The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection

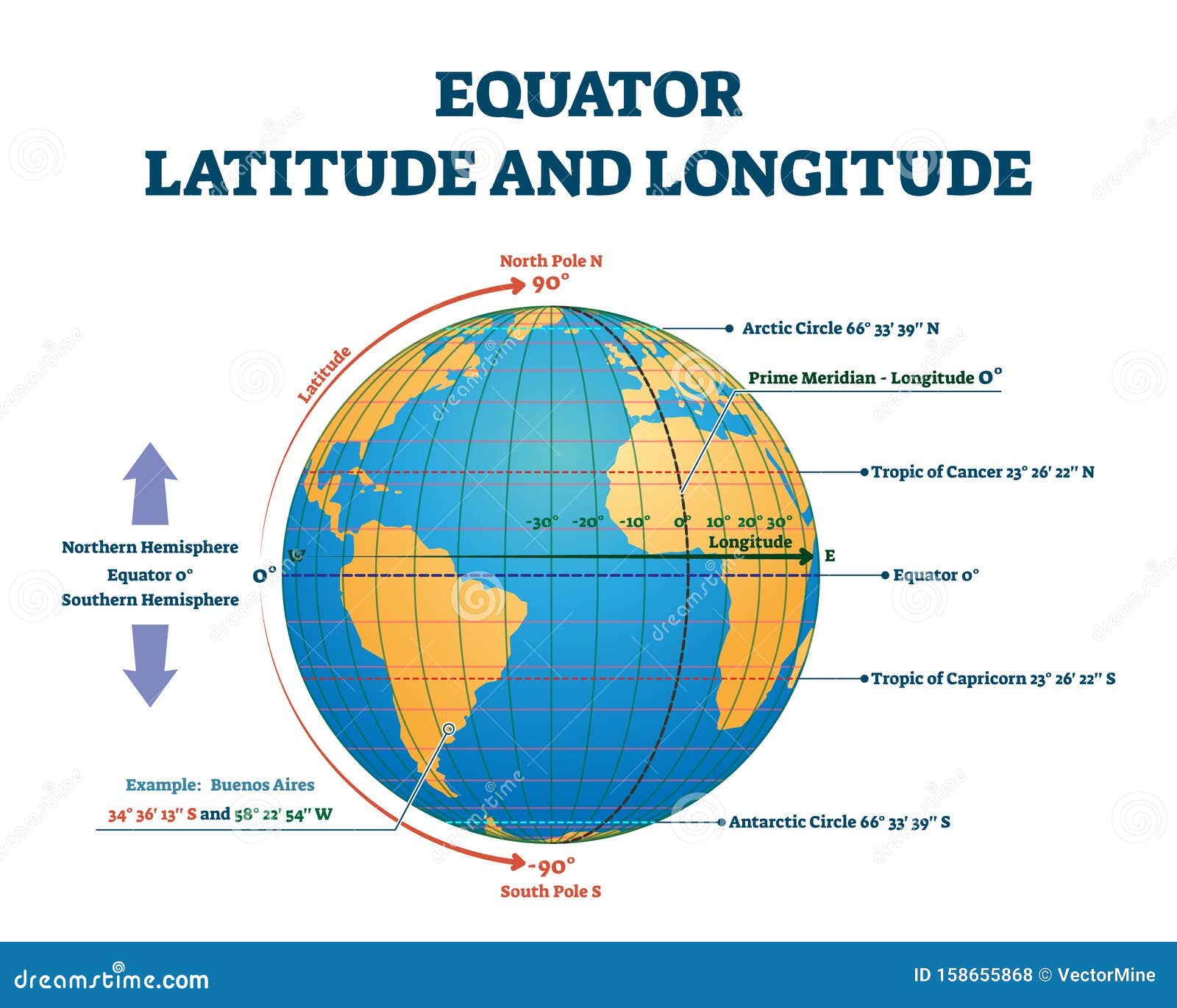
The equator, an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, is a fundamental geographical feature with significant implications for our understanding of the planet. This invisible line not only divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres but also plays a crucial role in shaping climate, culture, and even the distribution of life on Earth.
