Uncovering the Global Energy Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at World Oil Reserves
Related Articles: Uncovering the Global Energy Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at World Oil Reserves
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Uncovering the Global Energy Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at World Oil Reserves. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Uncovering the Global Energy Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at World Oil Reserves

The world’s thirst for energy remains insatiable, and oil, a crucial fuel source, continues to play a significant role in powering our modern world. Understanding the distribution of oil reserves across the globe is critical for policymakers, energy companies, and individuals alike. This exploration delves into the intricacies of global oil reserves, examining their geographical distribution, influential factors, and the implications for the future of energy.
Mapping the World’s Oil Reserves: A Visual Representation of Global Energy Assets
Visualizing oil reserves through maps provides a compelling and insightful understanding of the global energy landscape. These maps, often colored to indicate reserve concentration, reveal the uneven distribution of this vital resource. The Middle East, particularly Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and the United Arab Emirates, emerges as the region with the most significant oil reserves. Other prominent regions include North America (particularly Canada and the United States), South America (Venezuela and Brazil), Africa (Nigeria and Libya), and Asia (Russia and China).
Factors Shaping the Distribution of Oil Reserves: A Deeper Dive into Geological and Historical Influences
The distribution of oil reserves is not random; it is shaped by a complex interplay of geological and historical factors.
Geological Factors:
- Sedimentary Basins: Oil formation requires specific geological conditions, primarily the presence of sedimentary basins. These basins, formed over millions of years by the accumulation of organic matter, provide the necessary environment for the transformation of ancient organisms into hydrocarbons.
- Source Rocks: Within these basins, source rocks, rich in organic matter, serve as the foundation for oil formation. The type of organic matter, its burial depth, and the presence of heat and pressure contribute to the formation of oil.
- Reservoir Rocks: Once formed, oil migrates through porous and permeable reservoir rocks, such as sandstone and limestone, where it can be trapped and accumulated.
- Traps: The presence of geological traps, such as folds, faults, and salt domes, is crucial for preventing oil from escaping. These traps act as natural barriers, concentrating oil in specific locations.
Historical Factors:
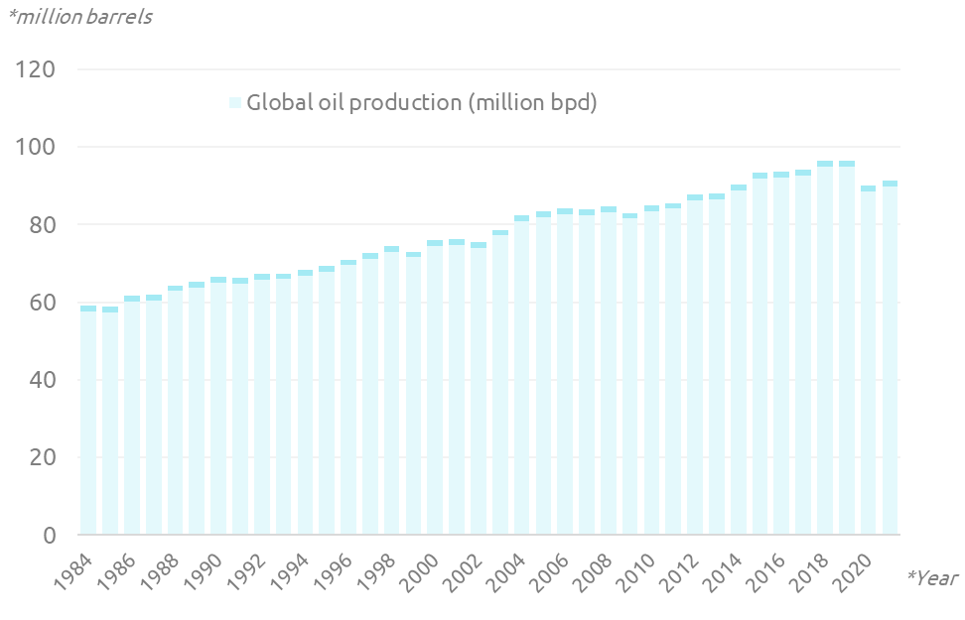
- Exploration and Discovery: The discovery and exploitation of oil reserves are influenced by historical events, technological advancements, and economic incentives. The development of drilling technologies and the growing demand for oil have played a pivotal role in identifying and extracting these reserves.
- Political Stability: The political landscape of oil-rich regions significantly influences the availability and accessibility of oil reserves. Political instability and conflicts can disrupt production and hinder exploration efforts.
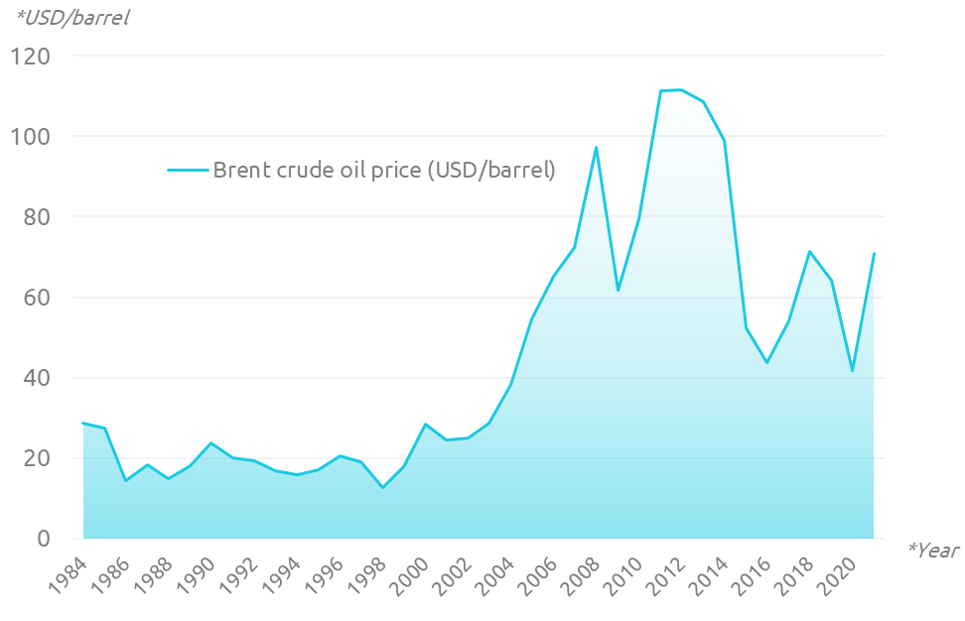
- Economic Factors: Global economic trends, including oil prices and demand, influence investment in exploration and production. High oil prices incentivize exploration and development, while low prices can discourage such activities.
