The Equator: An Imaginary Line with Real-World Significance
Related Articles: The Equator: An Imaginary Line with Real-World Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Equator: An Imaginary Line with Real-World Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: An Imaginary Line with Real-World Significance
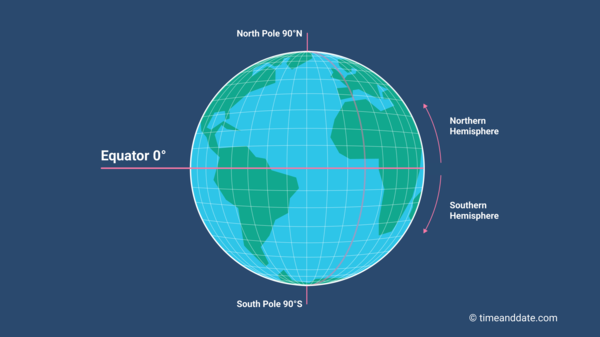
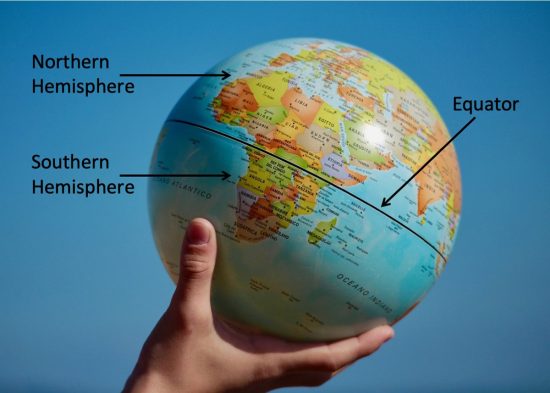
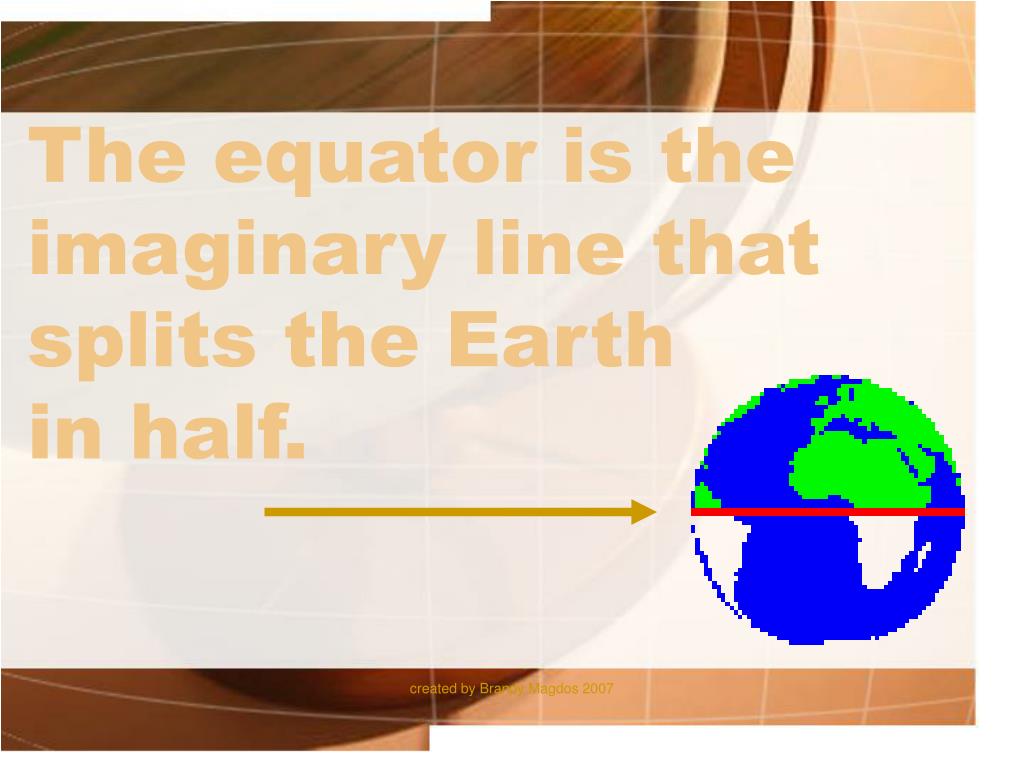
The Earth, a dynamic sphere spinning through space, is divided by an imaginary line known as the equator. This line, running horizontally around the globe at 0° latitude, holds immense significance in understanding the planet’s geography, climate, and even its cultural diversity.
