The Israeli Election Map: A Visual Guide to Political Power
Related Articles: The Israeli Election Map: A Visual Guide to Political Power
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Israeli Election Map: A Visual Guide to Political Power. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Israeli Election Map: A Visual Guide to Political Power

The Israeli electoral landscape is a complex and dynamic one, shaped by a multitude of factors including demographics, party platforms, and historical events. Understanding the intricacies of this landscape requires more than just a cursory glance at the results; it necessitates a deeper dive into the geographical distribution of votes, the regional dynamics, and the underlying trends that influence electoral outcomes.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Israeli election map, highlighting its significance in deciphering the country’s political landscape. We will explore the historical evolution of the map, examine the key geographical divisions and their political implications, and analyze the impact of demographic shifts on electoral outcomes.
The Israeli Election System and Its Impact on the Map
Israel utilizes a system of proportional representation, where parties compete for seats in the Knesset (parliament) based on the percentage of votes they receive nationwide. This system differs significantly from the "winner-take-all" system used in many other countries, where the candidate with the most votes in a particular district wins the seat.
The proportional representation system has several implications for the Israeli election map:
- No need for district-specific campaigns: Parties do not need to tailor their campaigns to specific regions, as they are competing for votes nationwide. This can lead to a more nationalized political discourse, with parties focusing on broader issues rather than localized concerns.
- Greater representation for smaller parties: The proportional system allows smaller parties with niche appeal to gain representation in the Knesset, even if they do not win a majority of votes in any particular district. This contributes to a more diverse and fragmented political landscape.
- Formation of coalition governments: Due to the fragmented nature of the political landscape, coalition governments are the norm in Israel. This necessitates a complex process of negotiations and compromises between different parties, often leading to shifting alliances and political instability.
