Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps with Loops: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps with Loops: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps with Loops: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps with Loops: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps with Loops: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding Java Maps: A Foundation for Iteration
- 3.2 The Power of Iteration: Unveiling the Contents of a Map
- 3.3 Exploring the Loop Landscape: Navigating Map Iteration Techniques
- 3.4 Choosing the Right Loop: A Guide to Effective Iteration
- 3.5 Beyond the Basics: Advanced Map Iteration Techniques
- 3.6 Common Scenarios: Applying Map Iteration in Real-World Applications
- 3.7 Frequently Asked Questions: Navigating the Nuances of Map Iteration
- 3.8 Tips for Effective Map Iteration: Optimizing Your Code
- 3.9 Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Map Iteration in Java
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps with Loops: A Comprehensive Guide
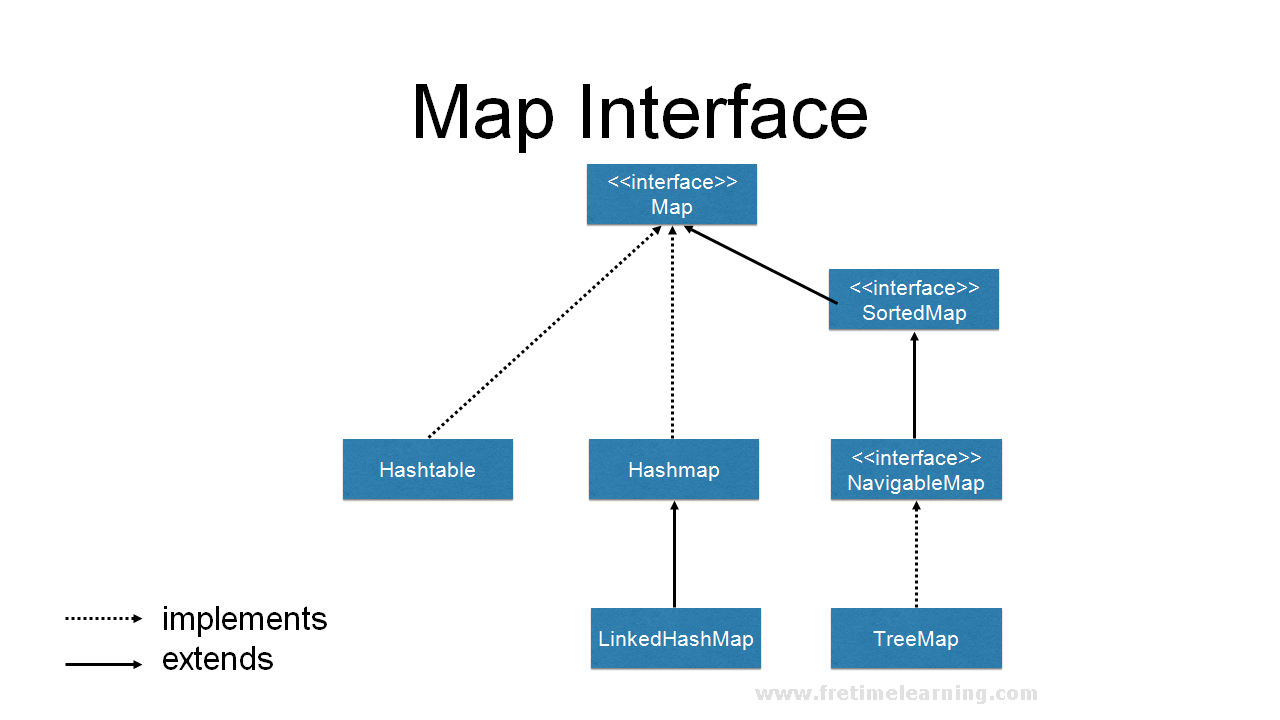
The Java Map data structure, a cornerstone of efficient data management, provides a powerful mechanism for storing key-value pairs. It allows for quick retrieval of values based on their associated keys, making it invaluable for a wide range of programming tasks. However, effectively iterating through the entries within a Map requires a thorough understanding of looping constructs and their application. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of Java Map iteration using loops, providing a detailed exploration of the various techniques and their practical implications.
Understanding Java Maps: A Foundation for Iteration
Before embarking on the intricacies of loop-based Map traversal, a solid grasp of the fundamental concepts behind Java Maps is essential.
