Understanding the Complex Landscape: A Guide to West Bank Settlements
Related Articles: Understanding the Complex Landscape: A Guide to West Bank Settlements
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Complex Landscape: A Guide to West Bank Settlements. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Complex Landscape: A Guide to West Bank Settlements

The West Bank, a strategically important and historically contentious territory, is home to a complex web of settlements established by Israel. Understanding the geography and distribution of these settlements is crucial for comprehending the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict and its implications. This article delves into the intricacies of West Bank settlements, exploring their history, distribution, and impact, while remaining objective and avoiding any biased perspectives.
A Historical Context: The Genesis of West Bank Settlements
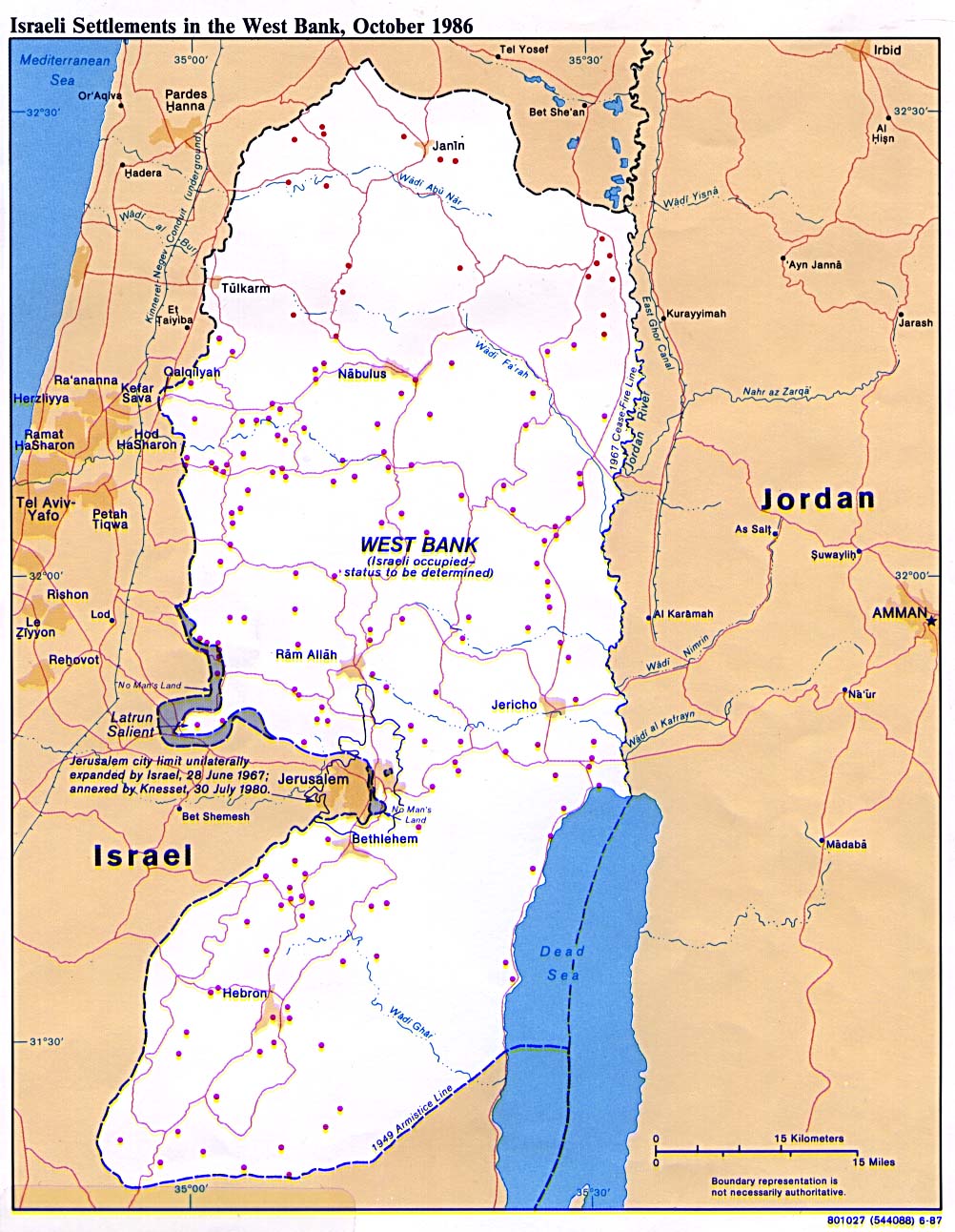
The establishment of Israeli settlements in the West Bank dates back to the Six-Day War of 1967, when Israel captured the territory from Jordan. Following the war, Israel began to build settlements, citing security concerns and historical and religious ties to the region. These settlements, initially small and scattered, have grown significantly over the decades, becoming a key feature of the West Bank’s landscape.