Historical Evolution of the Israeli Election Map
The Israeli election map has undergone significant transformations over the decades, reflecting the country’s evolving demographics, political landscape, and geopolitical realities.
- Early Years: In the early years of the State of Israel, the election map was largely defined by the geographic distribution of Jewish and Arab populations. The majority of Jewish voters were concentrated in the central and coastal regions, while Arab voters were primarily located in the north and south.
- The Rise of Religious Parties: The 1970s and 1980s witnessed the emergence of religious parties as significant players in Israeli politics. These parties, often associated with specific communities and ideologies, gained significant electoral support, particularly in the ultra-Orthodox strongholds of Jerusalem and Bnei Brak.
- The Impact of Peace Negotiations: The Oslo Accords and subsequent peace negotiations in the 1990s had a profound impact on the Israeli election map. The withdrawal from parts of the West Bank and the rise of a new generation of Israeli voters influenced voting patterns, with some areas experiencing a shift in political allegiances.
- The Rise of Right-Wing Parties: The 2000s saw the rise of right-wing parties like Likud and Yisrael Beiteinu, which gained significant electoral support, particularly in the settlements and peripheral regions. This shift reflected concerns about security, economic inequality, and the perceived threat from neighboring Arab states.
Key Geographical Divisions and Their Political Implications
The Israeli election map is marked by several key geographical divisions, each with its distinct political characteristics and voting patterns:
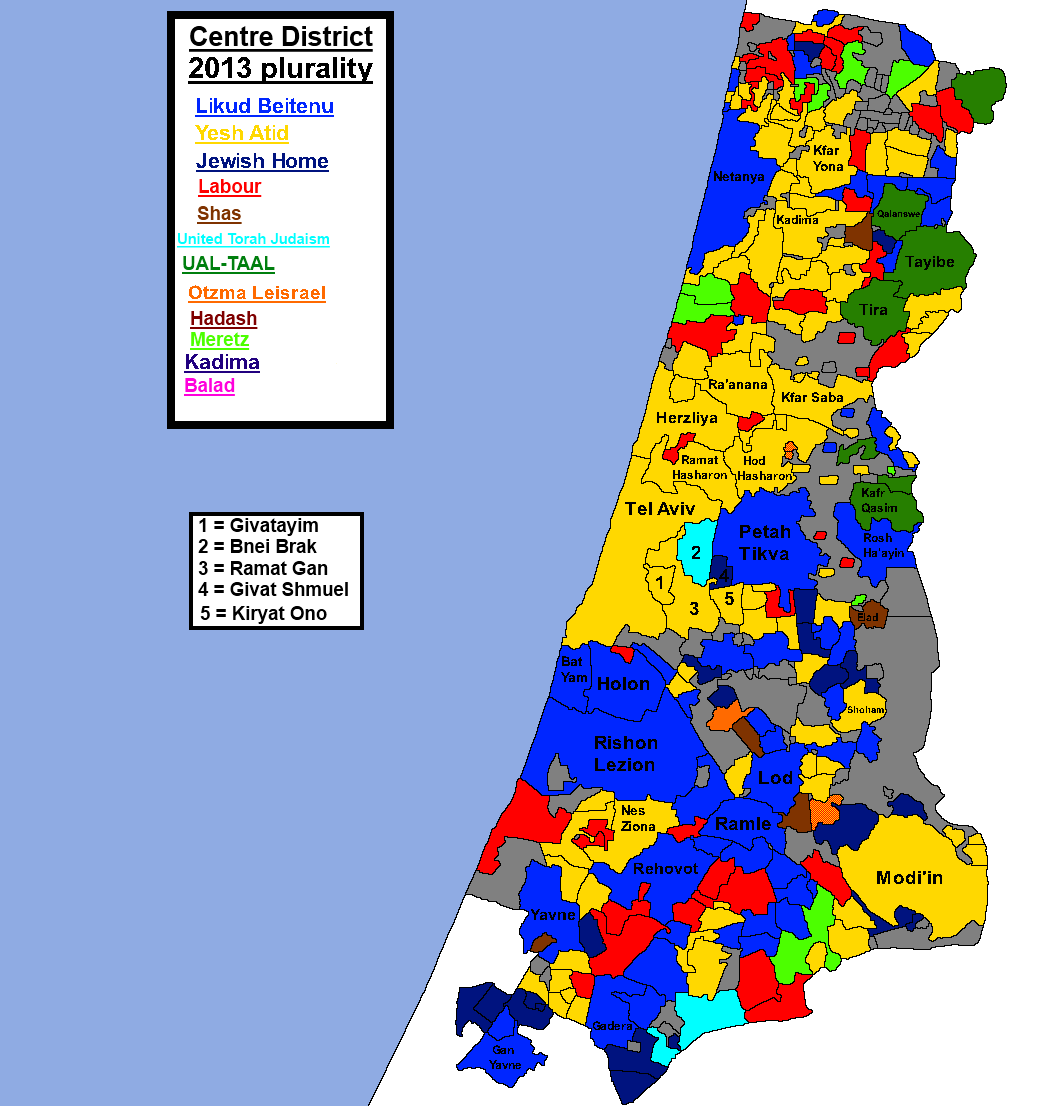
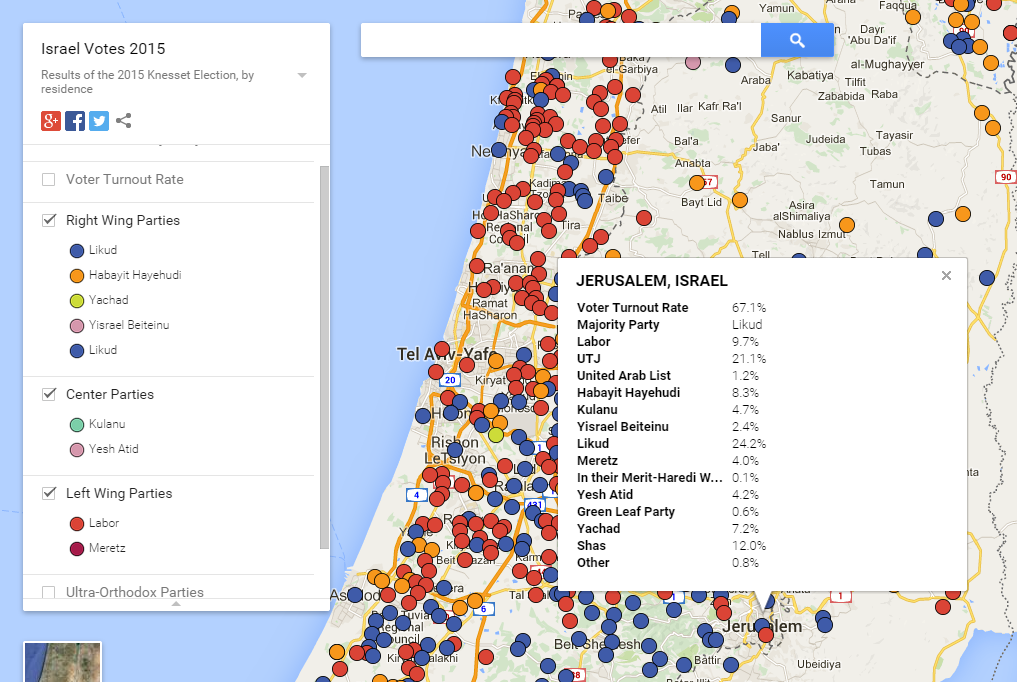
- Central Region: This region, encompassing Tel Aviv, Jerusalem, and surrounding areas, is considered the most politically diverse and competitive in Israel. It is home to a mix of urban and suburban populations, with a wide range of political views.
- Coastal Region: The coastal region, extending from Tel Aviv to Ashkelon, is known for its relatively liberal and secular voting patterns. It is home to a large concentration of high-tech industries and a significant population of young, educated voters.