A Defining Line: Understanding the Equator
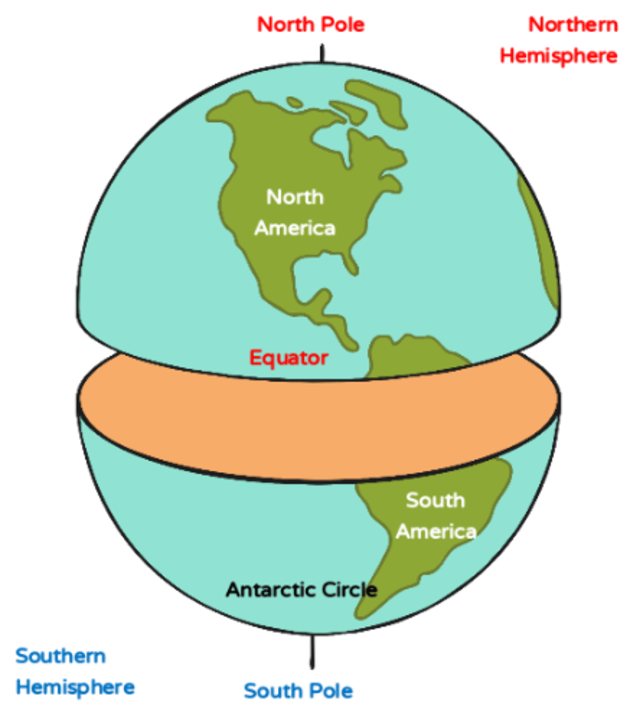
The equator is not a physical feature; it is a conceptual line marking the point where the Earth’s circumference is greatest. This line divides the globe into two hemispheres: the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. It is the foundation for the latitude system, a grid that helps us pinpoint locations on the Earth’s surface.
The Equator’s Influence on Climate and Geography
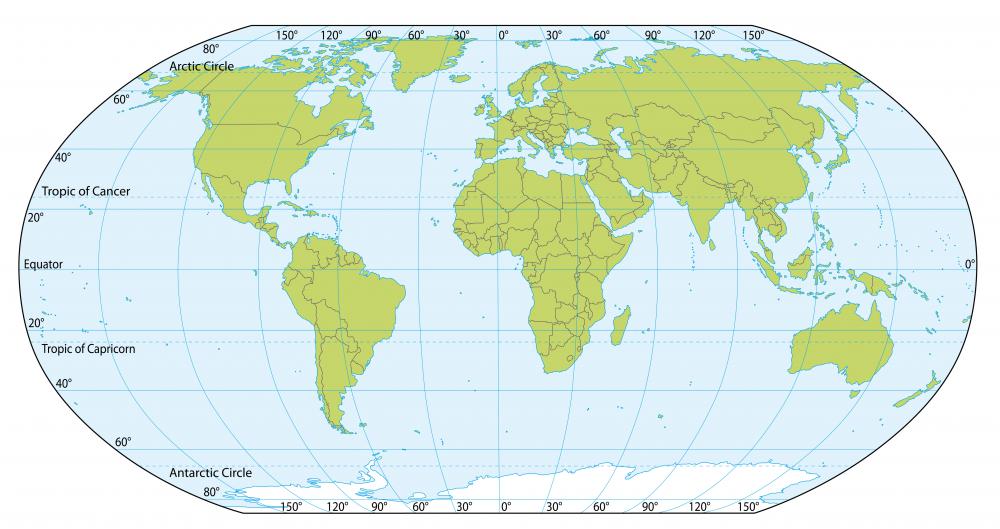
The equator’s position has a profound impact on the Earth’s climate and geography. It receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to consistently high temperatures and a tropical climate. This constant solar radiation fuels the formation of rainforests, characterized by high biodiversity and lush vegetation.
