Unraveling the Tapestry of History: A Comprehensive Guide to the Galilee and Judea Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of History: A Comprehensive Guide to the Galilee and Judea Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of History: A Comprehensive Guide to the Galilee and Judea Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of History: A Comprehensive Guide to the Galilee and Judea Map
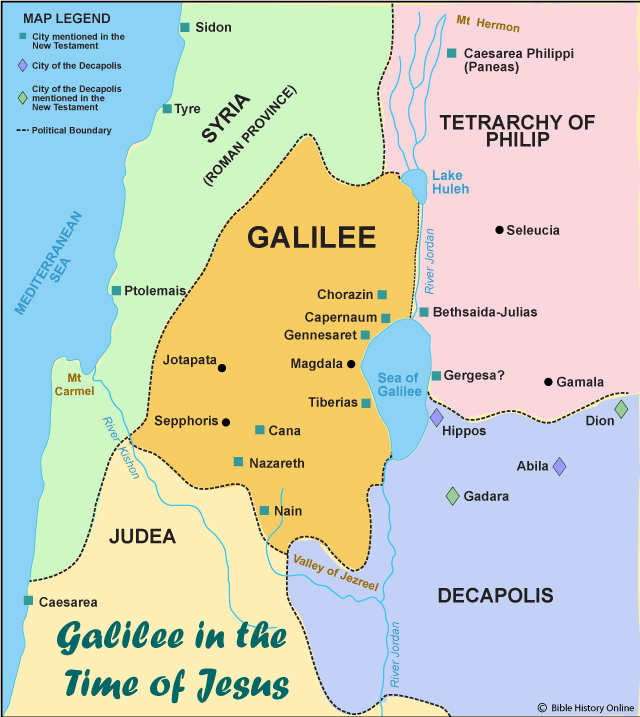
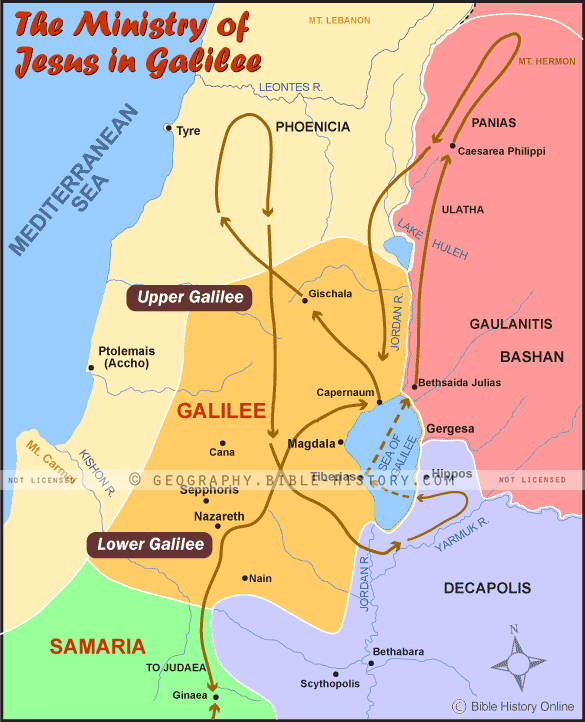
The Galilee and Judea map, a visual representation of two pivotal regions in ancient Israel, holds profound historical and religious significance. It serves as a window into the lives, beliefs, and struggles of people who shaped the course of history, impacting the world we know today. This article delves into the intricacies of this map, exploring its geographical features, historical context, and enduring relevance.
