Unraveling the Earth’s Scars: A Comprehensive Guide to the USGS Fault Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Earth’s Scars: A Comprehensive Guide to the USGS Fault Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Earth’s Scars: A Comprehensive Guide to the USGS Fault Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Earth’s Scars: A Comprehensive Guide to the USGS Fault Map

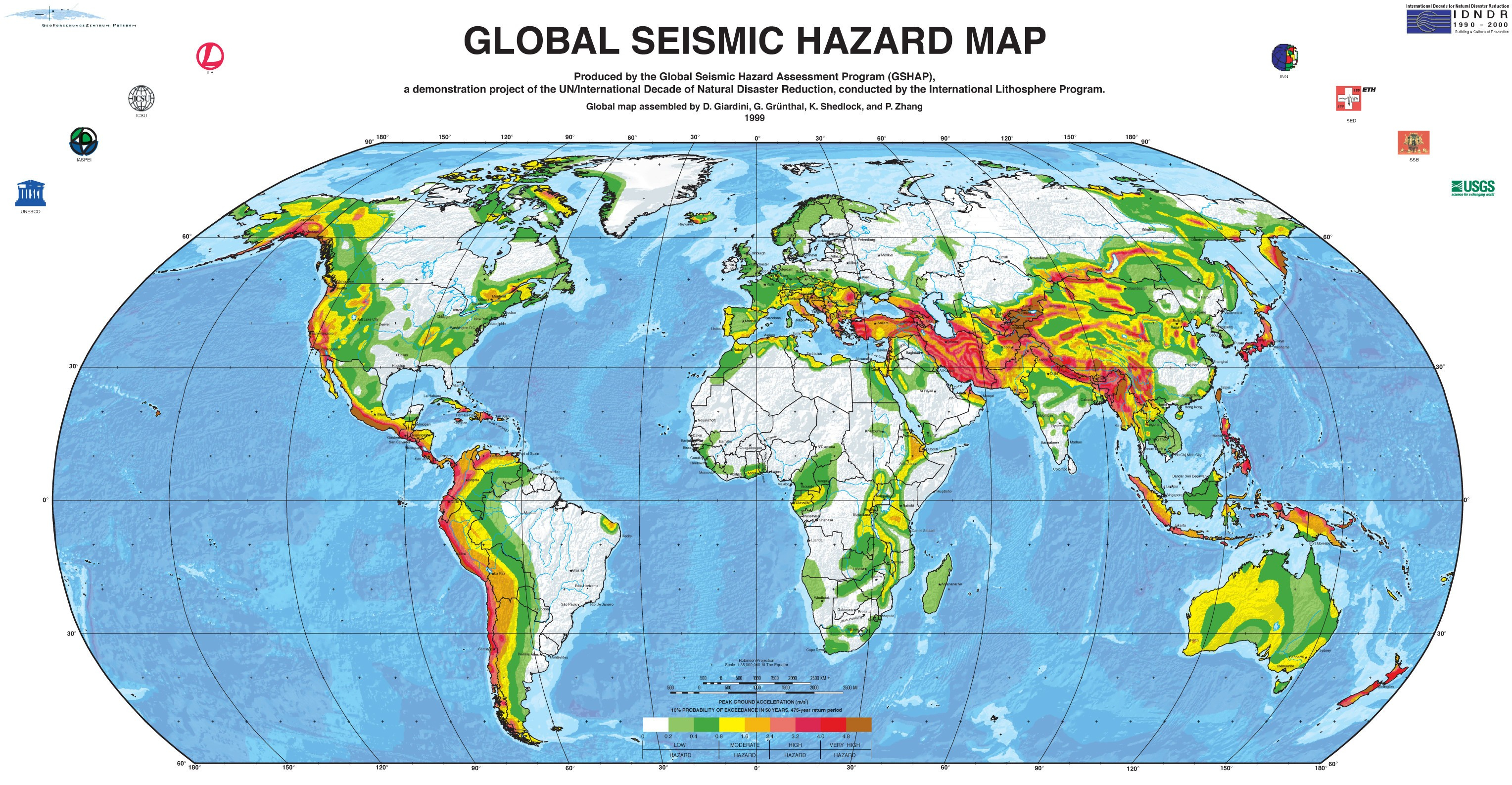
The Earth’s surface is a dynamic tapestry, constantly reshaped by the relentless forces of plate tectonics. These forces, driven by the movement of massive rock slabs beneath the surface, create fault lines – fractures in the Earth’s crust where rocks have moved past each other. Understanding these fault lines is crucial for mitigating seismic hazards, informing infrastructure development, and unraveling the geological history of our planet. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) has produced a comprehensive fault map, a valuable tool for researchers, policymakers, and the public alike.
