Charting the Course of Exploration: The Map Route of Henry Hudson
Related Articles: Charting the Course of Exploration: The Map Route of Henry Hudson
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Course of Exploration: The Map Route of Henry Hudson. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Course of Exploration: The Map Route of Henry Hudson

Henry Hudson, a renowned English explorer, embarked on several voyages in the early 17th century, leaving an indelible mark on the history of exploration and the cartographic understanding of North America. His voyages, primarily focused on discovering a Northwest Passage to Asia, led to the charting of significant portions of the North American coastline and the exploration of waterways that would later bear his name.
The First Voyage (1607):
Hudson’s first voyage, sponsored by the Muscovy Company, aimed to find a northeastern route to Asia. He sailed north along the coast of Norway, reaching the Barents Sea, but was forced to turn back due to the harsh conditions. This voyage, though unsuccessful in its primary objective, provided valuable information about the Arctic region and contributed to the burgeoning knowledge of the northern seas.
The Second Voyage (1609):
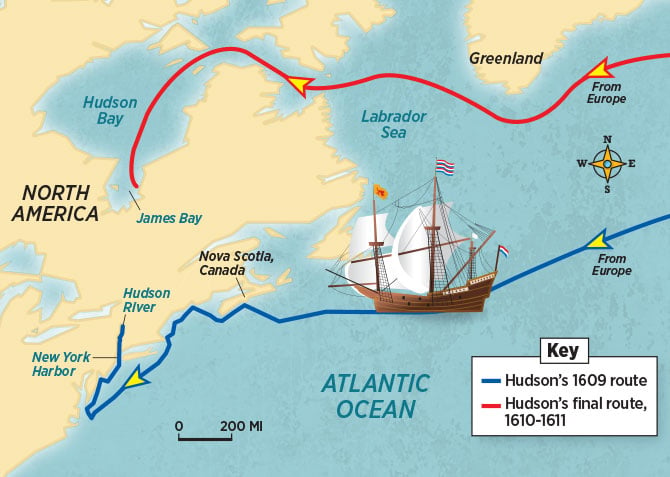
Funded by the Dutch East India Company, Hudson’s second voyage shifted focus to finding a westward route to Asia. He sailed south, exploring the coast of North America and navigating the waters of the Hudson River, named in his honor. He reached as far north as Albany, New York, before turning back due to the onset of winter. This voyage established the Dutch presence in the region and opened up the Hudson River Valley to trade and settlement.
The Third Voyage (1610-1611):
Hudson’s third and final voyage, sponsored by the English Muscovy Company, aimed to find the Northwest Passage. He sailed north through the Hudson Strait, entering what is now known as Hudson Bay. He spent the winter trapped in the bay’s ice, facing harsh conditions and dwindling supplies. Despite the hardships, Hudson continued his exploration, charting the coastline and mapping the bay. However, in the spring of 1611, mutiny broke out among the crew. Hudson, along with his son and several others, were set adrift in a small boat, never to be seen again.
The Significance of Hudson’s Map Route:
Henry Hudson’s voyages, despite their tragic ending, had a profound impact on the exploration and mapping of North America. His explorations contributed significantly to the understanding of the continent’s geography, opening up new territories for trade and settlement. His map route provided valuable information about the coastline, waterways, and indigenous populations, shaping the early European perception of the region.
Mapping the Route:
The First Voyage (1607):
- Hudson’s first voyage followed a northerly route along the coast of Norway, reaching the Barents Sea.
- The route can be visualized on modern maps by tracing the coastline of Norway northwards, passing through the Norwegian Sea and reaching the Barents Sea.
The Second Voyage (1609):
- Hudson’s second voyage followed a southerly route along the North American coast, navigating the Hudson River.
- The route can be visualized on modern maps by tracing the coastline of North America southward from the Labrador Sea, passing through the Strait of Belle Isle, along the coast of Newfoundland, and finally reaching the Hudson River.
The Third Voyage (1610-1611):
- Hudson’s third voyage followed a northerly route through the Hudson Strait and into Hudson Bay.
- The route can be visualized on modern maps by tracing the coastline of North America northward from the Atlantic Ocean, passing through the Hudson Strait, and entering Hudson Bay.
Importance of Hudson’s Map Route:
- Expansion of European Knowledge: Hudson’s voyages expanded European knowledge of the North American continent, providing valuable information about the coastline, waterways, and indigenous populations.
- Opening New Territories: Hudson’s explorations opened up new territories for trade and settlement, contributing to the growth of European colonies in North America.
- Foundation for Future Exploration: Hudson’s map route served as a foundation for future explorers, providing a starting point for further exploration and mapping of the region.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: Why did Henry Hudson embark on his voyages?
A: Hudson’s primary goal was to find a Northwest Passage to Asia, a route that would connect Europe to the East by sea. He believed that such a passage would provide a faster and more efficient route for trade with Asia.
Q: What were the main challenges faced by Hudson on his voyages?
A: Hudson faced numerous challenges on his voyages, including harsh weather conditions, treacherous waters, and the threat of mutiny. He also encountered resistance from indigenous populations who were already inhabiting the territories he explored.
Q: What were the main discoveries made by Hudson?
A: Hudson’s main discoveries include the Hudson River, Hudson Strait, and Hudson Bay, all of which were named in his honor. He also provided valuable information about the coastline of North America and the indigenous populations inhabiting the region.
Q: What is the legacy of Henry Hudson?
A: Hudson’s legacy is a complex one. He is remembered as a pioneering explorer who contributed significantly to the mapping and understanding of North America. However, he is also criticized for his treatment of indigenous populations and the tragic fate of his final voyage.
Tips for Understanding Hudson’s Map Route:
- Use online mapping tools: Utilize online mapping tools such as Google Maps or OpenStreetMap to visualize Hudson’s voyages and trace his route.
- Consult historical maps: Consult historical maps from the 17th century to gain a better understanding of the cartographic knowledge available to Hudson during his voyages.
- Read historical accounts: Read historical accounts of Hudson’s voyages to gain insights into the challenges he faced, the discoveries he made, and the context of his explorations.
Conclusion:
Henry Hudson’s voyages, though fraught with challenges and ultimately ending in tragedy, remain significant for their contribution to the exploration and mapping of North America. His map route, charting the coastline and waterways of the region, played a crucial role in shaping the early European understanding of the continent. His legacy, while complex, serves as a testament to the spirit of exploration and the enduring impact of human curiosity in pushing the boundaries of knowledge.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Course of Exploration: The Map Route of Henry Hudson. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!