Geographical Boundaries and Key Features
Galilee:
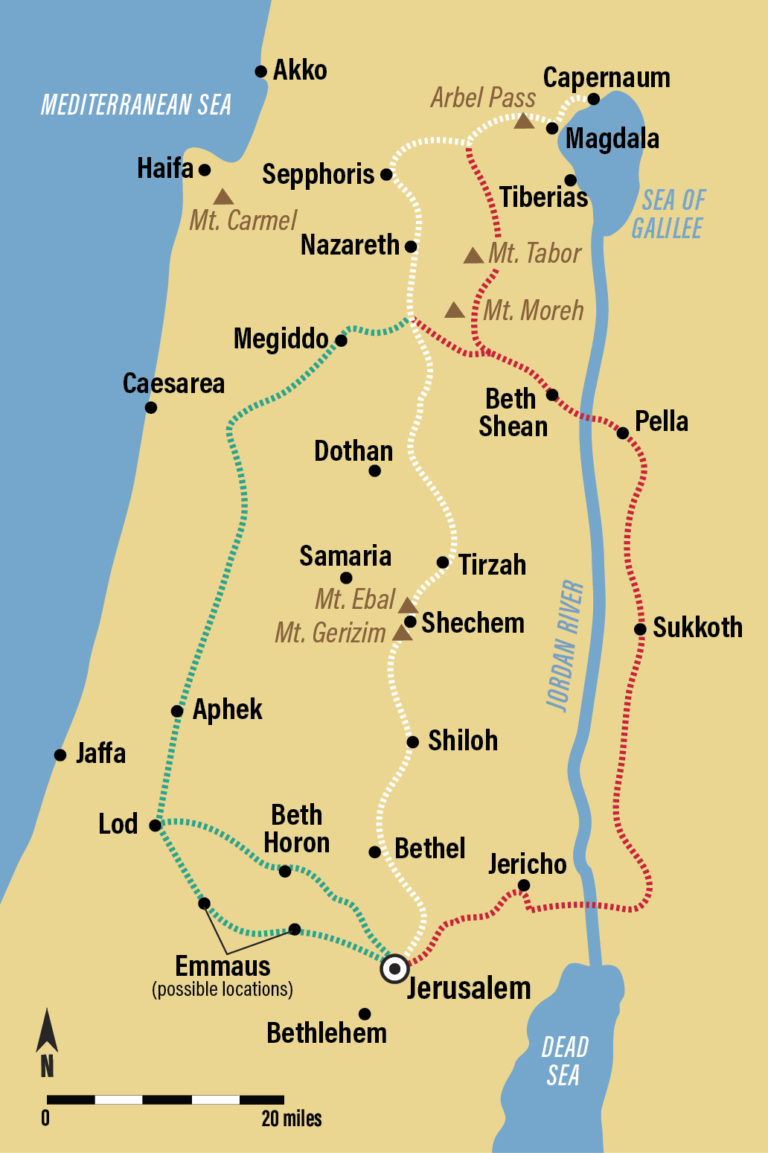
- Situated in northern Israel, Galilee encompasses a diverse landscape of rolling hills, fertile valleys, and the shores of the Sea of Galilee (also known as Lake Tiberias).
- It is divided into Upper Galilee, known for its mountainous terrain, and Lower Galilee, characterized by its rolling hills and fertile plains.
- The Sea of Galilee, a freshwater lake, played a crucial role in the region’s economy and transportation. It was also a focal point for the life and ministry of Jesus Christ.
- Major cities in Galilee included Sepphoris, Tiberias, and Nazareth, the birthplace of Jesus.