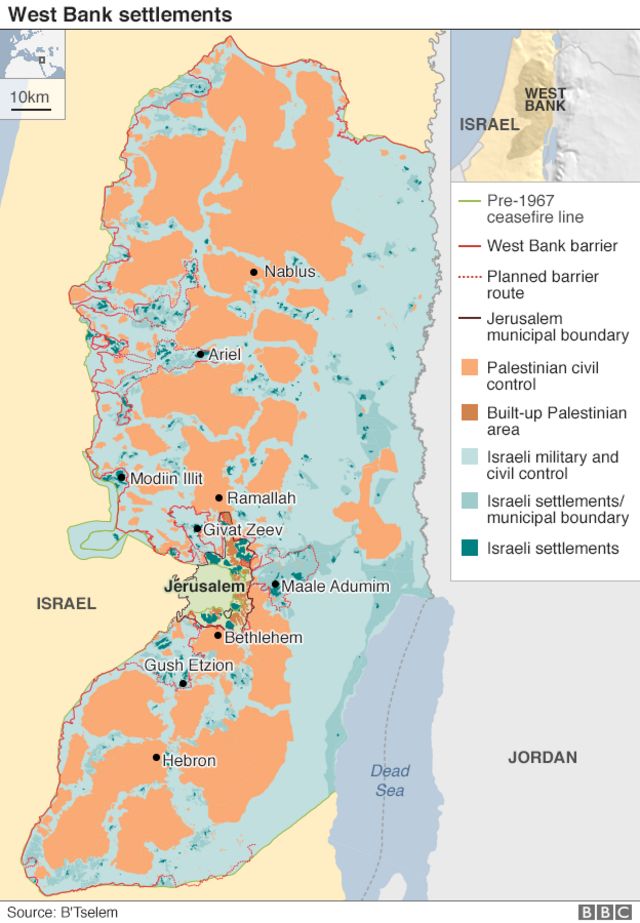
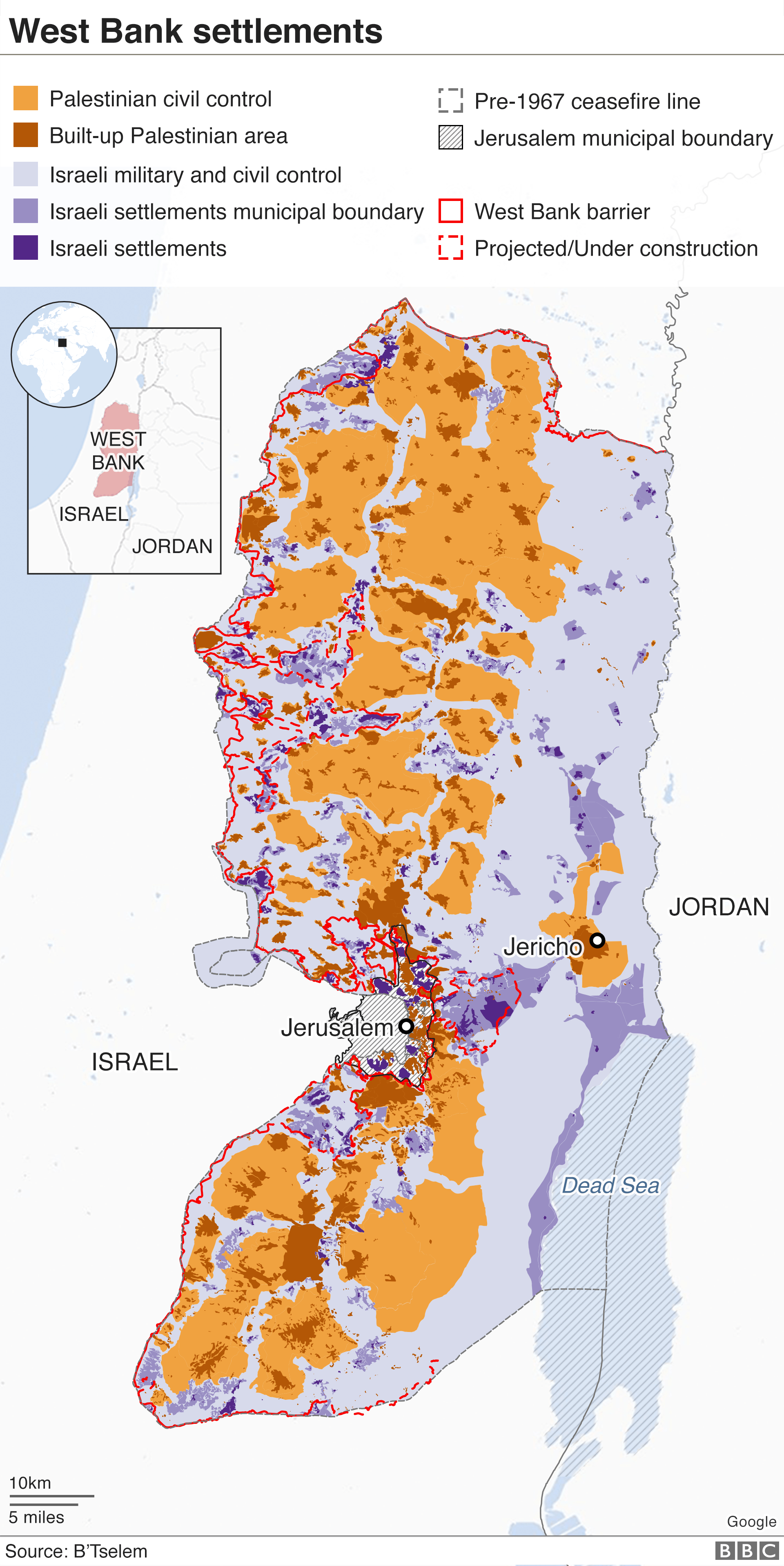
Mapping the Expanse: Understanding the Distribution of Settlements
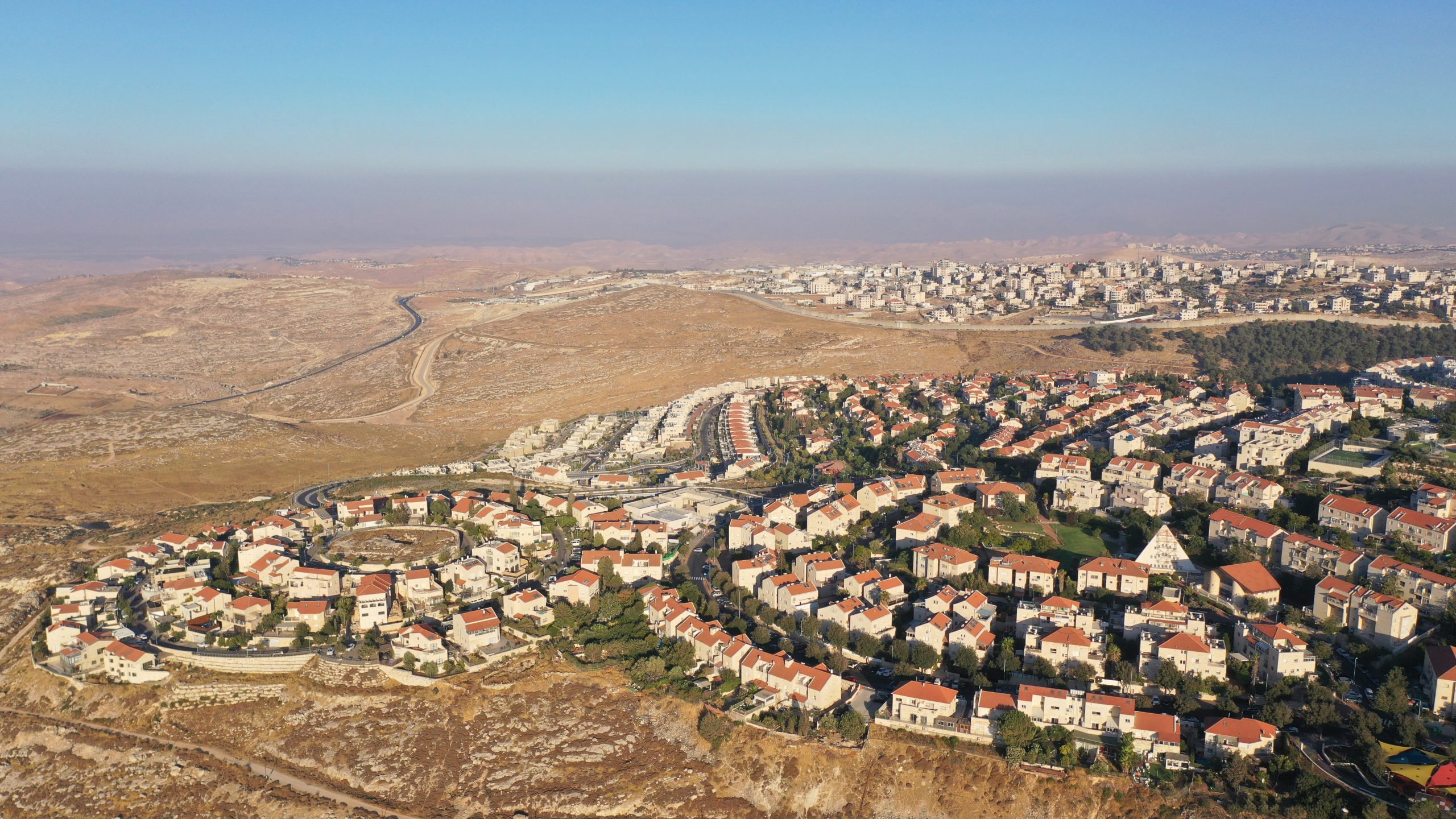
The West Bank settlements are distributed across the territory in a complex and often controversial pattern. They range from small, isolated outposts to large, densely populated urban centers.
- Major Settlement Blocks: These are the most significant and densely populated settlements, often connected to Israel proper by roads and infrastructure. They are strategically located near major cities and highways, providing access to resources and markets. Examples include Ariel, Ma’ale Adumim, and Gush Etzion.
- Smaller Settlements: Scattered across the West Bank, these smaller settlements often serve as agricultural hubs or offer a sense of community for settlers. Their size and isolation can pose challenges for their residents, but they are often strategically placed to control key land areas.
- Outposts: These are the most controversial type of settlement, often built on land claimed by Palestinians and lacking official authorization. They are often small and isolated, but their presence can contribute to tensions and hinder Palestinian access to land and resources.
