Charting the Path West: A Look at Pioneer California on Historical Maps
Related Articles: Charting the Path West: A Look at Pioneer California on Historical Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Path West: A Look at Pioneer California on Historical Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Path West: A Look at Pioneer California on Historical Maps

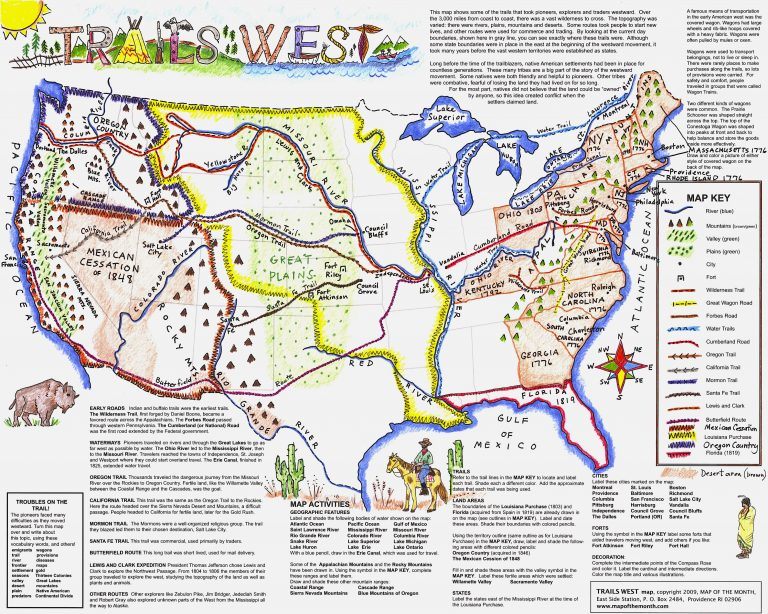
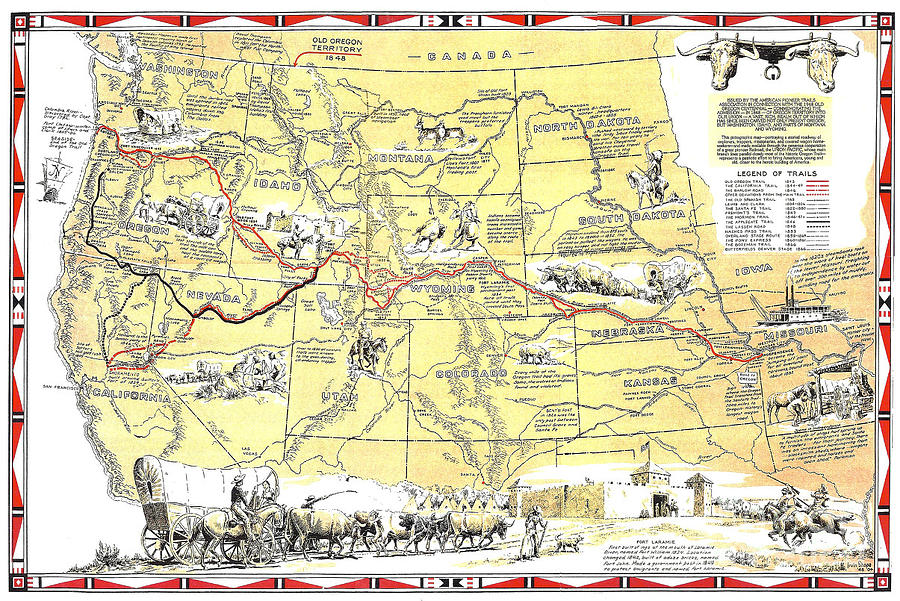
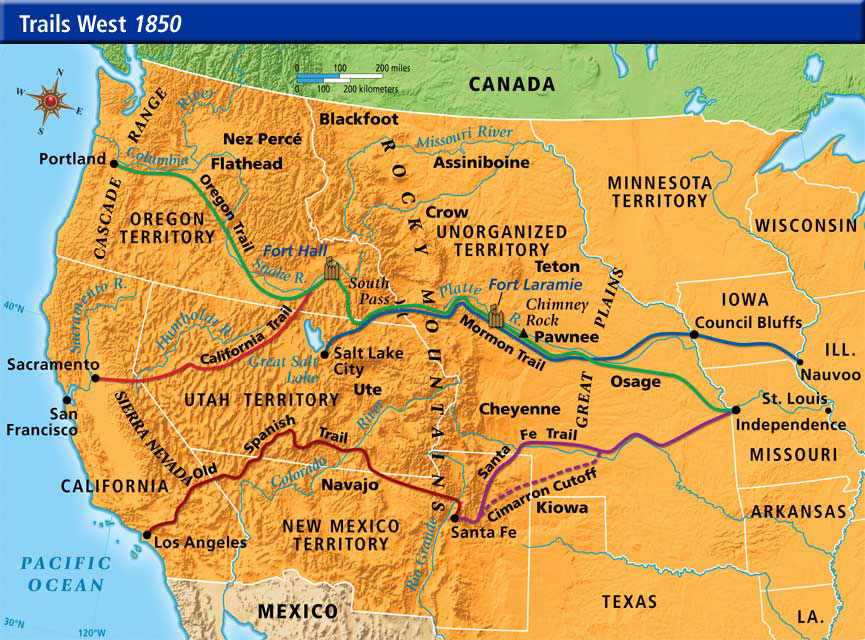
The history of California is intrinsically linked to the westward expansion of the United States, a journey marked by the arduous trails carved by pioneers seeking new opportunities and a fresh start. Historical maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding this pivotal period, offering a glimpse into the challenges, triumphs, and landscapes faced by these early settlers. This exploration delves into the significance of maps depicting Pioneer California, examining their historical context, geographical features, and lasting impact on our understanding of the state’s development.