- Northern Region: The northern region, encompassing Galilee and the Golan Heights, is characterized by a more diverse population, including a significant Arab minority. It is also home to a large number of kibbutzim and other agricultural communities.
- Southern Region: The southern region, including the Negev desert and the Gaza Strip, is characterized by a lower population density and a higher proportion of working-class voters. It is also home to a significant Bedouin population.
- Settlements: The settlements in the West Bank are a politically sensitive area, with voters often aligning with right-wing parties. The settlements are a source of ongoing controversy and are often the subject of international criticism.
Demographic Shifts and their Impact on the Election Map
The Israeli election map is constantly evolving, influenced by demographic shifts, such as changes in population growth, migration patterns, and socio-economic trends. These shifts can have a significant impact on electoral outcomes, altering the balance of power and influencing the formation of coalition governments.
- Arab Population Growth: The Arab population in Israel is growing at a faster rate than the Jewish population. This demographic shift has the potential to significantly impact future elections, particularly in areas with a large Arab population.
- Ultra-Orthodox Growth: The ultra-Orthodox population is also growing rapidly, particularly in Jerusalem and other religious centers. This growth has led to an increase in their political influence, with ultra-Orthodox parties playing a pivotal role in coalition governments.
- Immigration and Migration: Israel has a long history of immigration, with new arrivals from various countries bringing with them their own political perspectives and voting patterns. These patterns can influence the electoral landscape, particularly in areas with a high concentration of immigrants.
The Significance of the Israeli Election Map
Understanding the Israeli election map is crucial for anyone seeking to comprehend the country’s political dynamics. The map provides valuable insights into:
- The distribution of political power: The map reveals the geographic distribution of votes and the relative strength of different parties in different regions.
- The influence of demographics: The map highlights the impact of demographic shifts on electoral outcomes, such as the growing influence of the Arab and ultra-Orthodox populations.
- The formation of coalition governments: The map provides a visual representation of the political landscape, helping to explain the complex dynamics of coalition formation and the challenges of governance in a fragmented political system.
Conclusion
The Israeli election map is a dynamic and complex entity, reflecting the country’s multifaceted political landscape. It is a powerful tool for understanding the distribution of political power, the influence of demographics, and the formation of coalition governments. By analyzing the map’s historical evolution, key geographical divisions, and the impact of demographic shifts, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces shaping Israeli politics. As the country continues to evolve, the Israeli election map will continue to serve as a vital guide to its political landscape.
FAQs
1. What is the significance of the Israeli election map?
The Israeli election map is significant because it provides a visual representation of the distribution of political power, the influence of demographics, and the formation of coalition governments. It helps us understand the forces shaping Israeli politics and the dynamics of elections.
2. How does the proportional representation system impact the Israeli election map?
The proportional representation system eliminates the need for district-specific campaigns, allowing smaller parties to gain representation, and leading to the formation of coalition governments. This creates a more fragmented and diverse political landscape, with no single party typically holding a majority of seats.
3. What are some key geographical divisions in the Israeli election map?
Key divisions include the central region (Tel Aviv, Jerusalem), the coastal region (Tel Aviv to Ashkelon), the northern region (Galilee, Golan Heights), the southern region (Negev, Gaza Strip), and the settlements in the West Bank. Each region has its own distinct political characteristics and voting patterns.
4. How do demographic shifts influence the Israeli election map?
Demographic shifts, such as the growth of the Arab and ultra-Orthodox populations, and changes in immigration patterns, can significantly alter the electoral landscape. These shifts can impact the balance of power and influence the formation of coalition governments.
5. What are some future trends that could affect the Israeli election map?
Future trends to watch include continued population growth in Arab and ultra-Orthodox communities, the impact of technology on political engagement, and the evolving role of social media in shaping public opinion.
Tips for Understanding the Israeli Election Map
- Consult reliable sources: Refer to reputable news organizations, academic journals, and election analysis websites for accurate and unbiased information.
- Analyze historical trends: Examine past election results to identify patterns and understand the factors that have shaped the Israeli election map.
- Pay attention to demographics: Consider the impact of population growth, migration patterns, and socio-economic trends on voting behavior.
- Understand the political landscape: Familiarize yourself with the major political parties, their platforms, and their electoral bases.
- Stay informed about current events: Keep up with news about political campaigns, polls, and developments in the Israeli political system.
By following these tips, you can gain a deeper understanding of the Israeli election map and its significance in shaping the country’s political landscape.

![2019 Israeli Election by District and County [OC] : r/MapPorn](https://i.redd.it/w67tc6uclez21.png)

.png/220px-Winning_party_by_Locality_in_the_2022_Israeli_legislative_election_(English).png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Israeli Election Map: A Visual Guide to Political Power. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!