Unfurling the Colors: A Comprehensive Guide to the German Flag and Its Map
Related Articles: Unfurling the Colors: A Comprehensive Guide to the German Flag and Its Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unfurling the Colors: A Comprehensive Guide to the German Flag and Its Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unfurling the Colors: A Comprehensive Guide to the German Flag and Its Map

The German flag, with its bold black, red, and gold stripes, is a symbol of national identity, unity, and history. Its design, though simple, carries a rich tapestry of meaning, reflecting the country’s tumultuous past and hopeful future. Understanding the symbolism behind the flag and its intricate relationship with the geographical map of Germany provides a deeper appreciation for the nation’s cultural and political landscape.
The Tricolor: A Tale of Three Colors
The German flag, officially adopted in 1949, is a horizontal tricolour with three equal stripes: black at the top, red in the middle, and gold at the bottom. This seemingly straightforward design holds layers of historical and symbolic weight:
- Black: Represents the darkness and oppression of the past, specifically referencing the Napoleonic Wars and the subsequent era of German unification under Prussian dominance. It also symbolizes strength, seriousness, and the resilience of the German people.
- Red: Symbolizes courage, blood, and sacrifice. It evokes the spirit of revolution and the fight for freedom, particularly during the 1848 Revolution for German unification.
- Gold: Represents light, hope, and prosperity. It signifies the aspirations for a brighter future, a united Germany free from oppression, and a nation that values freedom and democracy.
The combination of these colors reflects the complex history of Germany, its struggles for unity, and its aspirations for a better future. It also signifies the nation’s values: strength, courage, and hope.
The Flag’s Journey Through Time
The German flag has evolved throughout history, reflecting the changing political landscape of the nation:
- 1848 Revolution: The black, red, and gold colors were first adopted as a symbol of German unity during the 1848 Revolution, a period of widespread political and social upheaval.
- German Empire (1871-1918): During the German Empire, the flag was officially recognized, but the black, white, and red tricolour of Prussia became the dominant national symbol.
- Weimar Republic (1919-1933): The black, red, and gold flag was re-adopted as the national flag of the Weimar Republic, signifying a return to democratic principles and a rejection of the Prussian monarchy.
- Nazi Germany (1933-1945): The Nazi regime replaced the black, red, and gold flag with a swastika flag, a symbol of hatred and oppression.
- Federal Republic of Germany (1949-present): After World War II, the black, red, and gold flag was re-adopted as the national flag of the Federal Republic of Germany, signifying a commitment to democracy, freedom, and unity.
The flag’s journey through time mirrors the complex and often turbulent history of Germany, reflecting its struggles and aspirations.
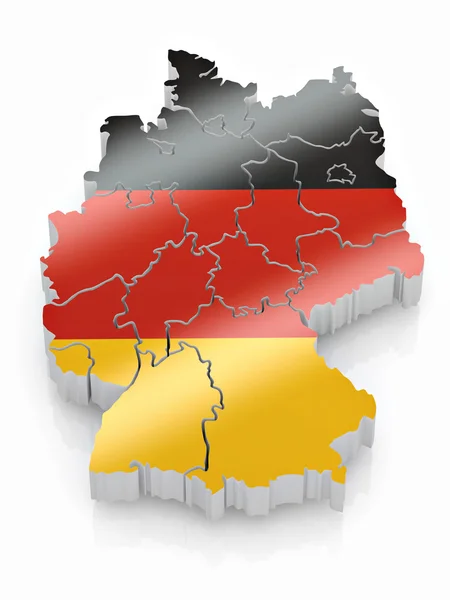
The Flag and the Map: A Symbiotic Relationship
The German flag, with its symbolic colors, is intrinsically linked to the geographical map of Germany. The flag represents the unity and strength of the nation, while the map reflects the diverse landscapes, regions, and cultural identities that make up Germany:
- Geographic Diversity: From the North Sea coast to the Alps, Germany boasts a diverse landscape, encompassing plains, forests, mountains, and rivers. This geographical diversity is reflected in the country’s cultural and linguistic diversity, with distinct regional identities and traditions.
