Tracing the Origins of the Mississippi: A Journey to the Headwaters
Related Articles: Tracing the Origins of the Mississippi: A Journey to the Headwaters
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Tracing the Origins of the Mississippi: A Journey to the Headwaters. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Tracing the Origins of the Mississippi: A Journey to the Headwaters
The Mississippi River, a majestic artery coursing through the heart of North America, holds a profound significance in the history, culture, and ecology of the continent. Its journey from humble beginnings to a mighty river is a testament to the forces of nature and the intricate web of life it sustains. Understanding the origins of this river, specifically its headwaters, offers a unique perspective on its vast influence.
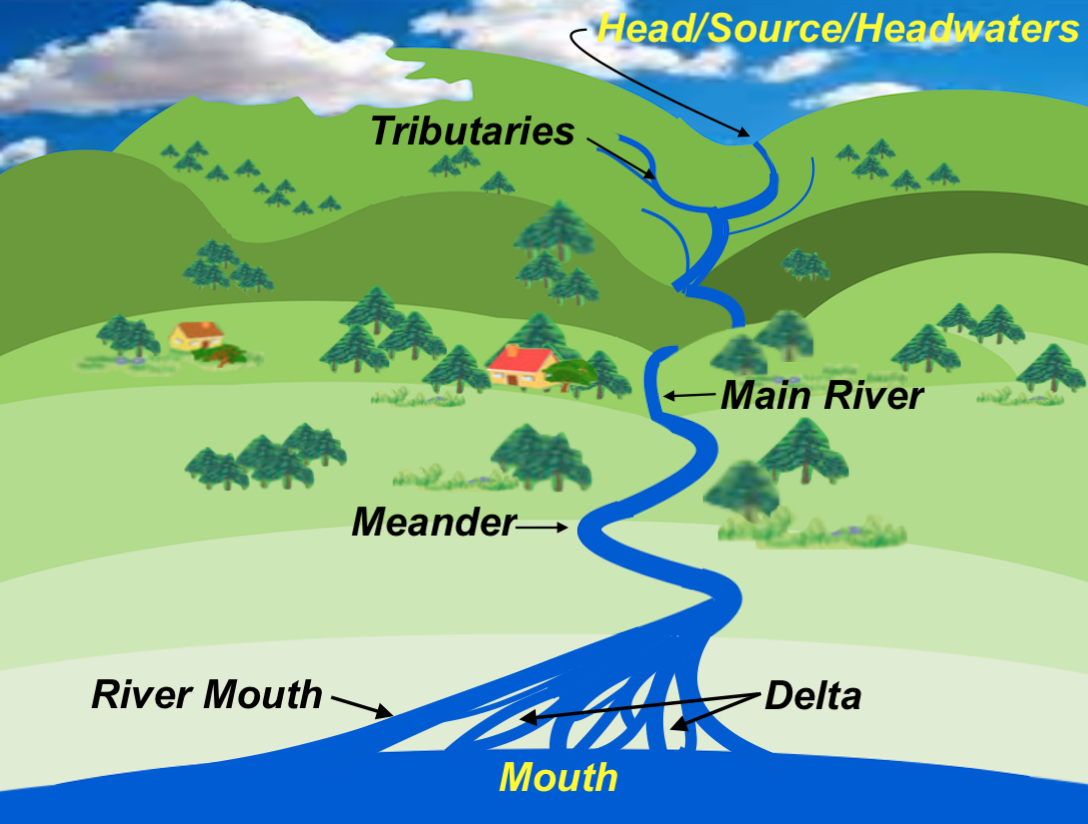