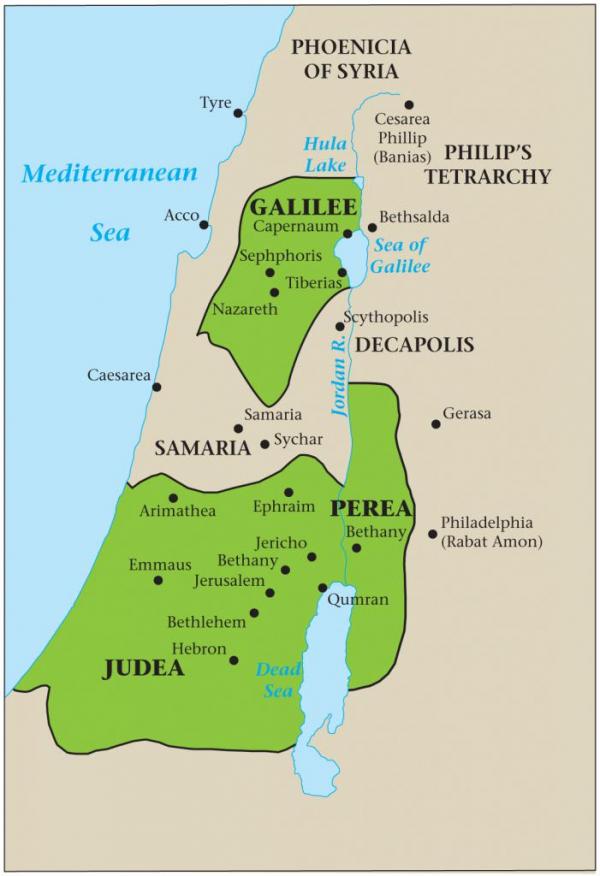
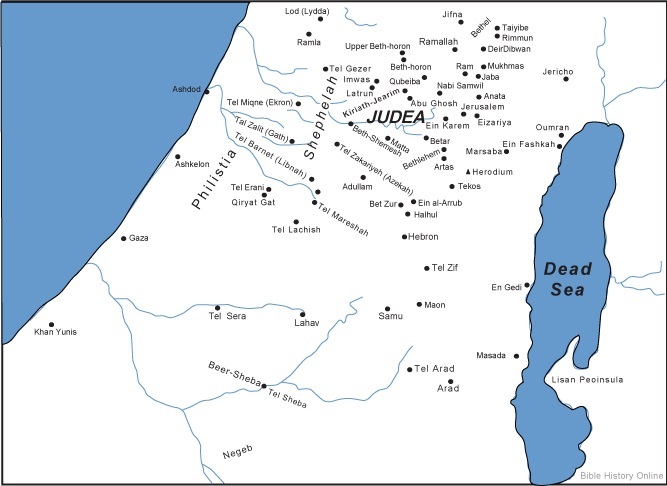
Judea:
- Located in central Israel, Judea encompasses the Judean Mountains, the Judean Desert, and the Dead Sea.
- It is characterized by its rugged terrain, with the Judean Mountains forming a natural barrier between the coastal plain and the Jordan Valley.
- The Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth, served as a source of salt and other minerals.
- Major cities in Judea included Jerusalem, Hebron, and Bethlehem.
Historical Significance
The regions of Galilee and Judea have been deeply intertwined with history for millennia. Their significance stems from their role as the cradle of Judaism and Christianity, as well as their strategic location at the crossroads of ancient trade routes.
The Rise of Judaism:
- The region was home to the ancient Israelites, who established the Kingdom of Israel in the 10th century BCE.
- Judea became the heartland of the Jewish faith, with Jerusalem emerging as its spiritual center.
- The Temple Mount in Jerusalem, housing the First and Second Temples, became a sacred site for Jewish worship.
The Birth of Christianity:
- Galilee and Judea were the settings for the life and ministry of Jesus Christ.
- Galilee, particularly the Sea of Galilee, witnessed Jesus’s teachings, miracles, and interactions with his disciples.
- Judea, specifically Jerusalem, was the site of Jesus’s crucifixion, resurrection, and ascension.
Roman Rule and the Jewish Revolt:
- The Roman Empire conquered Judea in 63 BCE, establishing a client kingdom under Herod the Great.
- The region experienced a period of relative peace and prosperity under Roman rule.
- However, tensions between the Jewish population and Roman authorities escalated, culminating in the Great Revolt of 66-70 CE.
- The destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem marked a pivotal moment in Jewish history, leading to the dispersal of the Jewish people.
The Byzantine and Arab Periods:
- Following the Roman period, Galilee and Judea were ruled by the Byzantine Empire, with Christianity becoming the dominant religion.
- The region was conquered by the Arab Rashidun Caliphate in the 7th century CE, marking the beginning of Islamic rule.
- This period witnessed the construction of mosques and the development of Arabic culture in the region.
The Ottoman Empire and Modern Israel:
- Galilee and Judea were incorporated into the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century.
- The region experienced a period of relative stability under Ottoman rule, but also witnessed waves of migration and conflict.
- In the 20th century, the region became the focal point of the Zionist movement, which aimed to establish a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
- The establishment of the State of Israel in 1948 led to the displacement of Palestinian Arabs and the outbreak of the Arab-Israeli conflict.