-
Key-Value Pairs: The core principle of a
Mapis its ability to store data in the form of key-value pairs. Each key uniquely identifies a specific value, enabling efficient retrieval. -
Immutability of Keys: Keys within a
Mapare immutable, meaning they cannot be changed once assigned. This ensures that the uniqueness of keys is maintained, facilitating consistent data access. -
Heterogeneous Data:
Mapsallow for the storage of diverse data types for both keys and values. This flexibility makes them adaptable to a wide variety of real-world scenarios.
The Power of Iteration: Unveiling the Contents of a Map
Iterating through a Map enables you to access and process each key-value pair individually. This is crucial for tasks like:
- Data Extraction: Retrieving specific values based on their associated keys.
- Data Modification: Updating or replacing values based on their corresponding keys.
- Data Transformation: Applying operations to values or keys, creating new data structures from existing ones.
Exploring the Loop Landscape: Navigating Map Iteration Techniques
Java provides a variety of loop constructs for iterating over Maps, each offering unique advantages and considerations:
1. The for Loop with keySet() Method:
This traditional for loop approach leverages the keySet() method of the Map interface. It retrieves a Set containing all the keys within the Map, allowing you to iterate over them directly.
Map<String, Integer> ages = new HashMap<>();
ages.put("Alice", 25);
ages.put("Bob", 30);
ages.put("Charlie", 28);
for (String key : ages.keySet())
System.out.println("Key: " + key + ", Value: " + ages.get(key));
2. The for Loop with entrySet() Method:
The entrySet() method provides a more comprehensive approach, returning a Set of Map.Entry objects. Each Entry encapsulates both the key and value, offering direct access to both elements during iteration.
Map<String, String> cities = new HashMap<>();
cities.put("Alice", "New York");
cities.put("Bob", "London");
cities.put("Charlie", "Paris");
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : cities.entrySet())
System.out.println("Key: " + entry.getKey() + ", Value: " + entry.getValue());
3. The forEach Loop with Lambda Expressions:
Java 8 introduced the forEach loop, which provides a more concise and efficient way to iterate over collections. This loop utilizes lambda expressions, allowing you to define the actions to be performed on each element within the Map.
Map<String, Double> salaries = new HashMap<>();
salaries.put("Alice", 60000.0);
salaries.put("Bob", 75000.0);
salaries.put("Charlie", 55000.0);
salaries.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println("Key: " + key + ", Value: " + value));4. The Iterator Interface:
The Iterator interface, a core element of Java’s collection framework, provides a powerful and flexible mechanism for iterating over collections. You can obtain an Iterator for a Map‘s entrySet() and use its methods (hasNext() and next()) to navigate through the entries.
Map<String, String> hobbies = new HashMap<>();
hobbies.put("Alice", "Painting");
hobbies.put("Bob", "Photography");
hobbies.put("Charlie", "Hiking");
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = hobbies.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext())
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println("Key: " + entry.getKey() + ", Value: " + entry.getValue());
Choosing the Right Loop: A Guide to Effective Iteration
The selection of the appropriate loop for iterating over a Map depends on the specific requirements and context of your code:
-
Simplicity and Clarity: For straightforward iteration tasks, the
forloop withkeySet()orentrySet()often provides a clear and concise solution. -
Conciseness and Efficiency: The
forEachloop with lambda expressions excels in scenarios where you need a compact and efficient approach, especially when working with functional programming paradigms. -
Flexibility and Control: The
Iteratorinterface offers the greatest flexibility and control, enabling you to customize the iteration process and handle specific conditions.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Map Iteration Techniques
While the standard loop constructs provide a solid foundation for Map iteration, certain advanced techniques enhance your ability to manipulate and analyze data within Maps:
-
Filtering Entries: Use the
stream()method to create a stream ofMap.Entryobjects, enabling you to apply filtering operations based on specific conditions. This allows you to extract relevant entries based on key or value criteria.
Map<String, Integer> scores = new HashMap<>();
scores.put("Alice", 85);
scores.put("Bob", 92);
scores.put("Charlie", 78);
scores.entrySet().stream()
.filter(entry -> entry.getValue() >= 90)
.forEach(entry -> System.out.println("Key: " + entry.getKey() + ", Value: " + entry.getValue()));-
Transforming Values: Utilize the
map()method to apply transformations to the values within theMap. This enables you to modify or derive new data based on the existing values.