The equator also plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s wind patterns. The intense solar radiation at the equator creates low atmospheric pressure, leading to the rising of warm, moist air. This rising air cools and condenses, forming clouds and precipitation. As the air cools and descends, it creates high-pressure zones further north and south, leading to the establishment of trade winds that blow towards the equator.
The Equator and Cultural Diversity
The equator’s influence extends beyond climate and geography; it also shapes cultural landscapes. The regions along the equator are home to a diverse range of cultures, each with unique traditions, languages, and ways of life. This diversity is a reflection of the rich natural resources and varied ecosystems found in these areas.
Navigating the World with the Equator
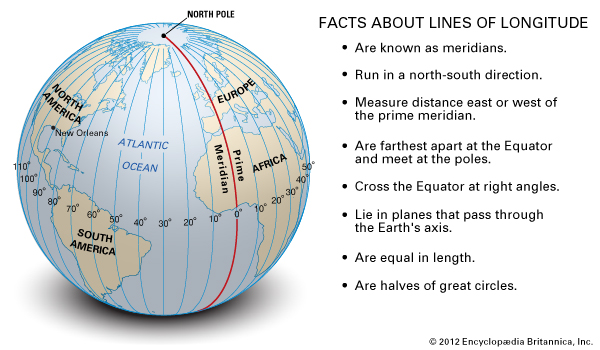
The equator is an essential tool for navigation. It serves as a reference point for calculating latitude, a key factor in determining a location’s position on the Earth’s surface. Sailors and explorers have relied on this imaginary line for centuries to chart their courses and navigate the vast oceans.
Exploring the Equator: A Journey Through Diverse Landscapes
The equator traverses a fascinating array of landscapes, from the dense rainforests of the Amazon basin to the towering mountains of the Andes. It passes through bustling cities like Quito, Ecuador, and Singapore, as well as remote villages nestled in the heart of tropical jungles.
The Equator’s Significance in Astronomy
The equator is not only important for geography and climate but also for astronomy. It defines the celestial equator, an imaginary line in the sky that is a projection of the Earth’s equator. The celestial equator serves as a reference point for astronomers, helping them track the movement of celestial bodies.
FAQs About the Equator
1. What is the difference between the equator and the prime meridian?
The equator is a horizontal line that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, while the prime meridian is a vertical line that divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
2. Is the equator a straight line?
The equator is not a straight line but a circle that runs around the Earth’s circumference at 0° latitude.
3. What is the significance of the equator in terms of time zones?
The equator serves as a reference point for calculating time zones. The International Date Line, which marks the transition from one day to the next, follows a path roughly parallel to the equator.
4. How does the equator influence the length of day and night?
At the equator, the length of day and night is approximately equal throughout the year. This is because the Earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees, and the equator lies directly on the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the sun.
5. What are some of the challenges faced by people living near the equator?
People living near the equator often face challenges related to extreme heat, humidity, and heavy rainfall. These conditions can lead to difficulties in agriculture, infrastructure development, and public health.
Tips for Understanding the Equator
- Use a globe or map: Visualizing the equator on a globe or map can help you understand its position and significance.
- Learn about the latitude and longitude system: The latitude and longitude system is based on the equator and the prime meridian, and understanding this system can help you navigate the world.
- Research the cultures and ecosystems found along the equator: The equator is home to a diverse range of cultures and ecosystems, and exploring these can provide valuable insights into the world’s diversity.
Conclusion
The equator, though an imaginary line, is a fundamental concept in understanding the Earth’s geography, climate, and cultural diversity. It serves as a reference point for navigation, a key factor in shaping climate patterns, and a symbol of the planet’s rich and varied landscapes. By understanding the equator, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our planet and the forces that shape its diverse ecosystems and cultures.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: An Imaginary Line with Real-World Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!