Navigating the Waters: Understanding and Utilizing Flood Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Waters: Understanding and Utilizing Flood Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waters: Understanding and Utilizing Flood Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Waters: Understanding and Utilizing Flood Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Waters: Understanding and Utilizing Flood Maps
- 3.1 Understanding Flood Maps: A Visual Guide to Risk
- 3.2 The Importance of Flood Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
- 3.3 Accessing and Utilizing Flood Maps: A Guide to Information
- 3.4 FAQs about Flood Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.5 Tips for Using Flood Maps Effectively: A Practical Guide
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Call for Informed Action
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Waters: Understanding and Utilizing Flood Maps
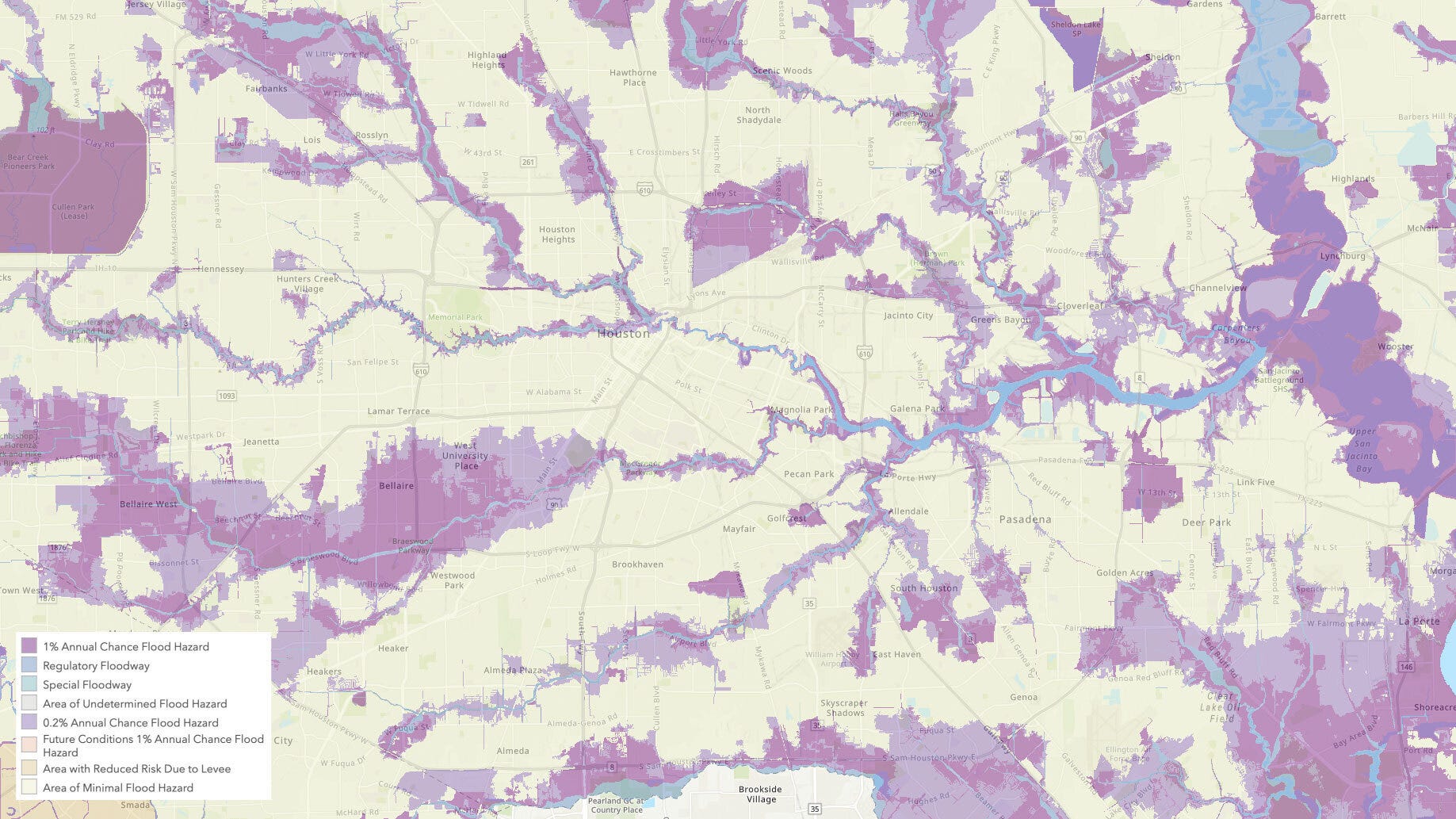
The specter of flooding looms large in a world increasingly impacted by climate change. As weather patterns become more erratic and extreme, the risk of flooding rises, threatening lives, property, and infrastructure. In this context, flood maps emerge as crucial tools for mitigating these risks, providing valuable insights into flood-prone areas and enabling informed decision-making.