Understanding the USGS Fault Map
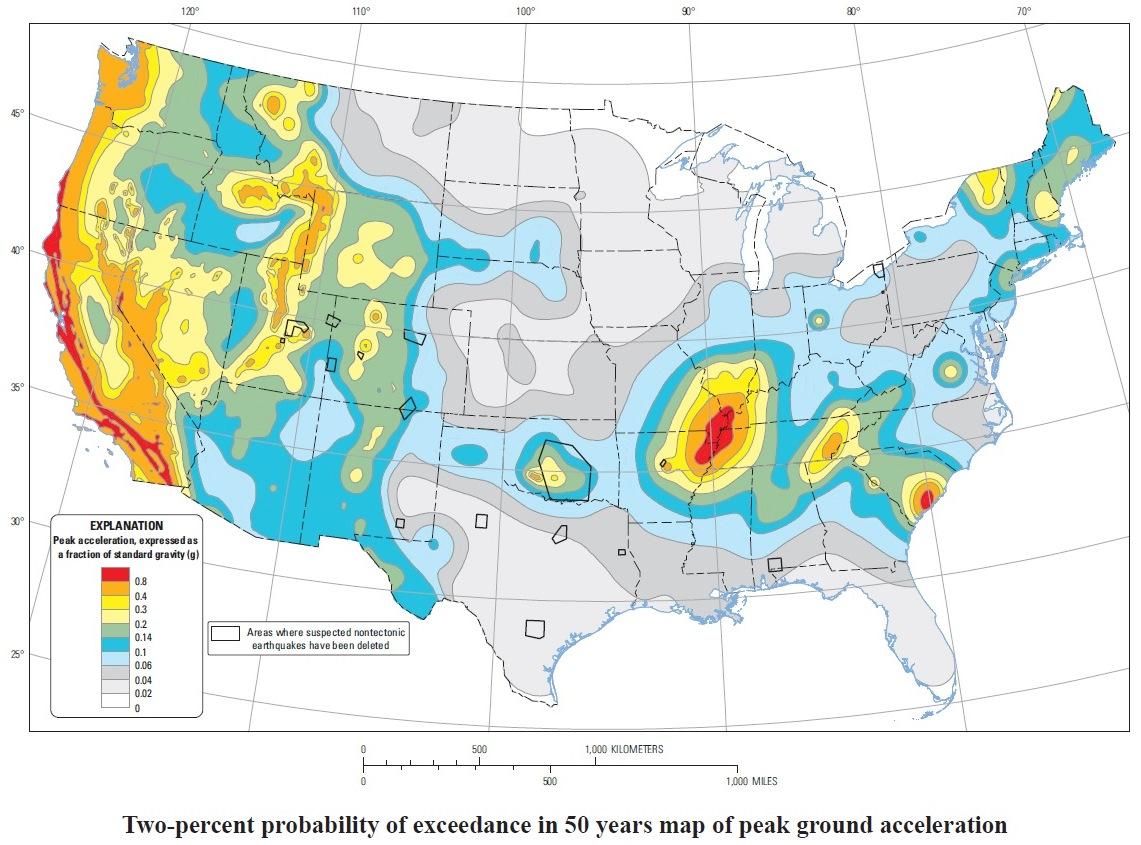
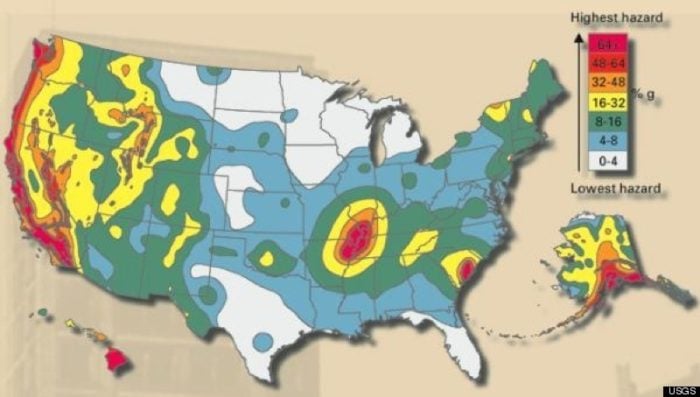
The USGS Fault Map, available online and in print, is a detailed representation of known active faults across the United States. This map, a culmination of decades of geological research, provides a visual representation of the Earth’s seismic vulnerabilities. It showcases the locations of faults, their estimated length and orientation, and the potential magnitude of earthquakes they can generate. This information is crucial for:
-
Earthquake Hazard Assessment: By identifying active fault lines, the map allows scientists to assess the likelihood and potential impact of earthquakes in specific regions. This information is vital for developing building codes, emergency preparedness plans, and land-use regulations.
-