Enduring Relevance
The Galilee and Judea map continues to hold immense relevance in the modern world. It serves as a reminder of the shared history and cultural heritage of Jews, Christians, and Muslims, and the enduring significance of the region in the Middle East.
Religious Pilgrimage:
- Jerusalem remains a sacred site for Jews, Christians, and Muslims, attracting millions of pilgrims annually.
- The Western Wall, a remnant of the Second Temple, is a site of intense prayer and reflection for Jews.
- The Church of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem, believed to be the site of Jesus’s crucifixion and resurrection, is a major pilgrimage destination for Christians.
Political and Social Issues:
- The region remains a focal point of conflict and negotiation between Israel and Palestine.
- The ongoing struggle for control of Jerusalem and other contested territories continues to shape the political landscape of the Middle East.
- The map highlights the complex social and economic challenges facing the region, including issues of poverty, unemployment, and access to resources.
Tourism and Cultural Heritage:
- Galilee and Judea are major tourist destinations, attracting visitors from around the world.
- Ancient ruins, historical sites, and religious landmarks draw tourists interested in exploring the region’s rich history and culture.
- The region also offers natural beauty, with scenic landscapes, hiking trails, and opportunities for outdoor recreation.
FAQs about the Galilee and Judea Map
1. What is the significance of the Sea of Galilee?
The Sea of Galilee, also known as Lake Tiberias, holds immense religious, historical, and economic significance. It was a vital source of fishing and transportation for the region, and it played a central role in the life and ministry of Jesus Christ. Many of his miracles, teachings, and interactions with his disciples took place on its shores.
2. Why is Jerusalem considered a holy city?
Jerusalem is considered a holy city by Jews, Christians, and Muslims due to its profound religious significance. It is the site of the Temple Mount, where the First and Second Temples stood, a sacred place for Jewish worship. Christians believe it to be the site of Jesus’s crucifixion, resurrection, and ascension. Muslims revere it as the site of the Dome of the Rock, believed to be the location of Muhammad’s ascension to heaven.
3. What was the impact of the destruction of the Second Temple?
The destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem in 70 CE marked a pivotal moment in Jewish history. It led to the dispersal of the Jewish people, known as the Diaspora, and the loss of a central place of worship. It also marked the beginning of a new era for Judaism, characterized by the development of Rabbinic Judaism and the emphasis on oral tradition.
4. How does the Galilee and Judea map relate to the modern-day conflict between Israel and Palestine?
The Galilee and Judea map provides a historical context for the ongoing conflict between Israel and Palestine. The region has been a subject of territorial disputes for centuries, with both sides claiming historical and religious ties to the land. The map highlights the complex geopolitical realities and the historical grievances that underpin the current conflict.
5. What are some of the challenges facing the region today?
The region faces numerous challenges, including poverty, unemployment, limited access to resources, and political instability. The ongoing conflict between Israel and Palestine has created a humanitarian crisis, with displacement, violence, and economic hardship affecting both sides. The region also faces environmental challenges, such as water scarcity and desertification.
Tips for Understanding the Galilee and Judea Map
- Study the map in conjunction with historical texts and timelines: This will help you understand the chronology of events and the relationships between different historical periods.
- Focus on key locations: Identify important cities, towns, and geographical features, and research their significance in historical and religious contexts.
- Explore the different religions and cultures: Understand the historical and religious significance of the region for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
- Consider the map’s broader context: The Galilee and Judea map is not simply a geographical representation; it reflects the complex history, culture, and politics of the region.
Conclusion
The Galilee and Judea map serves as a powerful reminder of the rich history and cultural heritage of the region. It encapsulates the stories of ancient civilizations, religious beliefs, and political struggles that have shaped the world we know today. Understanding the map’s geographical features, historical context, and enduring relevance is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the Middle East and its ongoing challenges. As we navigate the present and future, the lessons learned from the Galilee and Judea map can guide us towards a more peaceful and just world.


.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of History: A Comprehensive Guide to the Galilee and Judea Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!