A Controversial Landscape: The Impact of West Bank Settlements
The presence of settlements in the West Bank is a highly contested issue, with significant implications for both Israelis and Palestinians.
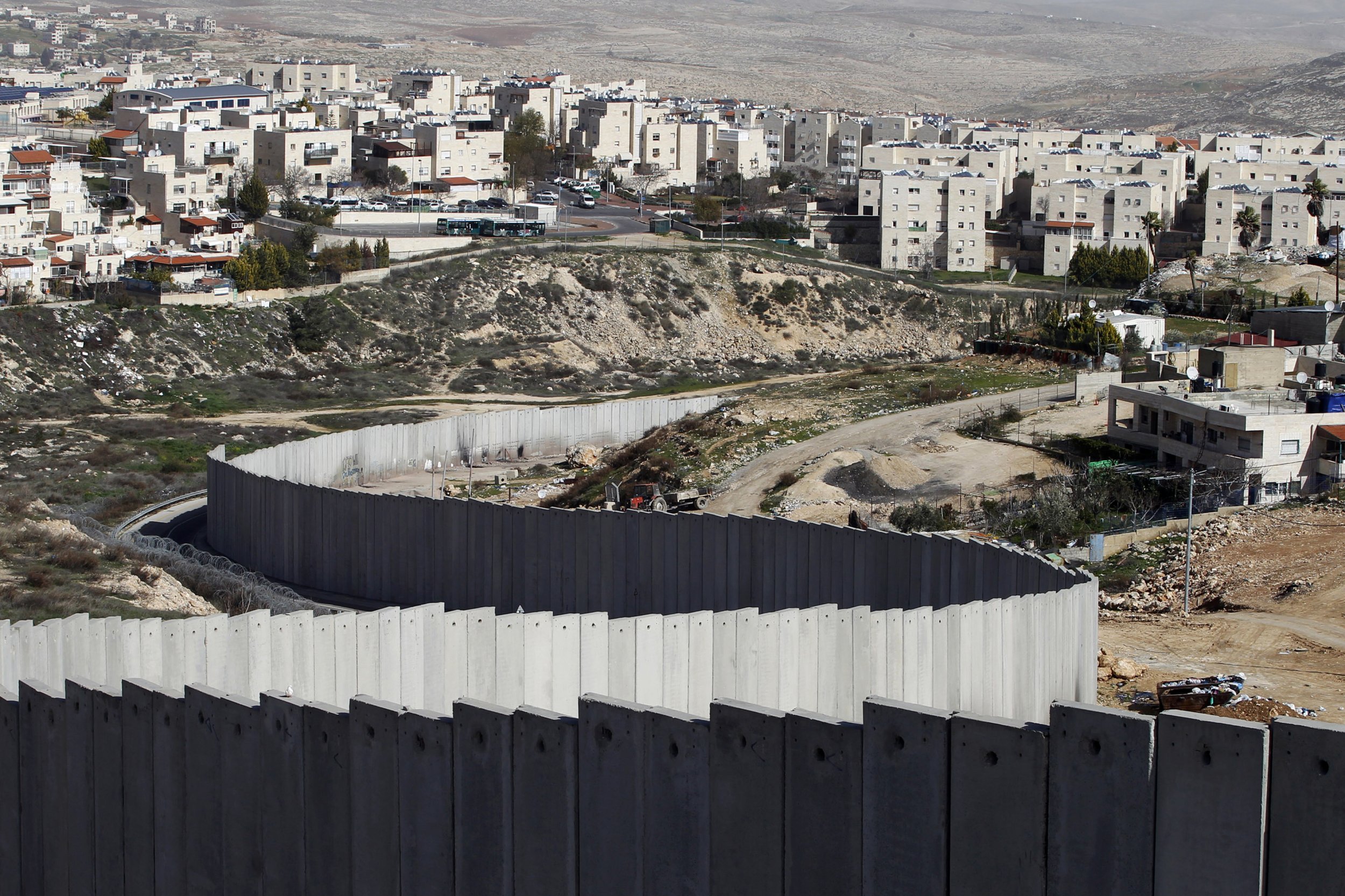
- Land Ownership and Access: The expansion of settlements has led to the appropriation of Palestinian land, limiting access to resources and hindering economic development. This has been a major source of tension and conflict.