The Importance of Understanding Global Oil Reserves: A Strategic Resource for the Future
Understanding the distribution of oil reserves is crucial for various reasons:
- Energy Security: Nations with abundant oil reserves enjoy greater energy security, as they have a reliable source of fuel for their economies and transportation sectors.
- Economic Growth: Oil exports contribute significantly to the economies of oil-producing countries, providing revenue for infrastructure development, social programs, and economic diversification.
- Global Energy Supply: The availability of oil reserves influences global energy supply, impacting the price of oil and the stability of energy markets.
- Strategic Planning: Governments, energy companies, and investors need to understand the global distribution of oil reserves to plan for future energy needs, invest in alternative energy sources, and develop sustainable energy strategies.
FAQs about World Oil Reserves
1. What are the largest oil reserves in the world?
Saudi Arabia boasts the world’s largest proven oil reserves, followed by Venezuela, Canada, Iran, and Iraq.
2. How are oil reserves measured?
Oil reserves are typically measured in barrels, with one barrel equaling 42 US gallons. Proven reserves refer to the estimated amount of oil that can be economically extracted with current technology.
3. How long will the world’s oil reserves last?
The estimated lifespan of oil reserves depends on factors such as consumption rates, technological advancements, and the discovery of new reserves. Current estimates suggest that known oil reserves could last for several decades.
4. What are the challenges associated with oil reserves?
Challenges include environmental concerns related to oil extraction and transportation, political instability in oil-producing regions, and the increasing demand for oil in a world striving for sustainable energy solutions.
5. What are the alternatives to oil?
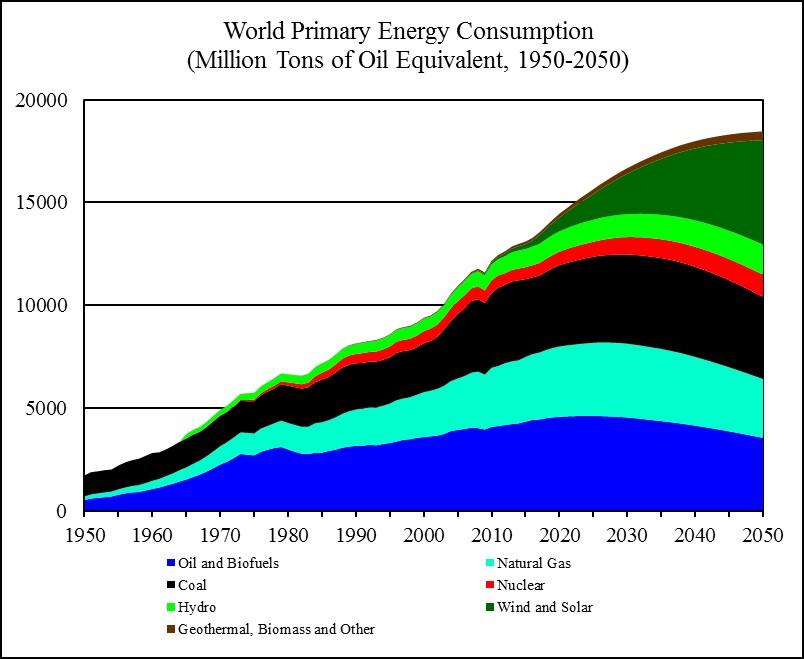
Alternative energy sources include renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass, as well as nuclear power.
Tips for Understanding World Oil Reserves
- Consult reputable sources: Refer to data from organizations like the US Energy Information Administration (EIA), the International Energy Agency (IEA), and OPEC to gain accurate information about global oil reserves.
- Visualize the data: Utilize maps and charts to understand the geographical distribution of oil reserves and their relative sizes.
- Follow industry news: Stay informed about developments in oil exploration, production, and consumption, as these factors impact the global oil market.
- Consider the broader context: Recognize the role of oil reserves in global energy security, economic development, and environmental sustainability.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Energy with an Understanding of Global Oil Reserves
The distribution of world oil reserves offers a compelling insight into the global energy landscape. While oil remains a vital fuel source, understanding its uneven distribution, the factors influencing its availability, and the challenges associated with its extraction is essential for navigating the future of energy. As the world strives for sustainable and diverse energy solutions, the map of world oil reserves serves as a reminder of the complex and ever-evolving nature of energy resources. By acknowledging the challenges and opportunities presented by global oil reserves, policymakers, energy companies, and individuals can work together to build a more secure, sustainable, and equitable energy future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Uncovering the Global Energy Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at World Oil Reserves. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!