Delving into the Headwaters:
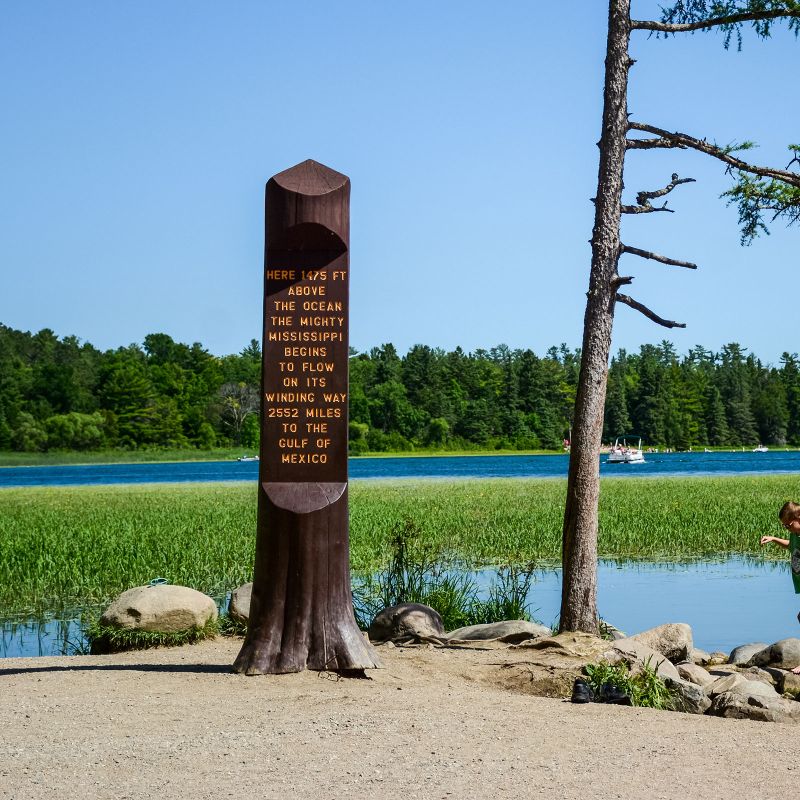
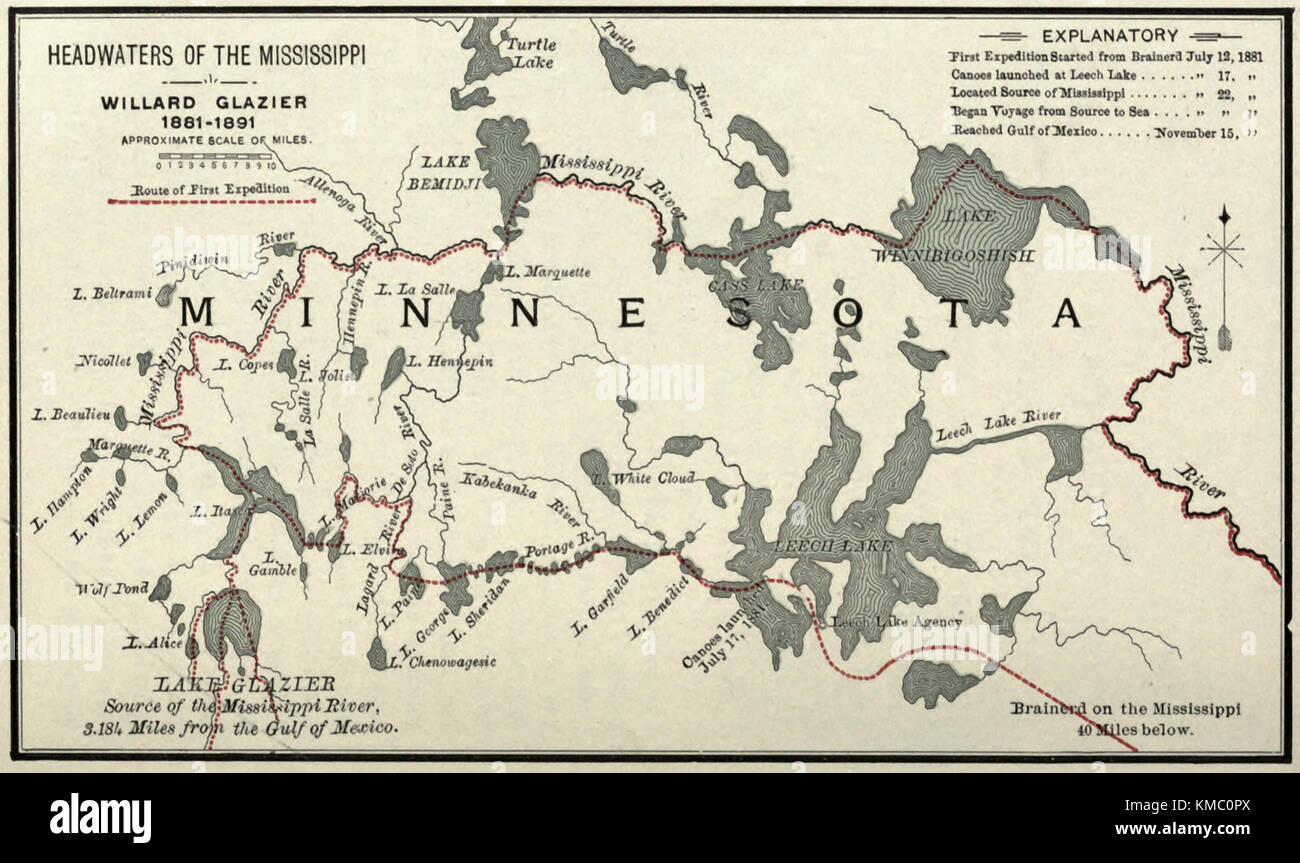
The Mississippi River’s headwaters, the source from which it originates, are located in the northern reaches of Minnesota, a region characterized by rolling hills, pristine lakes, and sprawling forests. The official source, recognized by the United States Geological Survey (USGS), is Lake Itasca, a tranquil body of water nestled amidst the boreal landscape.
However, the story of the Mississippi’s origins is not as simple as a single point of origin. The river’s flow is a complex interplay of tributaries, streams, and wetlands that contribute to its overall volume and character. Several other locations, including the Mississippi Headwaters State Forest and the Mississippi River Headwaters Scenic Byway, are considered integral to the river’s journey.