Infrastructure Planning and Development: The map helps engineers and planners to identify areas prone to seismic activity, guiding the design and construction of critical infrastructure, such as bridges, dams, and nuclear power plants. This ensures these structures are resilient to earthquake forces and minimize potential damage.
-
Geological Research and Understanding: The USGS Fault Map serves as a foundation for ongoing geological research. Scientists use the map to study fault behavior, understand the evolution of the Earth’s crust, and refine models of earthquake prediction.
Beyond the Lines: Unveiling the Significance of Fault Mapping
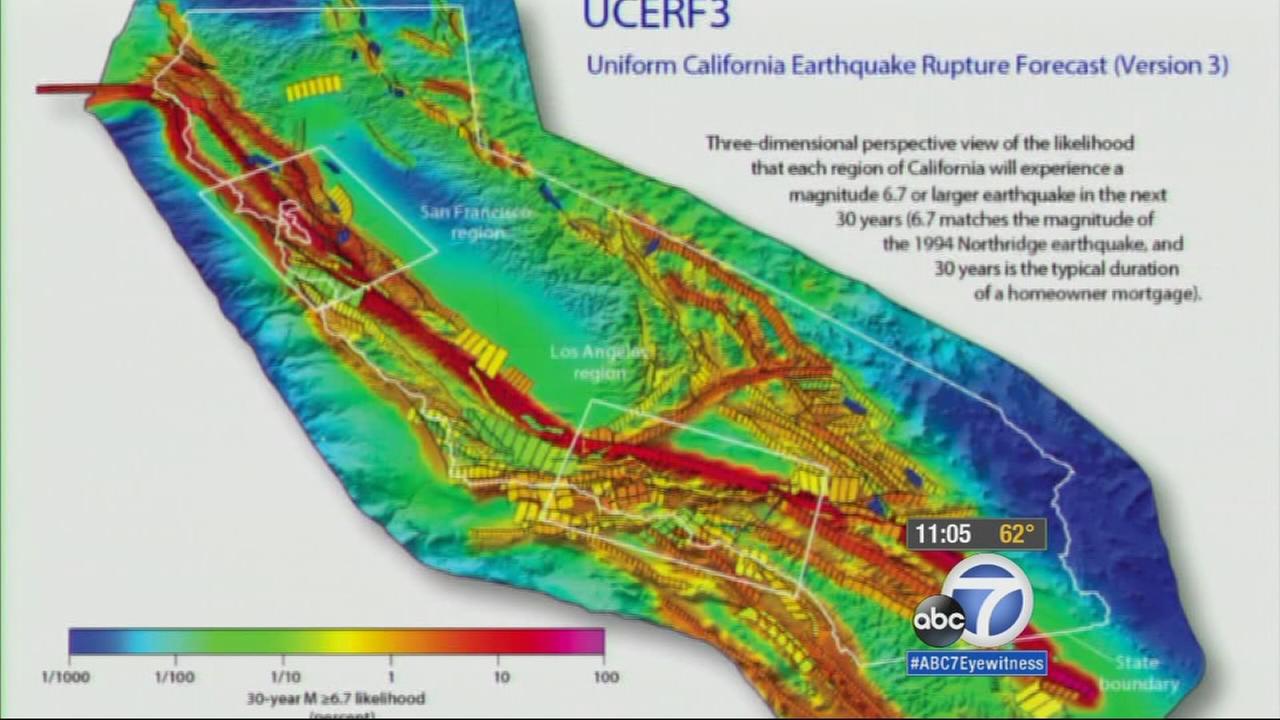
The USGS Fault Map is not merely a static representation of fault lines. It is a dynamic tool that evolves as research progresses and new data becomes available. Ongoing research, including field investigations, aerial imagery analysis, and advanced seismic monitoring, continuously refines our understanding of fault activity and their associated risks.