- Historical Boundaries: The map of Germany has been shaped by historical events, including wars, treaties, and political changes. The current borders of Germany reflect the outcomes of World War II and the subsequent reunification of East and West Germany in 1990.
- Regional Identity: The map of Germany highlights the distinct regions of the country, each with its own unique history, culture, and dialect. These regional identities are often reflected in local traditions, cuisine, and art.
The map of Germany serves as a visual representation of the nation’s geographical and cultural diversity, while the flag symbolizes the unity and shared identity that binds these diverse regions together.
The German Flag: A Symbol of Unity and Hope
The German flag, with its simple yet powerful design, represents more than just a nation’s colors. It embodies the spirit of unity, resilience, and hope that has guided Germany through its turbulent history. The flag serves as a reminder of the country’s commitment to democracy, freedom, and a brighter future.
FAQs about the German Flag and Map
Q: What is the official name of the German flag?
A: The official name of the German flag is the "Bundesflagge" (Federal Flag).
Q: Why are the colors of the German flag black, red, and gold?
A: The colors black, red, and gold were first adopted as a symbol of German unity during the 1848 Revolution. They represent the country’s history, its struggles for freedom, and its aspirations for a better future.
Q: What is the significance of the black color in the German flag?
A: Black represents the darkness and oppression of the past, specifically referencing the Napoleonic Wars and the subsequent era of German unification under Prussian dominance. It also symbolizes strength, seriousness, and the resilience of the German people.
Q: What is the significance of the red color in the German flag?
A: Red symbolizes courage, blood, and sacrifice. It evokes the spirit of revolution and the fight for freedom, particularly during the 1848 Revolution for German unification.
Q: What is the significance of the gold color in the German flag?
A: Gold represents light, hope, and prosperity. It signifies the aspirations for a brighter future, a united Germany free from oppression, and a nation that values freedom and democracy.
Q: How has the German flag evolved throughout history?
A: The German flag has evolved throughout history, reflecting the changing political landscape of the nation. It was first adopted during the 1848 Revolution, then replaced by the Prussian flag during the German Empire. It was re-adopted by the Weimar Republic and then replaced by the Nazi flag during the Nazi regime. Finally, it was re-adopted by the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949.
Q: What are the different regions of Germany?
A: Germany is divided into 16 federal states (Bundesländer), each with its own unique history, culture, and dialect. Some of the most well-known regions include Bavaria, Baden-Württemberg, North Rhine-Westphalia, and Saxony.
Q: How does the German map reflect the country’s cultural diversity?
A: The map of Germany highlights the distinct regions of the country, each with its own unique history, culture, and dialect. These regional identities are often reflected in local traditions, cuisine, and art.
Tips for Understanding the German Flag and Map
- Explore historical resources: Reading about the history of the German flag and the changing political landscape of the country can provide valuable insights into the symbolism and significance of the flag’s colors.
- Learn about the different regions of Germany: Researching the unique histories, cultures, and dialects of the different regions of Germany can help you understand the cultural diversity of the country and its relationship to the map.
- Visit museums and cultural institutions: Museums and cultural institutions in Germany often feature exhibits on the country’s history, art, and culture, providing valuable insights into the German flag and map.
- Engage with local communities: Interacting with people from different regions of Germany can help you gain a deeper understanding of the cultural diversity and regional identities that make up the nation.
Conclusion
The German flag and map are powerful symbols of national identity, unity, and history. The flag’s bold colors represent the nation’s struggles and aspirations, while the map reflects its diverse landscapes, regions, and cultural identities. By understanding the symbolism behind the flag and its intricate relationship with the geographical map of Germany, we gain a deeper appreciation for the nation’s rich history, cultural heritage, and aspirations for a united and prosperous future.




![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unfurling the Colors: A Comprehensive Guide to the German Flag and Its Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!