A Visual Representation of a Global Divide:
Maps depicting the equator serve as powerful visual aids, illustrating the fundamental division of the Earth into two distinct hemispheres. This simple line on a map highlights the stark differences in climate, vegetation, and even cultural practices that exist between the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
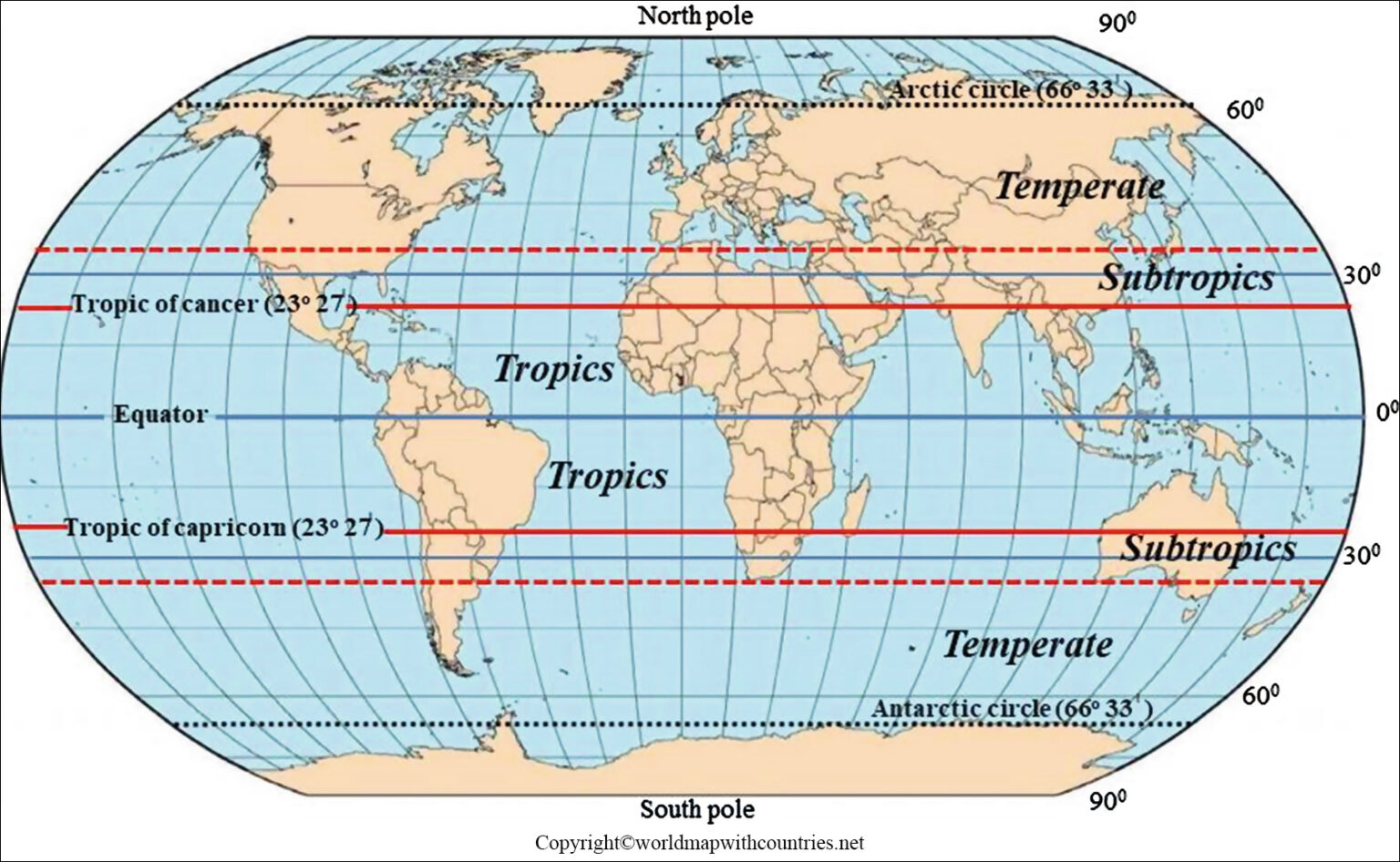
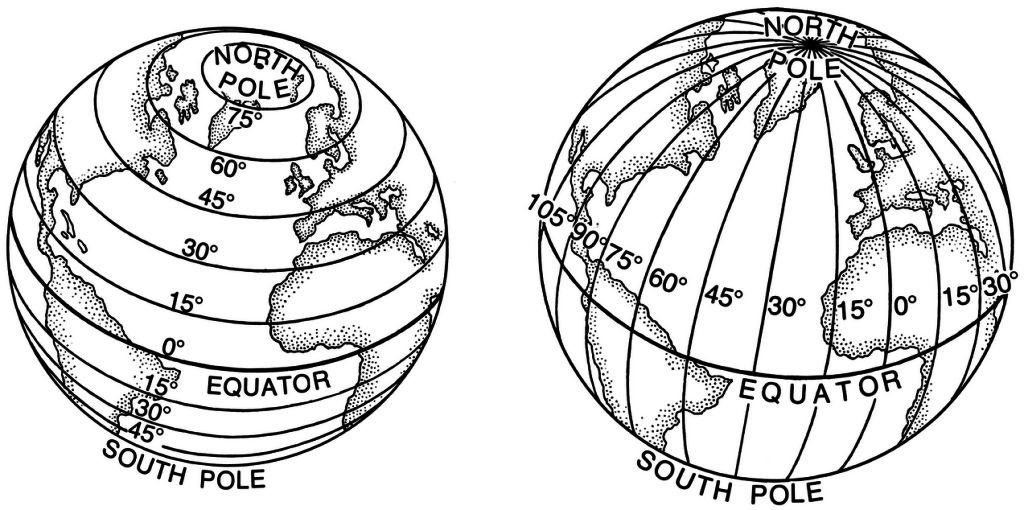
Understanding the Significance of Latitude:
The equator serves as the starting point for measuring latitude, a crucial geographical coordinate that defines a location’s position north or south of the equator. Latitude lines, which run parallel to the equator, are measured in degrees, with 0 degrees at the equator and 90 degrees at the North and South Poles.