Map<String, Integer> ages = new HashMap<>();
ages.put("Alice", 25);
ages.put("Bob", 30);
ages.put("Charlie", 28);
ages.entrySet().stream()
.map(entry -> new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue() + 1))
.forEach(entry -> System.out.println("Key: " + entry.getKey() + ", Value: " + entry.getValue()));-
Sorting Entries: The
sorted()method allows you to sort the entries within aMapbased on specific criteria, such as key or value order. This is particularly useful when you need to process data in a structured manner.
Map<String, Integer> ages = new HashMap<>();
ages.put("Alice", 25);
ages.put("Bob", 30);
ages.put("Charlie", 28);
ages.entrySet().stream()
.sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue())
.forEach(entry -> System.out.println("Key: " + entry.getKey() + ", Value: " + entry.getValue()));Common Scenarios: Applying Map Iteration in Real-World Applications
The ability to iterate over Maps is essential for a wide range of programming tasks:
-
Data Validation: Iterate through a
Mapcontaining user input to ensure that all required fields are filled correctly and meet specific validation criteria. -
Data Aggregation: Aggregate data from a
Mapbased on specific keys or values, calculating statistics like sums, averages, or counts. -
Data Visualization: Iterate through a
Mapto extract data for generating charts, graphs, or other visual representations of data. -
Data Processing: Apply transformations or modifications to data within a
Map, preparing it for further processing or analysis. -
Configuration Management: Read and process configuration files stored as
Maps, dynamically configuring applications based on user preferences or system settings.
Frequently Asked Questions: Navigating the Nuances of Map Iteration
1. Can I modify the Map while iterating over it using a traditional for loop?
Modifying a Map while iterating over it using a traditional for loop can lead to unexpected behavior and potential errors. This is because the iteration process relies on the keySet() or entrySet() methods, which provide a snapshot of the Map at the time of their invocation. Any modifications made to the Map during iteration may not be reflected in the iteration process.
2. What is the most efficient way to iterate over a Map?
The most efficient way to iterate over a Map depends on the specific requirements and the underlying implementation of the Map. For general purposes, the forEach loop with lambda expressions is generally considered more efficient than traditional for loops due to its optimized implementation. However, for complex operations or when dealing with large datasets, the Iterator interface may offer greater control and potential performance benefits.
3. Can I iterate over a Map in reverse order?
Yes, you can iterate over a Map in reverse order using the Iterator interface and the ListIterator class. The ListIterator provides methods like previous() and hasPrevious(), enabling you to traverse the entries in reverse order. However, it’s important to note that the order of iteration for a Map is not guaranteed to be consistent, as it depends on the underlying implementation.
4. How do I handle concurrent modifications to a Map during iteration?
Concurrent modifications to a Map during iteration can lead to unexpected behavior and potential errors. To handle such scenarios, it’s crucial to use concurrent data structures like ConcurrentHashMap. Alternatively, you can use synchronization mechanisms like locks to ensure thread safety during iteration.
5. Can I iterate over a Map using a stream without creating a new stream?
Yes, you can iterate over a Map using a stream without creating a new stream. This can be achieved by using the stream() method on the Map‘s entrySet() directly. This approach allows you to leverage the powerful stream API for filtering, mapping, and other operations without creating a separate stream object.
Tips for Effective Map Iteration: Optimizing Your Code
- Choose the Right Loop: Select the loop construct that best suits your needs, balancing simplicity, efficiency, and flexibility.
-
Avoid Modifying During Iteration: Be cautious when modifying a
Mapduring iteration, as it can lead to unexpected behavior. - Use Stream API: Utilize the Java Stream API for advanced operations like filtering, mapping, and sorting, enhancing your data processing capabilities.
-
Prioritize Efficiency: Consider using the
forEachloop with lambda expressions for concise and efficient iteration, especially when working with large datasets. -
Handle Concurrent Modifications: Implement appropriate concurrency mechanisms to handle concurrent modifications to a
Mapduring iteration, ensuring thread safety.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Map Iteration in Java
The ability to effectively iterate over Maps is a fundamental skill for any Java programmer. By understanding the various looping constructs, their advantages and disadvantages, and the advanced techniques available, you gain the power to unlock the full potential of Maps in your applications. Whether you’re processing user input, analyzing data, or dynamically configuring your applications, mastering Map iteration empowers you to write efficient, robust, and elegant Java code.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps with Loops: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!