Unveiling Nevada’s Majestic Peaks: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Mountainous Landscape
Related Articles: Unveiling Nevada’s Majestic Peaks: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Mountainous Landscape
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Nevada’s Majestic Peaks: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Mountainous Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Nevada’s Majestic Peaks: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Mountainous Landscape
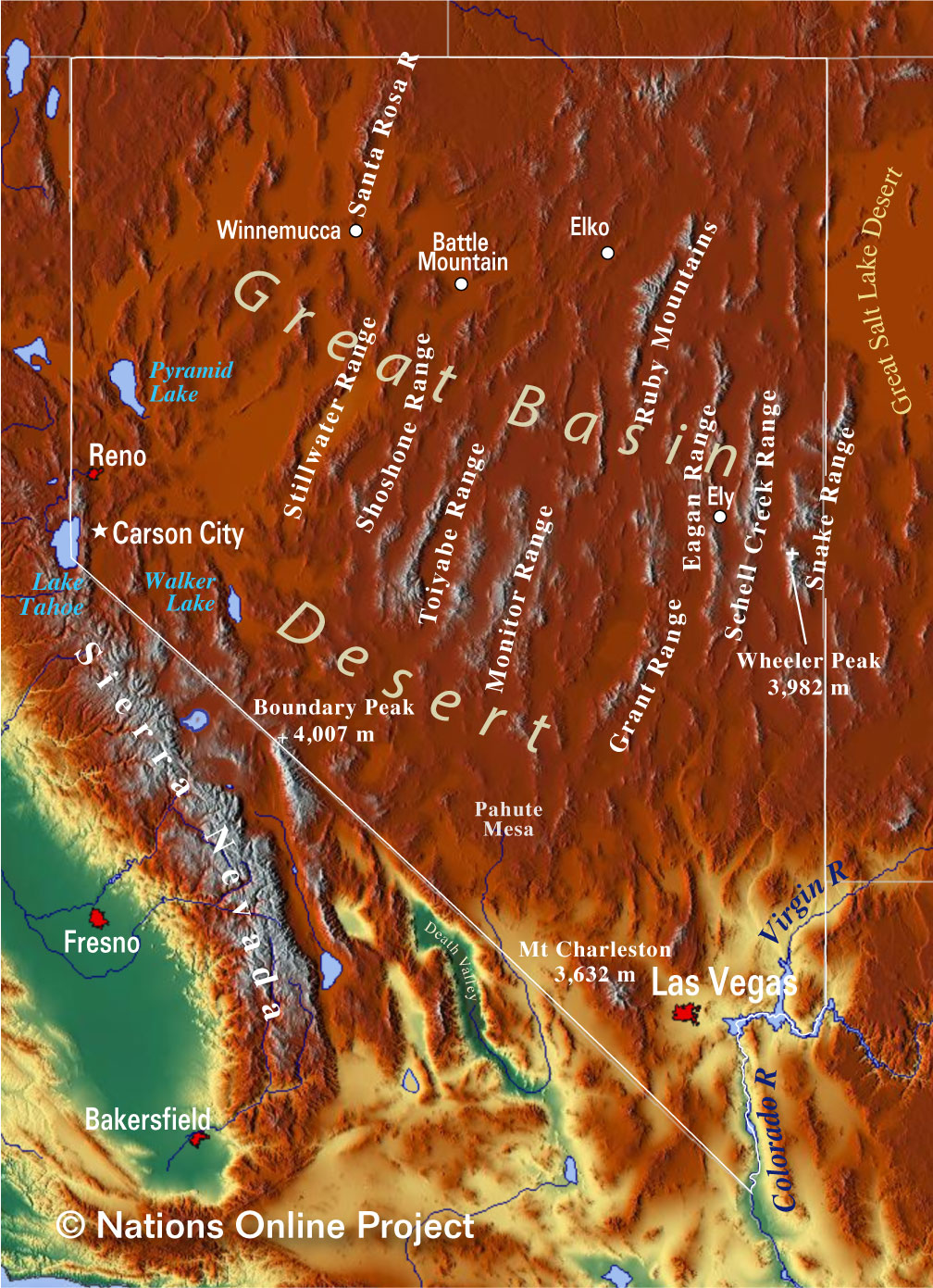
Nevada, often recognized for its glittering casinos and arid deserts, harbors a hidden treasure: a diverse and awe-inspiring mountainous landscape. From the towering peaks of the Sierra Nevada to the rugged ranges of the Great Basin, Nevada’s mountains play a vital role in the state’s ecology, economy, and cultural identity. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these mountain ranges is crucial for appreciating the state’s natural beauty and appreciating the unique challenges and opportunities they present.