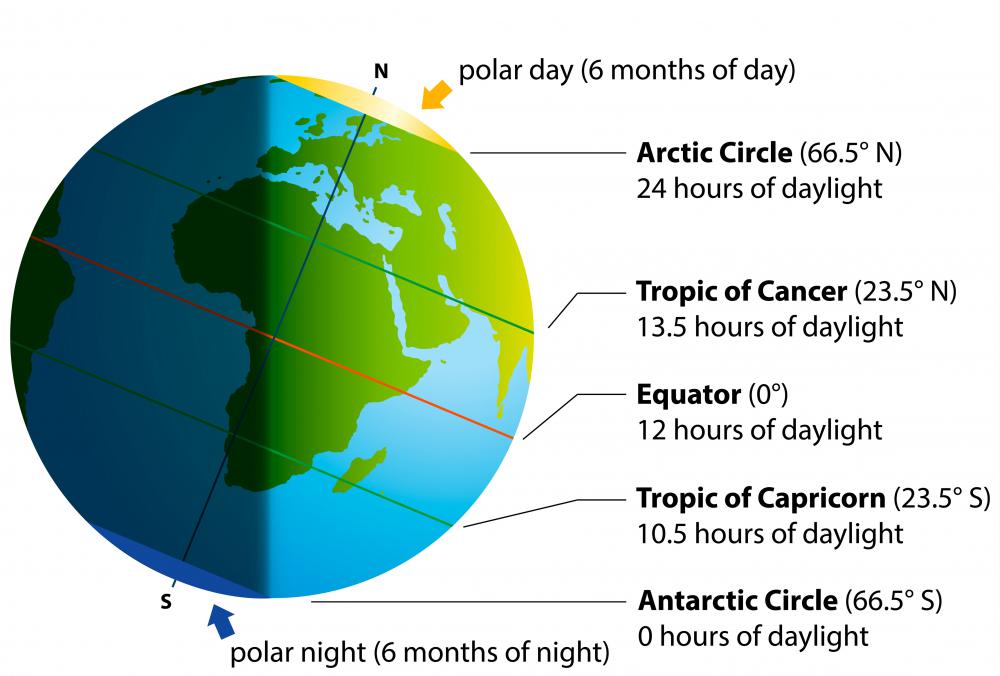
Climate and the Equator:
The equator plays a pivotal role in shaping the Earth’s climate patterns. Due to its position directly under the sun’s rays, the equator experiences consistently high temperatures and receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year. This intense solar radiation results in a tropical climate characterized by high humidity, abundant rainfall, and dense vegetation.
Biodiversity and the Equator:
The equatorial region is renowned for its incredible biodiversity, boasting a wide array of plant and animal species. The warm, humid climate and abundant rainfall create ideal conditions for the flourishing of diverse ecosystems, including rainforests, savannas, and coral reefs.
Cultural Diversity and the Equator:
The equator intersects numerous countries and cultures, leading to a rich tapestry of human diversity. From the vibrant traditions of South America to the diverse cultures of Africa and Southeast Asia, the equator is a meeting point for various languages, customs, and beliefs.
Navigational Significance:
For centuries, sailors and explorers have relied on the equator as a navigational reference point. Its precise location and the consistent patterns of celestial bodies near the equator have enabled accurate navigation and exploration throughout history.
The Equator in Global Affairs:
The equator’s significance extends beyond geography and climate. It plays a role in international relations and global affairs, particularly in discussions regarding climate change, resource management, and international cooperation.
Exploring the Equator: A Journey of Discovery:
Traveling along the equator offers a unique and enriching experience. From the lush rainforests of the Amazon to the bustling cities of Southeast Asia, a journey along the equator reveals the diversity of cultures, landscapes, and ecosystems that thrive in this special region.
FAQs about the Equator:
Q: What is the exact length of the equator?
A: The equator is approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles) long.
Q: Why is the equator hotter than other parts of the Earth?
A: The equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year due to its position directly under the sun’s rays. This intense solar radiation leads to consistently high temperatures.
Q: What are some notable countries that lie on the equator?
A: Some countries that lie on the equator include Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, Indonesia, and Kenya.
Q: How does the equator affect the Earth’s rotation?
A: The Earth’s rotation axis is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees, which causes the equator to experience the most direct sunlight throughout the year. This tilt also influences the Earth’s seasons.
Tips for Understanding Maps Depicting the Equator:
- Pay attention to the scale: The scale of the map will determine the level of detail and the accuracy of the information presented.
- Look for key geographical features: Identify other important features such as continents, oceans, and major cities to gain a better understanding of the equator’s location and significance.
- Consider the projection: Different map projections can distort the shape and size of the Earth, so it’s important to choose a projection that accurately represents the equator.
Conclusion:
The equator, a line of division and connection, is a fundamental geographical feature with profound implications for our understanding of the Earth. From shaping climate and influencing biodiversity to serving as a navigational reference point and a symbol of cultural diversity, the equator plays a vital role in our world. By studying maps depicting the equator, we can gain a deeper appreciation for this significant geographical feature and its impact on our planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!