Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Germany’s Geography
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Germany’s Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Germany’s Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Germany’s Geography
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Germany’s Geography
- 3.1 A Nation of Contrasts: Exploring Germany’s Physical Landscape
- 3.2 The Importance of Rivers and Waterways
- 3.3 The Impact of Germany’s Geography on its History and Culture
- 3.4 Understanding Germany’s Geography: An Essential Tool for Exploration
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions:
- 3.6 Tips for Exploring Germany’s Geography:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Germany’s Geography

Germany, a nation steeped in history and renowned for its cultural and economic prowess, boasts a diverse and intriguing geographical landscape. Understanding its physical layout is crucial for comprehending the country’s rich history, its unique cultural identity, and its significant role on the world stage. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed overview of Germany’s geography, exploring its key features and their implications.
A Nation of Contrasts: Exploring Germany’s Physical Landscape
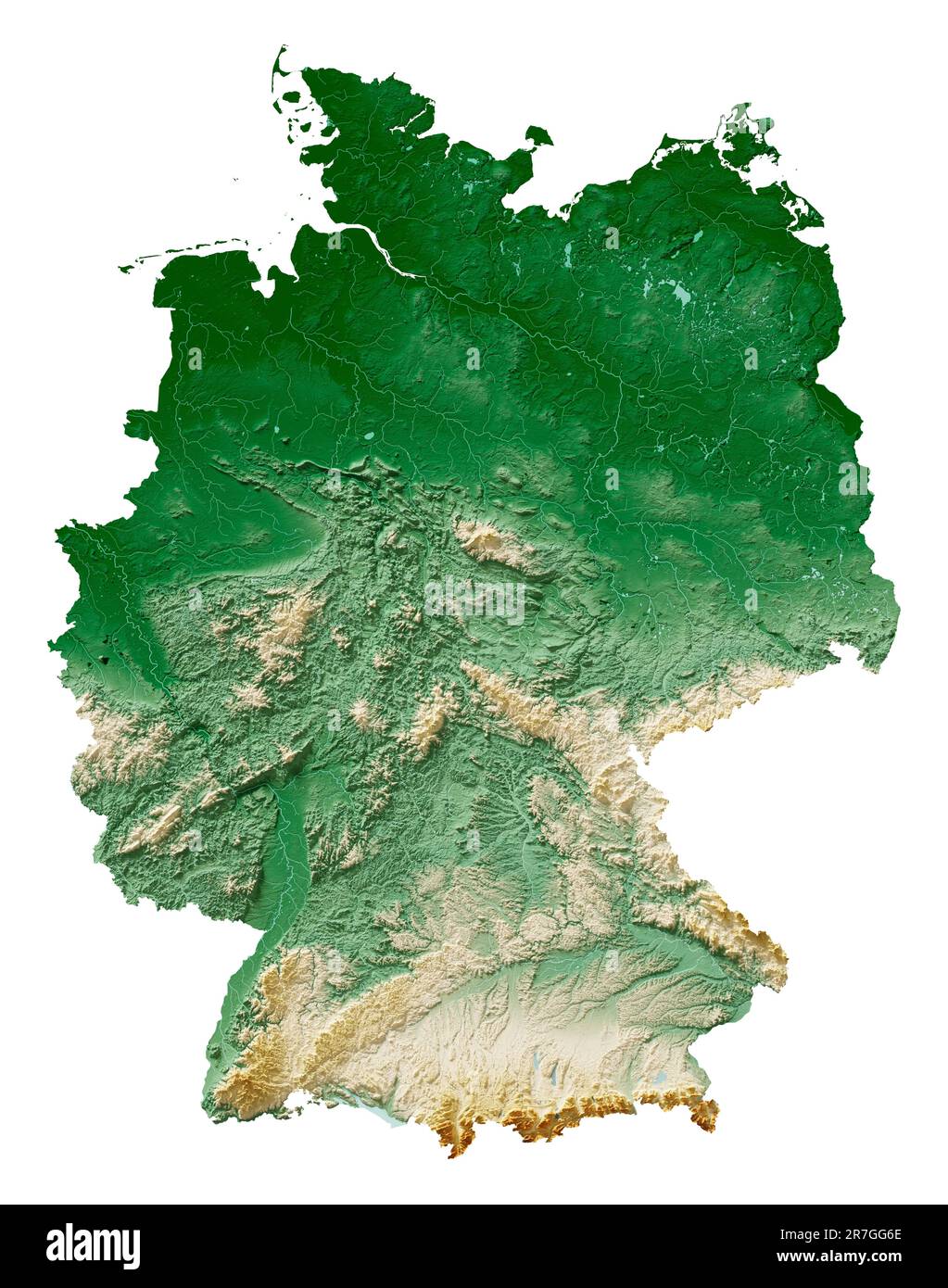
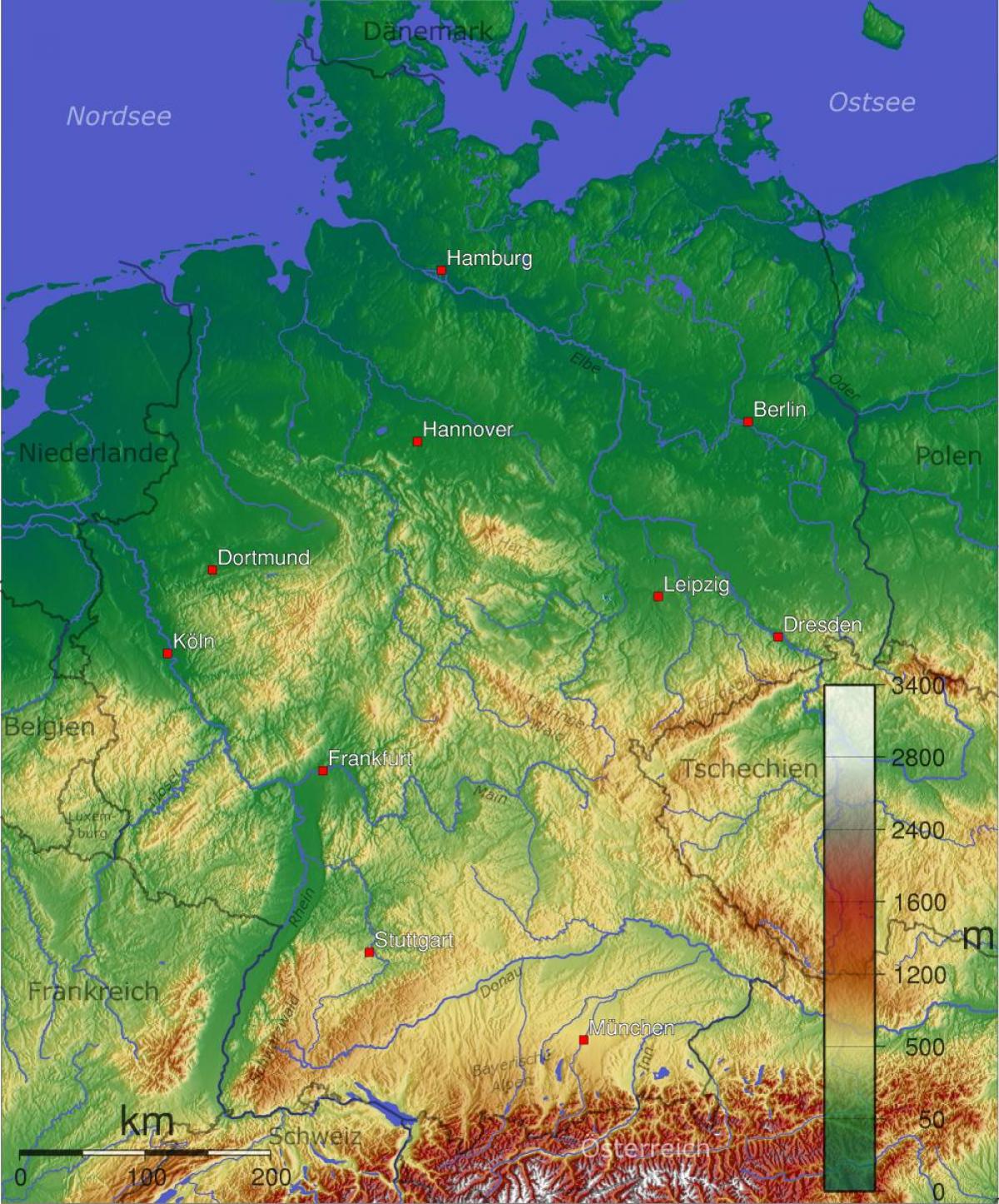
Germany’s physical landscape is a tapestry woven with diverse features, ranging from vast plains to towering mountains. This geographical variety has profoundly shaped the country’s history, its economic development, and its cultural identity.