A Map Unveils the Journey:
A map of the Mississippi River’s headwaters provides a visual narrative of its origins. It reveals a network of interconnected waterways, each contributing to the river’s growth. The map highlights the following key elements:
- Lake Itasca: The official source, marked by a small sign and a modest monument, provides a symbolic starting point for the Mississippi’s journey.
- The Mississippi Headwaters State Forest: This protected area encompasses a significant portion of the river’s upper reaches, safeguarding its natural beauty and ecological integrity.
- The Mississippi River Headwaters Scenic Byway: A designated scenic route that follows the river’s path, offering breathtaking views and access to various points of interest.
- Tributaries: Numerous smaller streams and rivers, such as the Kabetogama River and the Rainy River, contribute to the Mississippi’s flow, adding to its volume and carrying a diverse array of aquatic life.
Beyond the Map: The Significance of the Headwaters
The Mississippi River’s headwaters hold immense ecological, historical, and cultural significance:
Ecological Significance:
- Water Quality: The headwaters play a critical role in maintaining the overall water quality of the Mississippi River. The pristine conditions of these upper reaches ensure that the river flows downstream with relatively clean water, supporting a diverse array of aquatic life.
- Biodiversity: The headwaters region is home to a rich array of plant and animal species, including rare and endangered species. The diverse habitats, from wetlands to forests, provide essential breeding grounds and migration corridors for a wide range of wildlife.
- Water Cycle: The headwaters act as a vital source of water for the entire Mississippi River Basin. The precipitation that falls in this region ultimately contributes to the river’s flow, sustaining ecosystems and human communities downstream.
Historical Significance:
- Native American Culture: The headwaters region holds deep cultural significance for Indigenous peoples who have inhabited this area for millennia. Their traditions, stories, and knowledge about the land and water are deeply intertwined with the Mississippi River.
- Early Exploration: The Mississippi River played a pivotal role in the exploration and settlement of North America. Early explorers, such as Jacques Marquette and Louis Jolliet, used the river as a route to navigate the continent and establish trade routes.
Cultural Significance:
- Tourism and Recreation: The headwaters region is a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts, offering opportunities for fishing, canoeing, hiking, and wildlife viewing. The scenic beauty and tranquility of the area attract visitors from around the world.
- Inspiration and Symbolism: The Mississippi River, from its headwaters to its delta, holds a powerful place in the American imagination. It has inspired countless works of art, literature, and music, reflecting the river’s role as a symbol of strength, resilience, and the interconnectedness of life.
Preservation and Management:
Protecting the Mississippi River’s headwaters is essential for safeguarding its ecological integrity, cultural heritage, and the well-being of communities throughout the river basin. Various organizations and initiatives are working to ensure the long-term health of the river, including:
- The Mississippi River Headwaters Board: This organization, established by the state of Minnesota, works to protect and enhance the natural resources of the headwaters region.
- The Mississippi River Headwaters Scenic Byway: This designated route promotes responsible tourism and appreciation for the natural beauty of the area.
- Local conservation groups: Numerous non-profit organizations are dedicated to protecting the headwaters, focusing on issues such as water quality, habitat restoration, and public education.
FAQs:
Q: What is the exact location of the Mississippi River’s headwaters?
A: The official source is Lake Itasca, located in Itasca State Park, Minnesota. However, the river’s origins are more complex, with numerous tributaries and wetlands contributing to its flow.
Q: Why is the Mississippi River’s headwaters important?
A: The headwaters play a vital role in maintaining the river’s water quality, supporting biodiversity, and sustaining ecosystems throughout the Mississippi River Basin.
Q: What are some threats to the Mississippi River’s headwaters?
A: Threats include pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and urban development; habitat loss due to deforestation and land use changes; and climate change, which can alter precipitation patterns and impact water availability.
Q: How can I help protect the Mississippi River’s headwaters?
A: You can support organizations dedicated to conservation efforts, practice responsible outdoor recreation, and advocate for policies that protect water quality and habitat.
Tips for Visiting the Mississippi River Headwaters:
- Plan your visit: Consider the time of year and weather conditions when planning your trip.
- Respect the environment: Pack out everything you pack in, avoid disturbing wildlife, and stay on designated trails.
- Learn about the area: Visit local museums, historical sites, and visitor centers to gain a deeper understanding of the region’s history and culture.
- Support local businesses: Patronize businesses that promote sustainable practices and contribute to the local economy.
Conclusion:
The Mississippi River’s headwaters, a seemingly humble origin, hold the key to understanding the river’s immense power and influence. From its source in Lake Itasca, the river embarks on a journey that shapes the landscape, sustains life, and connects communities across a vast expanse. By understanding the importance of these origins, we can better appreciate the interconnectedness of the natural world and work to ensure the Mississippi River’s health and vitality for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Tracing the Origins of the Mississippi: A Journey to the Headwaters. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!