Key Features of the USGS Fault Map
The USGS Fault Map encompasses a multitude of features that make it an invaluable resource:
-
Comprehensive Coverage: The map covers all 50 states, including Alaska, Hawaii, and US territories, providing a comprehensive overview of fault lines across the nation.
-
Detailed Information: Each fault is accompanied by detailed information, including its length, orientation, age, and estimated earthquake potential. This information is crucial for understanding the specific risks associated with each fault.
-
Interactive Online Interface: The USGS offers an interactive online version of the fault map, allowing users to zoom in on specific regions, explore individual faults, and access detailed data.
-
Data Accessibility: The USGS makes its fault map data freely available to the public, enabling researchers, educators, and individuals to access and utilize this information for various purposes.
FAQs about the USGS Fault Map
Q: What is the purpose of the USGS Fault Map?
A: The USGS Fault Map aims to provide a comprehensive and accurate representation of active fault lines across the United States. This information is essential for understanding earthquake hazards, informing infrastructure development, and supporting geological research.
Q: How is the USGS Fault Map created?
A: The USGS Fault Map is a product of extensive geological research, including field investigations, aerial imagery analysis, and the interpretation of seismic data. The map is continuously updated as new information becomes available.
Q: How often is the USGS Fault Map updated?
A: The USGS Fault Map is updated on an ongoing basis as new data becomes available. Major updates are typically released every few years, but smaller revisions may occur more frequently.
Q: Can the USGS Fault Map predict earthquakes?
A: While the USGS Fault Map identifies areas prone to earthquakes, it cannot predict when or where an earthquake will occur. Earthquake prediction remains a complex and challenging scientific endeavor.
Q: What is the difference between active and inactive faults?
A: Active faults are those that have moved in the recent geological past and are considered likely to move again in the future. Inactive faults have not moved in the recent geological past and are less likely to pose an immediate seismic hazard.
Q: How can I use the USGS Fault Map to prepare for earthquakes?
A: The USGS Fault Map can help you understand your local earthquake risk and take appropriate steps to prepare. This includes securing heavy objects, developing an emergency plan, and learning how to respond during an earthquake.
Tips for Using the USGS Fault Map
-
Understand Your Local Risk: Use the USGS Fault Map to identify active faults in your region and assess your potential earthquake risk.
-
Prepare for Earthquakes: Develop an emergency plan, secure heavy objects, and learn how to respond during an earthquake.
-
Support Research and Education: Encourage funding for earthquake research and education, as this helps improve our understanding of seismic hazards and develop better mitigation strategies.
Conclusion
The USGS Fault Map is a vital tool for understanding the Earth’s dynamic nature and mitigating seismic hazards. By providing a comprehensive representation of active fault lines, it empowers individuals, communities, and policymakers to make informed decisions about land use, infrastructure development, and emergency preparedness. As our understanding of plate tectonics and earthquake hazards continues to evolve, the USGS Fault Map will remain a critical resource for navigating the complexities of our dynamic planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Earth’s Scars: A Comprehensive Guide to the USGS Fault Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!