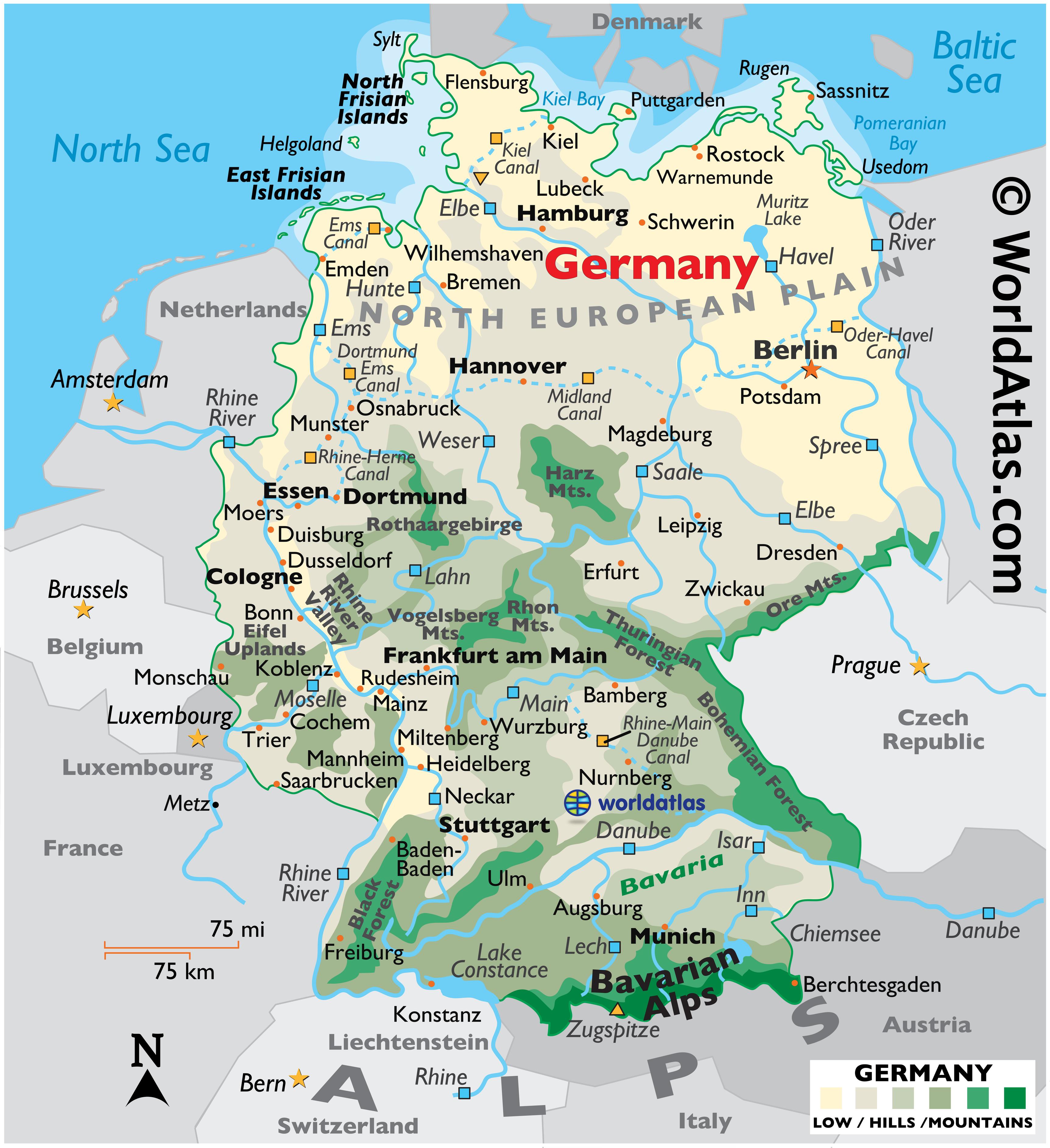
1. The North German Plain:
The North German Plain, stretching across the northern portion of the country, is characterized by flat, fertile land. This region is a major agricultural hub, producing wheat, barley, potatoes, and sugar beets. The Elbe, Weser, and Oder rivers flow through this plain, providing vital waterways for transportation and commerce. The Baltic Sea coastline further contributes to the region’s economic significance.
2. The Central Uplands:
The Central Uplands, a region of rolling hills and low mountains, occupy the central portion of Germany. This region is home to the Harz Mountains, the Thuringian Forest, and the Franconian Jura. The Central Uplands are known for their picturesque landscapes and their abundant forests, which are vital for timber production and recreation.
3. The Southern Highlands:
The Southern Highlands, located in southern Germany, are characterized by the towering Alps, the Black Forest, and the Bavarian Alps. These mountain ranges are renowned for their stunning scenery, offering opportunities for hiking, skiing, and other outdoor activities. The Alps, in particular, are a significant watershed, providing water for many of Germany’s major rivers.