- Political and Security Implications: The settlements are seen by many Palestinians as a barrier to achieving a two-state solution, while their presence also complicates security arrangements and exacerbates tensions in the region.
- International Law and Condemnation: The international community, including the United Nations, has consistently condemned the settlements as illegal under international law, arguing they constitute a violation of Palestinian rights and hinder the prospects for peace.
Navigating the Complexity: A Deeper Dive into Key Aspects
1. The Legal Status of Settlements:
The legal status of settlements remains a contentious issue. While Israel claims a legal right to establish settlements in the West Bank, the international community, including the International Court of Justice, considers them illegal under international law. The Fourth Geneva Convention prohibits the transfer of a state’s civilian population to occupied territory, a principle often cited in condemning the settlements.
2. The Role of International Organizations:
The United Nations, through its Security Council resolutions and reports, has repeatedly condemned the settlements and called for their cessation. The European Union has also implemented policies to restrict trade with settlements and has criticized their expansion. These efforts aim to pressure Israel to comply with international law and promote a peaceful resolution to the conflict.
3. The Impact on Palestinian Life:
The presence of settlements has had a profound impact on Palestinian life in the West Bank. Limited access to land and resources, coupled with restrictions on movement and economic opportunities, has created significant hardship for Palestinian communities. The settlements also contribute to the fragmentation of Palestinian territory, making it difficult to establish a viable and independent Palestinian state.
4. The Search for a Peaceful Resolution:
The issue of settlements is a major obstacle to achieving a peaceful and lasting solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Negotiations between the two parties have repeatedly stalled over the question of settlements, highlighting their central role in the conflict.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Why are settlements considered illegal under international law?
A: The international community, based on the Fourth Geneva Convention, considers settlements illegal because they involve the transfer of a state’s civilian population to occupied territory. This is deemed a violation of international law and Palestinian rights.
Q: What are the main arguments in favor of settlements?
A: Supporters of settlements argue that they are necessary for security reasons, citing the history of conflict in the region. They also emphasize historical and religious ties to the land and believe that settlements are a legitimate expression of Jewish self-determination.
Q: What are the main arguments against settlements?
A: Opponents of settlements argue that they are illegal under international law and constitute a violation of Palestinian rights. They also contend that settlements hinder the prospects for peace and a two-state solution, as they contribute to the fragmentation of Palestinian territory and limit Palestinian access to resources.
Q: What are the potential consequences of continued settlement expansion?
A: Continued settlement expansion could further exacerbate tensions and conflict in the region, potentially leading to increased violence and instability. It could also make a two-state solution increasingly difficult to achieve, as it would require a significant redrawing of borders and potentially lead to the displacement of Palestinian communities.
Tips for Understanding the West Bank Settlement Landscape:
- Consult Reliable Sources: Rely on reputable news organizations, academic journals, and international organizations for accurate information on the West Bank settlements.
- Consider Multiple Perspectives: Explore the perspectives of both Israelis and Palestinians, recognizing the complexities and historical context of the conflict.
- Engage in Critical Thinking: Analyze information critically, considering the motivations and biases of different sources.
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on developments related to settlements, as the situation is constantly evolving.
Conclusion:
The West Bank settlement landscape is a complex and contentious issue, deeply intertwined with the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Understanding the history, distribution, and impact of settlements is crucial for comprehending the ongoing conflict and its implications for the future of the region. It is important to approach this topic with sensitivity and objectivity, acknowledging the perspectives of all parties involved and seeking a peaceful resolution based on international law and respect for human rights.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Complex Landscape: A Guide to West Bank Settlements. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!