Understanding Flood Maps: A Visual Guide to Risk
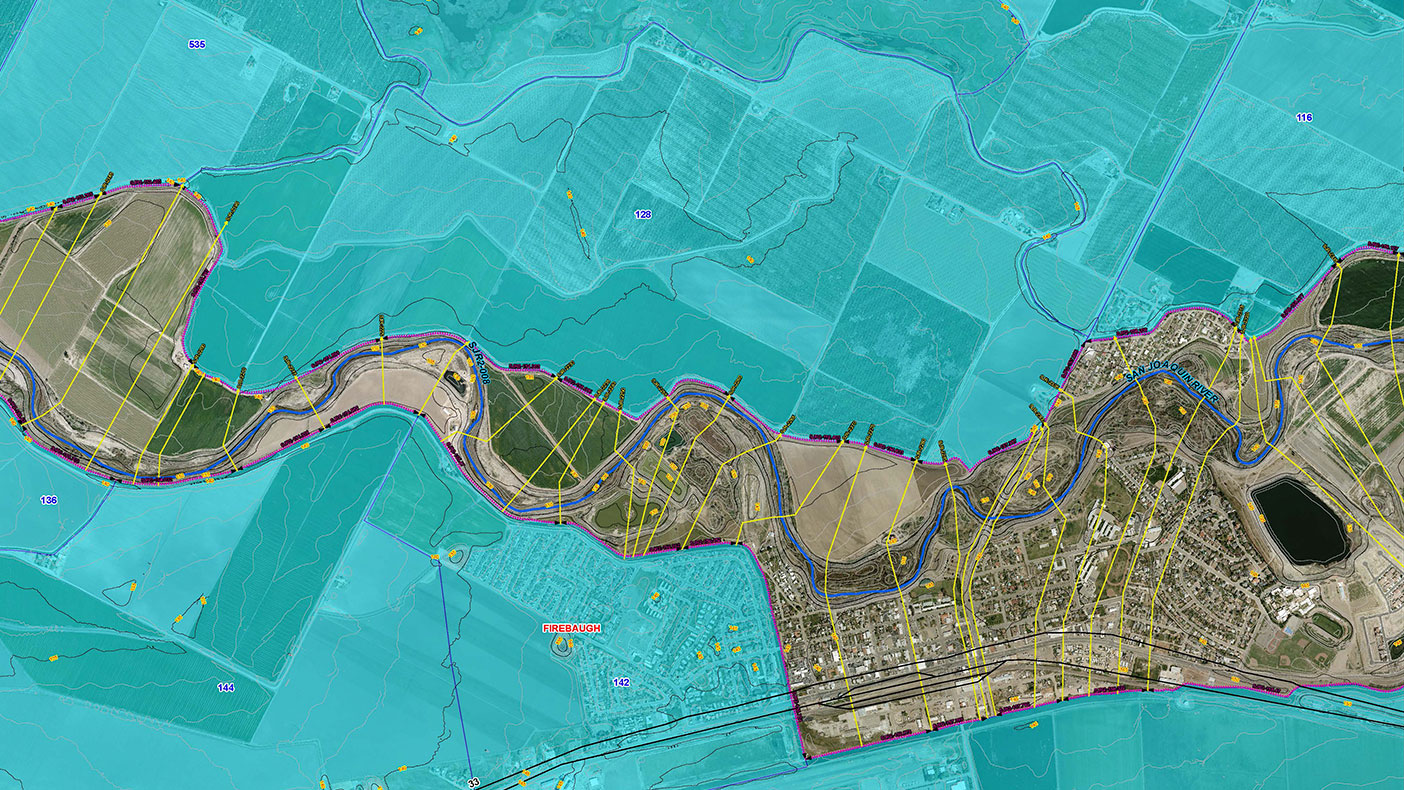
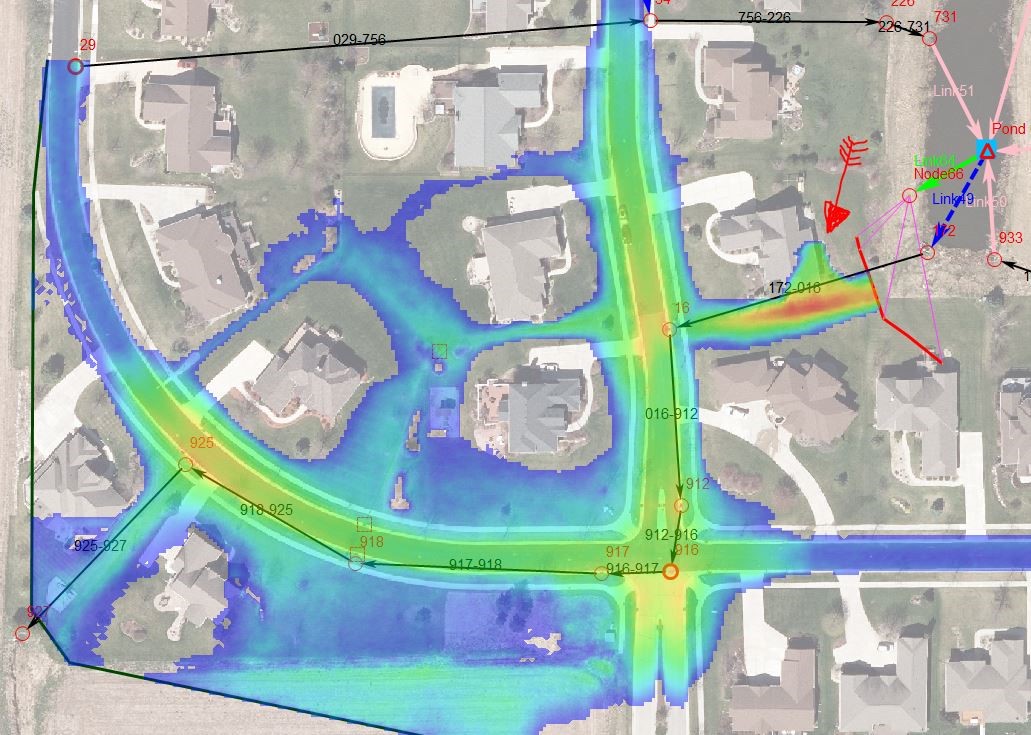
Flood maps are visual representations of areas susceptible to flooding. They depict the extent and depth of potential flooding, often categorized by severity levels based on factors like flood frequency, duration, and water depth. These maps are not static but dynamic, reflecting the ever-changing landscape of flood risks.
Types of Flood Maps:
- Flood Hazard Maps: These maps identify areas at risk of flooding based on historical data and flood modeling. They typically display flood zones, inundation depths, and potential flood pathways.
- Flood Risk Maps: These maps go beyond hazard identification, incorporating factors like population density, property value, and critical infrastructure to assess the potential impact of flooding. They provide a more nuanced understanding of risk by considering both the physical hazard and its socio-economic consequences.
- Real-Time Flood Maps: These maps utilize sensor data and hydrological models to provide up-to-date information on current flood conditions. They are particularly valuable during active flood events, enabling rapid response and evacuation efforts.
The Importance of Flood Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
Flood maps serve as vital resources for a multitude of stakeholders, each leveraging their unique benefits:
1. Government Agencies:
- Disaster Planning and Response: Flood maps inform the development of emergency preparedness plans, evacuation routes, and resource allocation strategies for flood events.
- Infrastructure Development: They guide infrastructure projects, ensuring that roads, bridges, and other critical infrastructure are designed and located to minimize flood risks.
- Land Use Planning: Maps help in zoning regulations, preventing development in high-risk areas and promoting sustainable land use practices.
2. Insurance Companies:
- Risk Assessment: Flood maps enable insurance companies to assess the risk of flood damage for properties, informing premium calculations and coverage decisions.
- Flood Insurance Programs: They contribute to the development of flood insurance programs, ensuring adequate coverage for vulnerable areas.
