China’s Geographic Position: A Global Powerhouse at the Heart of Asia
Related Articles: China’s Geographic Position: A Global Powerhouse at the Heart of Asia
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to China’s Geographic Position: A Global Powerhouse at the Heart of Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
China’s Geographic Position: A Global Powerhouse at the Heart of Asia

China, the world’s most populous nation, occupies a strategically significant position in East Asia. Its vast territory stretches across a diverse landscape, encompassing mountains, deserts, plains, and coastlines, making it a land of immense geographical and cultural variety. Understanding China’s location on the map reveals a complex tapestry of historical, economic, and political influences that have shaped its destiny and continue to influence its global role.
A Land of Extremes: China’s Geographic Features
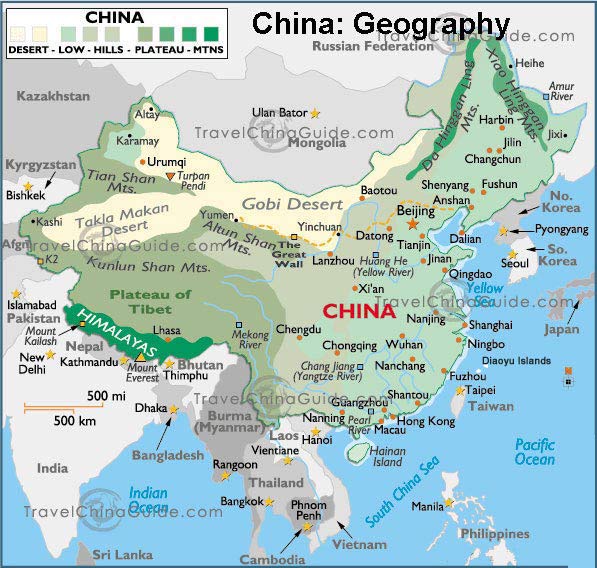
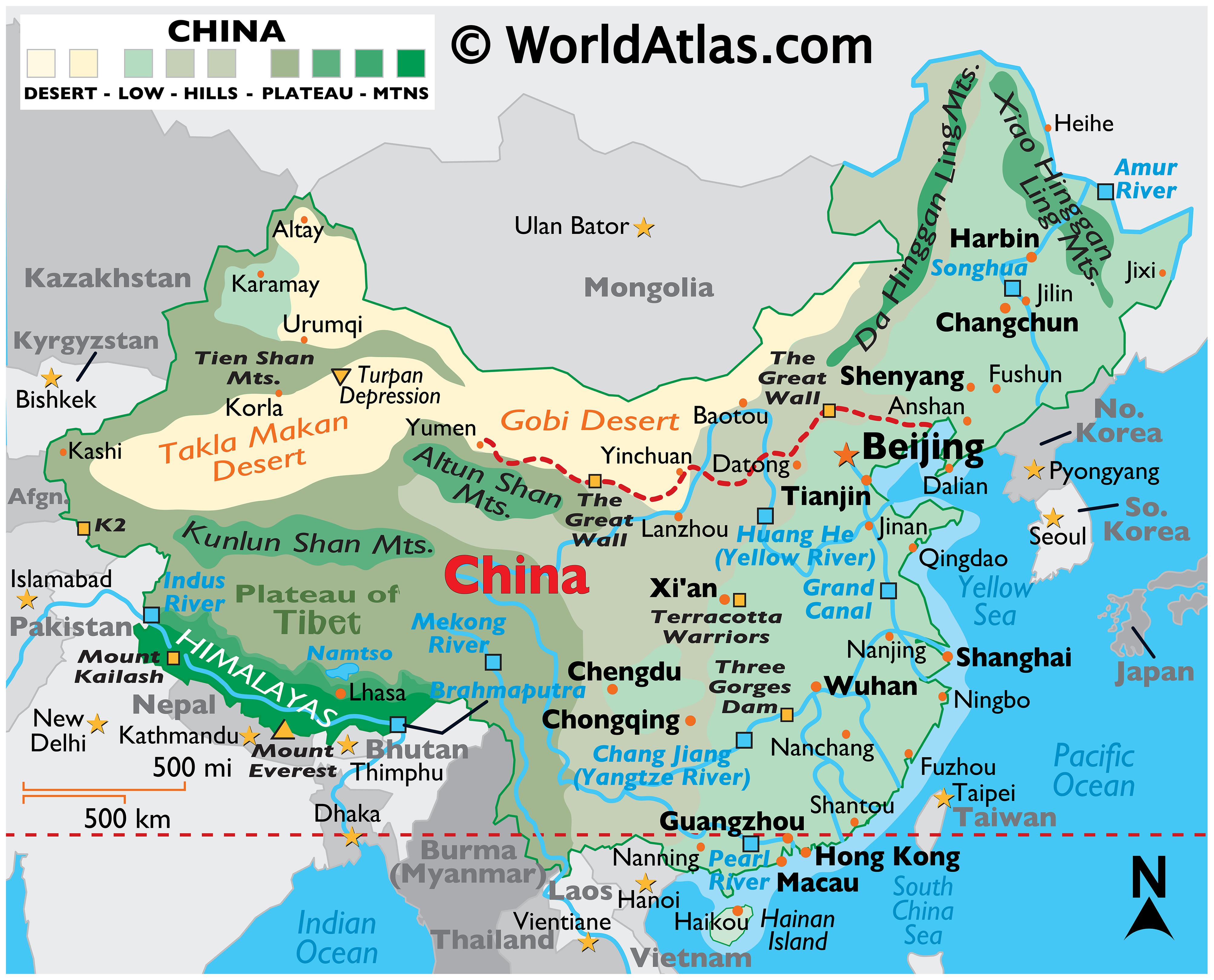
China’s geographical expanse, spanning over 9.6 million square kilometers, is a testament to its diverse terrain. The country’s northern border stretches along the vast Mongolian steppe, while the south borders the tropical jungles of Southeast Asia. The towering Himalayas, home to Mount Everest, form a natural barrier along the western frontier, separating China from South Asia. To the east, the country’s long coastline faces the Pacific Ocean, offering access to vital maritime trade routes.