4. The German Coastlines:
Germany boasts coastlines along the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. The North Sea coast is characterized by sandy beaches, while the Baltic Sea coast features a mix of sandy beaches and rocky cliffs. The North Sea coastline is important for fishing and shipping, while the Baltic Sea coastline is popular for tourism.
The Importance of Rivers and Waterways
Rivers and waterways have played a pivotal role in Germany’s history and development. The Rhine, the Elbe, and the Danube are among the most important rivers, serving as vital transportation routes and sources of hydroelectric power. These rivers also contribute to the country’s agricultural productivity, providing irrigation for crops.
1. The Rhine River:
The Rhine River, one of Europe’s most important waterways, flows through western Germany. It is a major transportation route for goods and people, connecting Germany to other European countries. The Rhine Valley is also a significant wine-producing region, known for its high-quality Riesling wines.
2. The Elbe River:
The Elbe River flows through northern Germany, connecting the country’s interior to the North Sea. It is a major transportation route for goods and is also important for tourism. The Elbe River is known for its picturesque scenery, particularly in the Elbe Sandstone Mountains.
3. The Danube River:
The Danube River, Europe’s second-longest river, flows through southeastern Germany. It is a vital transportation route, connecting Germany to other countries in Central and Eastern Europe. The Danube Valley is also known for its agricultural productivity and its rich cultural heritage.
The Impact of Germany’s Geography on its History and Culture
Germany’s diverse geographical landscape has had a profound impact on its history and culture.
1. Political and Economic Development:
Germany’s central location in Europe has made it a crossroads for trade and cultural exchange. Its fertile plains have supported a thriving agricultural economy, while its rivers have provided vital transportation routes. The country’s abundant natural resources, including coal, iron ore, and timber, have also played a significant role in its economic development.
2. Cultural Identity:
Germany’s diverse landscape has fostered a rich and varied cultural identity. The country’s mountains have inspired folklore and legends, while its rivers have been the subject of numerous poems and songs. The country’s cities, built along major rivers and trade routes, have become centers of art, music, and literature.
3. Environmental Challenges:
Germany’s geography also presents certain environmental challenges. The country’s industrial development has led to air and water pollution, while its dense population has put pressure on its natural resources. Climate change is also a growing concern, threatening to alter Germany’s landscape and its agricultural productivity.
Understanding Germany’s Geography: An Essential Tool for Exploration
A thorough understanding of Germany’s geography is essential for anyone seeking to explore the country’s rich history, its vibrant culture, and its stunning natural beauty. By appreciating the interplay of its physical features, its historical development, and its cultural identity, one can gain a deeper appreciation for this fascinating and complex nation.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the major geographical features of Germany?
A: Germany’s major geographical features include the North German Plain, the Central Uplands, the Southern Highlands, and its coastlines along the North Sea and the Baltic Sea.
Q: What are the most important rivers in Germany?
A: The most important rivers in Germany are the Rhine, the Elbe, and the Danube.
Q: How has Germany’s geography influenced its history and culture?
A: Germany’s central location in Europe has made it a crossroads for trade and cultural exchange. Its fertile plains have supported a thriving agricultural economy, while its rivers have provided vital transportation routes. The country’s abundant natural resources have also played a significant role in its economic development.
Q: What are some of the environmental challenges facing Germany?
A: Germany faces environmental challenges such as air and water pollution, pressure on natural resources due to its dense population, and the threat of climate change.
Tips for Exploring Germany’s Geography:
- Visit a variety of regions: Explore the North German Plain, the Central Uplands, the Southern Highlands, and Germany’s coastlines to experience the country’s diverse landscape.
- Take a river cruise: A river cruise along the Rhine, the Elbe, or the Danube offers a unique perspective on Germany’s geography and its history.
- Go hiking or skiing in the mountains: The Alps, the Black Forest, and the Bavarian Alps offer stunning scenery and opportunities for outdoor activities.
- Visit a national park: Germany has numerous national parks, protecting its diverse natural landscapes and wildlife.
- Learn about Germany’s environmental challenges: Understanding the country’s environmental challenges can help you appreciate the importance of sustainable tourism and environmental protection.
Conclusion:
Germany’s geography is a tapestry woven with diverse features, from vast plains to towering mountains, from fertile valleys to rugged coastlines. Understanding this complex landscape is crucial for comprehending the country’s history, its culture, and its place in the world. By exploring its geographical features and appreciating their impact on its development, one can gain a deeper understanding and appreciation for this fascinating and complex nation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Germany’s Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!