Unpacking the Tapestry of Pennsylvania’s Population: A Comprehensive Look at the 2000 Census
Related Articles: Unpacking the Tapestry of Pennsylvania’s Population: A Comprehensive Look at the 2000 Census
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unpacking the Tapestry of Pennsylvania’s Population: A Comprehensive Look at the 2000 Census. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unpacking the Tapestry of Pennsylvania’s Population: A Comprehensive Look at the 2000 Census
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unpacking the Tapestry of Pennsylvania’s Population: A Comprehensive Look at the 2000 Census
- 3.1 A Snapshot of Pennsylvania in 2000: Unveiling the Distribution of its Inhabitants
- 3.2 Understanding the Importance of Population Distribution: Its Impact on Society and Development
- 3.3 FAQs: Unraveling Common Questions about Pennsylvania’s Population Map
- 3.4 Tips for Analyzing Population Maps: A Guide for Effective Interpretation
- 3.5 Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding Pennsylvania’s Dynamics
- 4 Closure
Unpacking the Tapestry of Pennsylvania’s Population: A Comprehensive Look at the 2000 Census
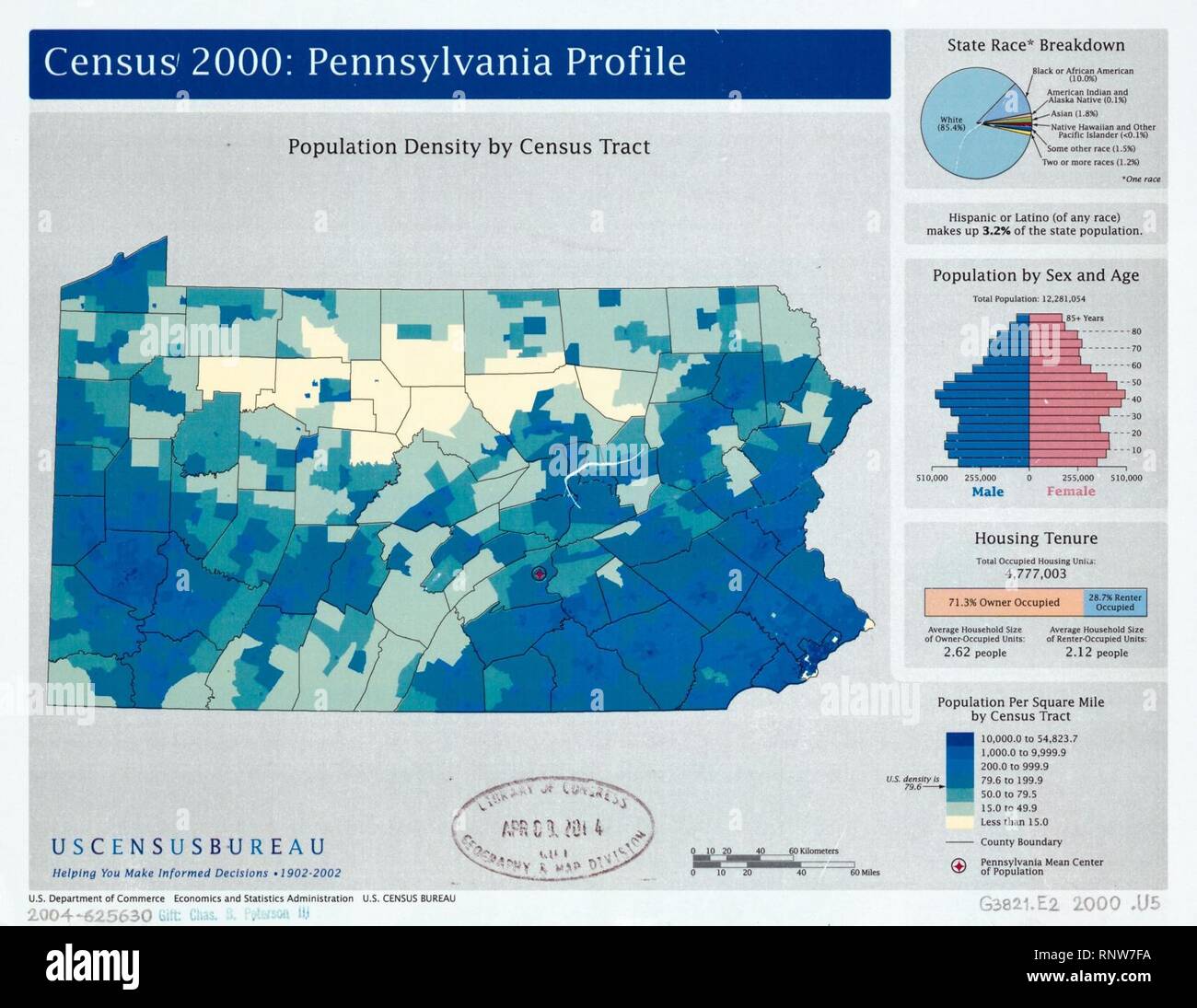
Pennsylvania, the Keystone State, boasts a rich history and diverse population, its demographics shifting and evolving over time. Understanding the distribution of its inhabitants is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike, as it informs critical decisions about infrastructure, resources, and community development. This article delves into the population map of Pennsylvania based on the 2000 Census, exploring its key features, trends, and insights.
