and strategic locations of the conflict.
4. How can historical maps be used in research and education?
Historical maps serve as invaluable resources for researchers and educators, providing visual evidence of historical events, geographic changes, and societal trends. They can be used to analyze the impact of historical events on the landscape, study the development of settlements and infrastructure, and explore the changing perceptions of space and place.
5. What are some resources for accessing historical maps of the United States?
There are numerous resources for accessing historical maps of the United States, including:
- The Library of Congress: The Library of Congress holds a vast collection of historical maps, including maps of the United States, individual states, and cities.
- The National Archives and Records Administration: The National Archives houses a collection of historical maps related to the United States government, including maps of military campaigns, land surveys, and census data.
- The American Geographical Society Library: The American Geographical Society Library holds a collection of maps from around the world, including a significant collection of historical maps of the United States.
- Online databases: Online databases, such as the David Rumsey Map Collection and the National Map, offer access to a wide range of historical maps, searchable by location, date, and other criteria.
Tips for Using Historical Maps:
- Consider the context: Historical maps were created for specific purposes, reflecting the knowledge and biases of their time. It is important to consider the context of the map, including the date of creation, the intended audience, and the motivations of the cartographer.
- Examine the details: Pay attention to the details on the map, including the scale, the symbols used, and the geographic features depicted. These details can offer insights into the accuracy, purpose, and perspective of the map.
- Compare and contrast: Compare different maps of the same region or time period to identify variations in representation, accuracy, and perspective. This can help to understand the evolving understanding of a particular place or event.
- Use the map as a tool for research: Historical maps can serve as a starting point for research, leading to the discovery of new sources, the identification of key locations, and the development of research questions.
Conclusion:
Historical maps of the United States are more than just static representations of the past. They are dynamic documents that reflect the nation’s evolving identity, its physical landscape, and its enduring quest for understanding. By exploring these maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of American history, the ingenuity of its cartographers, and the enduring power of visual representation. As we navigate the digital age, it is essential to remember the rich cartographic legacy that continues to inform our understanding of the world and the place we call home.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the American Landscape: A Journey Through Historical Maps of the United States. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!