3. Individuals and Communities:
- Property Valuation: Flood maps can influence property values, providing homeowners with a realistic understanding of potential flood risks.
- Informed Decision-Making: They empower individuals to make informed decisions about property purchase, insurance coverage, and flood mitigation measures.
- Community Awareness: Maps raise awareness about flood risks, encouraging proactive measures to reduce vulnerability and promote community resilience.
Accessing and Utilizing Flood Maps: A Guide to Information
Various sources provide access to flood maps, each catering to specific needs and audiences:
1. Government Websites:
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA): FEMA provides comprehensive flood maps, including Flood Insurance Rate Maps (FIRMs), for the United States.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): NOAA offers a range of flood-related data and maps, including real-time flood forecasts and historical flood information.
- State and Local Agencies: Many states and local governments maintain their own flood maps, providing localized information relevant to specific regions.
2. Private Companies and Organizations:
- Insurance Companies: Many insurance companies provide access to flood maps for their policyholders, facilitating risk assessment and coverage decisions.
- Mapping and GIS Companies: Companies specializing in mapping and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) often develop and distribute flood maps, catering to commercial and research applications.
3. Online Platforms:
- Google Maps: Google Maps integrates flood information into its platform, displaying flood zones and historical flood data.
- Flood Forecasting Websites: Several websites offer real-time flood forecasts and maps, providing up-to-date information on flood conditions.
Utilizing Flood Maps Effectively:
- Understand Map Limitations: Flood maps are based on historical data and modeling, and their accuracy can be influenced by various factors. It is important to understand their limitations and consider them as tools for risk assessment rather than absolute guarantees.
- Consult with Experts: For critical decisions related to infrastructure, development, or property purchase, consult with professionals like engineers, hydrologists, or risk assessors to interpret flood maps accurately.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of updates and changes to flood maps, as flood risks can evolve over time due to climate change, land use changes, or other factors.
FAQs about Flood Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
1. How are flood maps created?
Flood maps are typically created using a combination of historical flood data, topographic surveys, hydrological modeling, and geographic information systems (GIS). They involve analyzing past flood events, identifying flood-prone areas, and simulating potential future flood scenarios.
2. What information do flood maps provide?
Flood maps provide information about the extent and depth of potential flooding, including flood zones, inundation depths, and potential flood pathways. They may also include information about flood frequency, duration, and the severity of potential damage.
3. Are flood maps always accurate?
Flood maps are based on the best available data and modeling techniques, but they are not always perfectly accurate. They can be influenced by factors such as climate change, land use changes, and the availability of data. It is important to consider the limitations of flood maps and consult with experts for critical decisions.
4. How can I use flood maps to protect my property?
Flood maps can help you assess the risk of flooding to your property and make informed decisions about flood mitigation measures. They can guide you in choosing appropriate insurance coverage, elevating your home, or implementing other flood-proofing strategies.
5. What are the benefits of using flood maps for community planning?
Flood maps are essential for community planning, enabling governments and organizations to make informed decisions about land use, infrastructure development, emergency preparedness, and disaster response. They help to minimize flood risks, protect lives and property, and promote community resilience.
Tips for Using Flood Maps Effectively: A Practical Guide
1. Understand the Scale and Units: Pay attention to the scale and units used on the map, as they determine the level of detail and the accuracy of the information.
2. Consider the Date of the Map: Flood maps can become outdated due to changes in flood risks or data updates. Ensure you are using the most recent available map.
3. Interpret Flood Zones: Understand the different flood zones depicted on the map and their associated risk levels.
4. Identify Critical Infrastructure: Locate critical infrastructure such as schools, hospitals, and power stations on the map to assess their vulnerability to flooding.
5. Engage with Local Authorities: Consult with local authorities and emergency management agencies to understand their flood preparedness plans and evacuation procedures.
Conclusion: A Call for Informed Action
Flood maps are indispensable tools for navigating the complexities of flood risks. By providing a visual understanding of flood-prone areas, they empower individuals, communities, and governments to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and build resilience in the face of increasingly frequent and severe flood events.
As climate change continues to reshape our world, the importance of flood maps will only grow. By leveraging their insights and integrating them into planning, development, and emergency response strategies, we can better protect ourselves and our communities from the devastating consequences of flooding.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waters: Understanding and Utilizing Flood Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!