A Snapshot of Pennsylvania in 2000: Unveiling the Distribution of its Inhabitants
The 2000 Census provides a detailed picture of Pennsylvania’s population landscape, revealing significant regional variations and urban-rural contrasts. The map illustrates the concentration of population in the southeastern portion of the state, with the Philadelphia metropolitan area emerging as the most densely populated region. This trend is driven by historical factors, including industrial development, access to transportation networks, and economic opportunities.
Major Population Centers:
- Philadelphia Metropolitan Area: This urban hub, encompassing Philadelphia County and surrounding counties, serves as the state’s most populous region. The city of Philadelphia itself is home to a significant population, contributing to the area’s density.
- Pittsburgh Metropolitan Area: Located in the western part of the state, Pittsburgh and its surrounding counties exhibit a concentrated population, driven by the city’s historical role as a center of steel production and manufacturing.
- Harrisburg Metropolitan Area: Situated in the central region of the state, Harrisburg and its surrounding counties demonstrate a moderate population density, influenced by the state capital’s administrative functions and proximity to other urban centers.
Beyond the Major Cities:
While the southeastern and southwestern regions exhibit higher population densities, the map reveals a diverse range of population patterns across the state. Rural areas, particularly in the northern and western regions, exhibit lower population densities, reflecting a historical emphasis on agriculture and resource extraction.
Key Findings:
- Urban-Rural Divide: The 2000 Census data highlights a stark contrast between urban and rural areas in Pennsylvania. Urban centers exhibit higher population densities, while rural areas generally have lower population concentrations.
- Regional Variations: The map reveals significant regional differences in population density, with the southeastern region demonstrating the highest concentration, followed by the southwestern region.
- Growth and Decline: The census data also provides insights into population growth and decline in different regions. Urban areas, particularly in the southeastern region, experienced significant population growth during the late 20th century. Meanwhile, some rural areas experienced population decline, reflecting economic shifts and demographic trends.
Understanding the Importance of Population Distribution: Its Impact on Society and Development
The population map of Pennsylvania offers a valuable resource for understanding the state’s demographics and its implications for various sectors:
1. Planning and Development:
- Infrastructure Development: Knowledge of population distribution guides the planning and development of infrastructure, including transportation networks, water and sanitation systems, and energy infrastructure. Areas with higher population densities require more robust infrastructure to meet the needs of residents.
- Housing and Development: The map informs the development of housing and residential areas, ensuring adequate supply and distribution to meet the demands of different regions and population segments.
2. Economic Development:
- Business Location and Investment: Businesses use population data to make informed decisions about location, targeting markets, and allocating resources. Areas with higher population densities offer greater market potential, while areas with lower densities may present opportunities for niche businesses or industries.
- Job Creation and Workforce Development: The map provides insights into the distribution of skilled workers and potential workforce needs in different regions, informing workforce development programs and job creation initiatives.
3. Social Services and Healthcare:
- Healthcare Access and Distribution: Population data helps determine the distribution of healthcare facilities and services, ensuring equitable access to care across different regions.
- Education and Social Programs: The map informs the allocation of resources and the development of educational and social programs, tailoring them to the specific needs of different communities.
4. Environmental Planning:
- Land Use and Resource Management: Population density and distribution influence land use planning, environmental protection, and resource management. Areas with higher population densities require careful consideration of environmental impacts and sustainable development practices.
FAQs: Unraveling Common Questions about Pennsylvania’s Population Map
1. What factors contribute to the high population density in the southeastern region of Pennsylvania?
The southeastern region of Pennsylvania, including the Philadelphia metropolitan area, has historically experienced significant population growth due to several factors:
- Industrial Development: The region emerged as a major center for manufacturing and industry during the 19th and 20th centuries, attracting workers from various parts of the state and beyond.
- Transportation Networks: The region is well-connected by major transportation networks, including highways, railroads, and ports, facilitating commerce and attracting businesses and residents.