A Tapestry of Trails: Mapping the Pioneer Journey
The most iconic representation of Pioneer California is undoubtedly the California Trail, a network of routes that stretched across thousands of miles from the Missouri River to the Pacific Coast. These trails were not single, well-defined paths but rather a series of interconnected routes, often diverging and converging, influenced by natural obstacles, weather conditions, and the preferences of individual travelers. Early maps, often hand-drawn and based on limited information, captured the evolving nature of these trails, highlighting key landmarks, water sources, and potential dangers.
Navigating the Unknown: The Role of Maps in Pioneer Exploration
For pioneers, maps were not merely navigational aids but crucial tools for survival. They provided essential information about the terrain, identifying mountain passes, river crossings, and potential hazards. Maps also served as guides for finding food and water sources, critical for sustaining life during the long and arduous journey. Furthermore, maps helped pioneers communicate with each other, sharing information about conditions and routes, fostering a sense of community and collaboration.
Early Maps: A Window into Pioneer Experiences
John Charles Frémont’s maps, particularly his 1845 map of the Oregon Trail, stand out as groundbreaking contributions to the cartographic understanding of the West. Frémont, a military explorer and cartographer, meticulously documented his expeditions, providing detailed accounts of terrain, vegetation, and indigenous populations. His maps, often featuring handwritten notes and sketches, offered a unique perspective on the challenges and beauty of the westward journey.
The Importance of Indigenous Knowledge in Pioneer Mapping
It is crucial to acknowledge the significant role of Indigenous peoples in shaping the understanding of the West. Long before European explorers arrived, Native American tribes possessed extensive knowledge of the land, its resources, and its hazards. Pioneer maps often incorporated Indigenous place names, trails, and knowledge, highlighting the interconnectedness of different cultures in navigating the vast western landscape.
Beyond the Trail: Mapping California’s Transformation
As pioneers settled in California, maps played a crucial role in shaping the state’s development. Land surveys, conducted by government officials and private surveyors, established property boundaries, facilitating the growth of settlements and agricultural development. Maps also guided the construction of roads, railroads, and infrastructure, transforming California from a sparsely populated frontier into a burgeoning state.
The Enduring Legacy of Pioneer California Maps
Today, historical maps of Pioneer California offer a rich tapestry of information, providing insights into the lives and experiences of those who ventured west. They reveal the challenges and triumphs of the journey, the intricate relationship between humans and the environment, and the evolution of the American West. These maps serve as invaluable resources for historians, genealogists, and anyone interested in understanding the complex and fascinating story of California’s early development.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What were the primary purposes of maps for pioneers traveling to California?
Pioneer maps served several crucial purposes:
- Navigation: Guiding travelers across vast distances, identifying key landmarks, and navigating treacherous terrain.
- Survival: Locating water sources, food supplies, and potential hazards.
- Communication: Sharing information about conditions, routes, and potential dangers with fellow travelers.
- Land Ownership: Establishing property boundaries and facilitating land claims.
2. How did Indigenous knowledge influence Pioneer maps?
Indigenous tribes possessed deep knowledge of the land, its resources, and its hazards. Pioneer maps often incorporated Indigenous place names, trails, and knowledge, reflecting the interconnectedness of different cultures in navigating the West.
3. What were some of the challenges faced by cartographers in creating maps of Pioneer California?
Early mapmakers faced numerous challenges:
- Limited Information: Explorers often had limited knowledge of the vast and uncharted territory.
- Technological Constraints: Early mapping tools were less precise and accurate than modern technologies.
- Lack of Standardization: There was no consistent system for representing geographical features, leading to inconsistencies between different maps.
- Indigenous Resistance: Native American tribes often resisted European exploration and mapping efforts, limiting access to certain areas.
4. What are some notable examples of early maps depicting Pioneer California?
Notable examples include:
- John Charles Frémont’s 1845 map of the Oregon Trail: This map provided detailed information about the terrain, vegetation, and indigenous populations along the trail.
- The 1849 "Map of the Gold Region of California": This map, created during the California Gold Rush, highlighted key gold mining areas and settlements.
- The 1850 "Map of the State of California": This map depicted the state’s newly established boundaries and major settlements.
5. How are historical maps of Pioneer California used today?
Historical maps of Pioneer California continue to be valuable resources for:
- Historical Research: Providing insights into the lives and experiences of early settlers.
- Genealogical Research: Tracing the movements of ancestors and understanding their settlement patterns.
- Environmental Studies: Analyzing land use patterns and the impact of human activity on the environment.
- Educational Purposes: Teaching students about the history of the West and the significance of maps in exploration and development.
Tips for Studying Pioneer California Maps
- Examine the Map’s Context: Consider the date, creator, and purpose of the map to understand its limitations and biases.
- Compare Different Maps: Comparing multiple maps from the same period can reveal inconsistencies and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
- Look for Symbols and Legends: Pay attention to the symbols and legends used on the map to interpret its information.
- Consider the Scale: Understand the scale of the map to accurately judge distances and the size of features.
- Research the Historical Context: Explore historical accounts, diaries, and other primary sources to gain a deeper understanding of the events depicted on the map.
Conclusion
Maps of Pioneer California are not simply static representations of the past but powerful tools for understanding the complex and dynamic history of the state. They offer a glimpse into the challenges and triumphs of westward expansion, the vital role of Indigenous knowledge, and the lasting impact of human activity on the landscape. By studying these maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the journeys of those who forged the path West, paving the way for the California we know today.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Path West: A Look at Pioneer California on Historical Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!