The Significance of China’s Location
China’s location at the heart of Asia has profound implications for its history, culture, and global influence.
-
Historical Crossroads: Situated at the crossroads of ancient trade routes like the Silk Road, China has long been a bridge between East and West, fostering cultural exchange and economic prosperity. This strategic location exposed China to diverse influences, shaping its unique cultural identity.
-
Economic Powerhouse: China’s vast landmass, rich natural resources, and abundant workforce have fueled its economic growth. Its location provides access to vital shipping lanes and trade routes, allowing it to become a global manufacturing and exporting hub.
-
Regional Influence: China’s geographical proximity to its neighboring countries has shaped its regional relationships. It plays a significant role in regional security and economic cooperation, often acting as a mediator and facilitator in resolving regional conflicts.
-
Global Power: China’s strategic location has propelled its rise as a global power. Its economic and military strength, coupled with its historical significance, has made it a key player in international affairs, influencing global politics and economics.
Exploring China’s Geographic Divisions
To fully understand China’s location on the map, it is essential to explore its major geographical divisions:
-
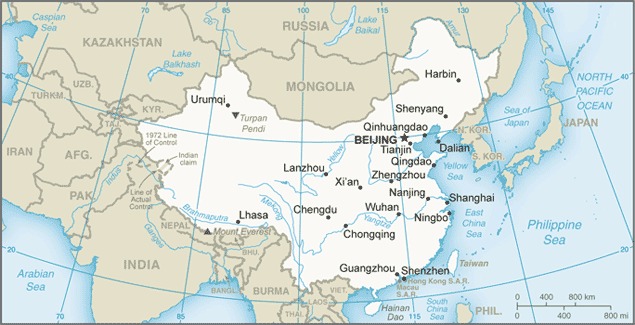
North China Plain: This fertile plain, encompassing the Yellow River basin, has been the cradle of Chinese civilization. It is a densely populated region with significant agricultural production and major urban centers like Beijing and Tianjin.
-
Northeast China: Known as Manchuria, this region is characterized by its vast grasslands and fertile black soil. It is a major industrial center and a key source of agricultural products.
-
East China: This region, encompassing the Yangtze River delta, is China’s economic powerhouse. Shanghai, the country’s largest city and a global financial center, is located in this region.
-
South China: This region, encompassing the Pearl River delta, is known for its subtropical climate and rich biodiversity. It is a major agricultural and industrial hub, home to cities like Guangzhou and Shenzhen.
-
Southwest China: This region, encompassing the Tibetan Plateau and the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, is characterized by its high altitudes and diverse ethnicities. It is a source of important natural resources and a popular destination for tourism.
-
Northwest China: This region, encompassing the Taklamakan Desert and the Gobi Desert, is characterized by its arid climate and sparse population. It is a source of important mineral resources and a key region for the development of infrastructure.
FAQs: Understanding China’s Geographic Context
1. What are the major rivers in China?
China is home to several major rivers, including the Yellow River, the Yangtze River, the Pearl River, and the Mekong River. These rivers play a crucial role in irrigation, transportation, and economic development.
2. What are the major mountain ranges in China?
China is home to several major mountain ranges, including the Himalayas, the Kunlun Mountains, the Tian Shan Mountains, and the Qinling Mountains. These mountains are a source of important natural resources and play a significant role in shaping the country’s climate and biodiversity.
3. What are the major deserts in China?
China is home to several major deserts, including the Taklamakan Desert, the Gobi Desert, and the Badain Jaran Desert. These deserts are characterized by their arid climate and sparse vegetation.
4. What is the significance of the Three Gorges Dam?
The Three Gorges Dam, located on the Yangtze River, is the world’s largest hydroelectric dam. It plays a significant role in flood control, power generation, and navigation.
5. What are the major cities in China?
China is home to several major cities, including Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Chongqing, and Tianjin. These cities are major economic and cultural centers, playing a significant role in the country’s development.
Tips for Learning More about China’s Geography
-
Explore online maps: Utilize online mapping tools like Google Maps and Bing Maps to visualize China’s location and its major geographical features.
-
Consult atlases and geographical texts: Refer to detailed atlases and geographical textbooks to gain a deeper understanding of China’s geography, including its physical features, climate, and vegetation.
-
Watch documentaries and films: Explore documentaries and films that focus on China’s geography and its impact on the country’s history, culture, and development.
-
Travel to China: Experiencing China firsthand is the best way to appreciate its diverse geography and cultural richness. Visit different regions of the country to witness the unique landscapes and local traditions.
Conclusion: China’s Geography – A Foundation for its Global Role
China’s location on the map is not merely a geographical fact; it is a defining element of its history, culture, and global influence. Its strategic position at the heart of Asia has shaped its destiny, fueled its economic rise, and positioned it as a key player in the global arena. Understanding China’s geography is crucial for appreciating its past, present, and future, as it continues to shape the world’s political and economic landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into China’s Geographic Position: A Global Powerhouse at the Heart of Asia. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!