- Economic Opportunities: The presence of major industries, universities, and government institutions in the southeastern region creates a diverse range of economic opportunities, drawing residents and businesses.
2. How does the population map reflect the impact of historical events on Pennsylvania’s demographics?
The population map of Pennsylvania reflects the influence of historical events on its demographics, including:
- Industrial Revolution: The rise of industrial centers, such as Philadelphia and Pittsburgh, led to significant population growth in those regions, attracting workers from rural areas and beyond.
- Immigration Waves: Pennsylvania has historically been a destination for immigrants, particularly from Europe and Asia, contributing to the diversity and growth of its population.
- Rural-Urban Migration: The 20th century witnessed a shift in population from rural areas to urban centers, driven by economic opportunities and advancements in technology.
3. How does the population map of Pennsylvania compare to other states in the United States?
Compared to other states, Pennsylvania exhibits a moderate population density, ranking around the middle of the pack. However, the state’s population distribution demonstrates significant regional variations, with the southeastern region exhibiting higher density than other parts of the state.
4. What are the implications of population growth and decline in different regions of Pennsylvania?
Population growth in certain regions can lead to challenges in providing adequate infrastructure, housing, and services, while population decline in other regions can result in economic hardship and social challenges.
5. How does the population map of Pennsylvania inform policy decisions and resource allocation?
Policymakers and planners use population data to make informed decisions about infrastructure investment, resource allocation, and service delivery. For example, areas with higher population densities may require more resources for transportation, healthcare, and education.
Tips for Analyzing Population Maps: A Guide for Effective Interpretation
- Focus on Density: Pay attention to the areas with the highest and lowest population densities, as these provide insights into the distribution of people across the state.
- Consider Regional Variations: Recognize that population patterns vary significantly across different regions of Pennsylvania, reflecting historical, economic, and social factors.
- Analyze Change Over Time: Compare population maps from different census years to identify trends in population growth, decline, and migration.
- Connect to Other Data: Integrate population data with other relevant datasets, such as economic indicators, social demographics, and environmental data, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the state’s dynamics.
- Use Mapping Software: Utilize geographic information system (GIS) software or online mapping tools to visualize and analyze population data in a more interactive and dynamic manner.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding Pennsylvania’s Dynamics
The population map of Pennsylvania, particularly the 2000 Census data, provides a valuable snapshot of the state’s demographics and its implications for various sectors. By understanding the distribution of its inhabitants, policymakers, businesses, and individuals can make informed decisions about resource allocation, infrastructure development, and community planning. The map serves as a vital tool for navigating the complexities of Pennsylvania’s population landscape and fostering a more equitable and prosperous future for all its residents.






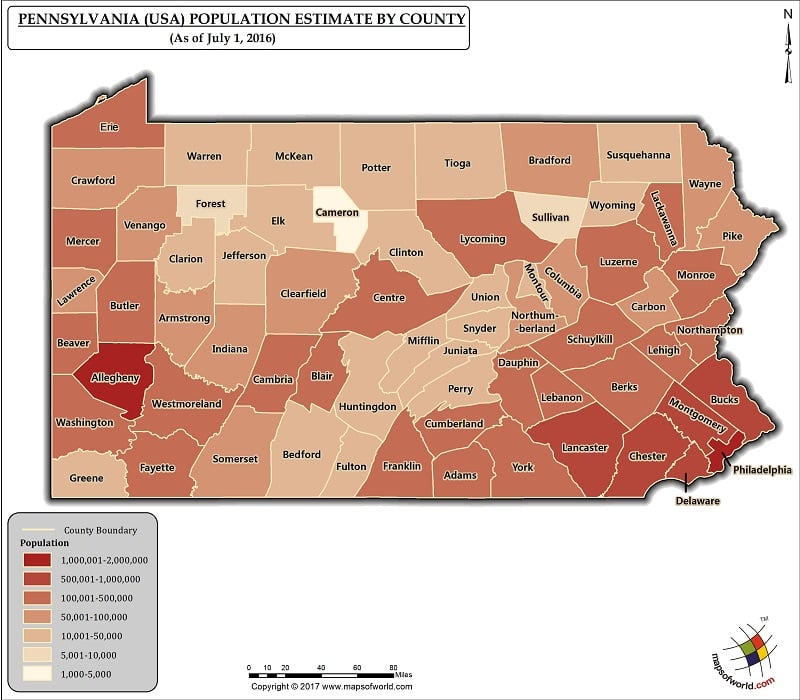
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unpacking the Tapestry of Pennsylvania’s Population: A Comprehensive Look at the 2000 Census. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!