A Tapestry of Mountain Ranges:
Nevada’s mountainous terrain is a captivating mosaic, comprised of several distinct mountain ranges:
-
The Sierra Nevada: This iconic range, stretching across California and Nevada, is renowned for its towering granite peaks, including Mount Whitney, the highest point in the contiguous United States. Within Nevada, the Sierra Nevada encompasses the Toiyabe Range, the White Mountains, and the Inyo Mountains, offering breathtaking views and challenging hiking trails.
-
The Great Basin Ranges: This vast expanse of mountains and valleys covers the majority of Nevada’s landscape. Characterized by rugged, often isolated peaks, the Great Basin Ranges offer a unique and diverse ecosystem. Notable ranges include the Snake Range, the Ruby Mountains, the Spring Mountains, and the Toquima Range, each possessing its own distinct geological history and ecological features.
-
The Basin and Range Province: Extending beyond Nevada’s borders, the Basin and Range Province encompasses a vast area of the western United States. This region is characterized by a series of parallel mountain ranges separated by broad, flat valleys. The Basin and Range Province plays a significant role in shaping Nevada’s climate, hydrology, and biodiversity.
A Visual Guide: The Nevada Mountains Map
Navigating the complex tapestry of Nevada’s mountains requires a visual aid. A comprehensive Nevada mountains map provides an essential tool for understanding the spatial distribution of these ranges and their interconnectedness. Such maps often incorporate various layers of information, including:
- Topographic Elevation: Depicting the heights of different mountain ranges and peaks, allowing for visual identification of the highest and most challenging areas.
- Range Boundaries: Clearly delineating the extent of individual mountain ranges, aiding in understanding their spatial relationships and ecological connections.
- Major Highways and Roads: Providing crucial information for planning travel and accessing specific mountain areas.
- Designated Wilderness Areas: Highlighting areas protected for their natural beauty and ecological significance, offering opportunities for backcountry exploration.
- National Parks and Monuments: Identifying areas managed by the National Park Service, offering diverse recreational opportunities and cultural experiences.
The Significance of Nevada’s Mountains:
Beyond their aesthetic appeal, Nevada’s mountains hold immense ecological, economic, and cultural significance.
Ecological Significance:
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Nevada’s mountains provide habitat for a wide range of flora and fauna, including endemic species found nowhere else in the world. The diverse ecosystems, ranging from alpine meadows to desert scrublands, support a complex web of life.
- Water Sources: Mountain ranges act as crucial watersheds, collecting snow and rainfall that feeds rivers and streams, providing essential water resources for human populations and ecosystems.
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests and vegetation in Nevada’s mountains play a vital role in absorbing atmospheric carbon dioxide, contributing to mitigating climate change.
Economic Significance:
- Tourism and Recreation: Nevada’s mountains attract millions of visitors annually, seeking opportunities for hiking, camping, skiing, and other outdoor activities. This tourism industry contributes significantly to the state’s economy.
- Mining and Energy Resources: Nevada’s mountains contain valuable mineral deposits and renewable energy sources, providing economic opportunities and challenges related to resource extraction and environmental sustainability.
- Ranching and Agriculture: Mountain meadows and valleys provide grazing lands for livestock, contributing to the state’s agricultural sector.
Cultural Significance:
- Native American Heritage: Nevada’s mountains have been home to Native American tribes for millennia, who have developed deep cultural connections to the land and its resources.
- Historical Significance: Mountains played a crucial role in the exploration and settlement of Nevada, providing routes for early travelers and miners.
- Recreation and Lifestyle: Mountains offer a unique lifestyle for those seeking solitude, adventure, and connection with nature.
Navigating the Mountains: Practical Tips for Visitors and Residents:
- Plan Ahead: Research your destination, considering elevation changes, trail conditions, weather forecasts, and necessary permits.
- Be Prepared: Pack appropriate clothing, food, water, and safety equipment, including a map, compass, and first-aid kit.
- Respect the Environment: Practice Leave No Trace principles, minimizing your impact on the natural environment and respecting wildlife.
- Stay Informed: Be aware of potential hazards, including wildlife encounters, extreme weather, and altitude sickness.
- Seek Local Guidance: Consult with park rangers, local guides, or experienced hikers for advice and information specific to your chosen destination.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the highest mountains in Nevada?
A: The highest point in Nevada is Wheeler Peak in the Snake Range, reaching an elevation of 13,065 feet. Other notable high peaks include Boundary Peak in the White Mountains (13,143 feet) and Mount Charleston in the Spring Mountains (11,916 feet).
Q: What are the best hiking trails in Nevada mountains?
A: Nevada offers a diverse range of hiking trails, catering to different skill levels and interests. Popular trails include the Tahoe Rim Trail, the Mount Charleston Trail, and the Flume Trail.
Q: Are there any ski resorts in Nevada mountains?
A: Nevada is home to several world-class ski resorts, including Mount Charleston, Heavenly, and Kirkwood, offering a variety of slopes and amenities.
Q: What are the best times to visit Nevada mountains?
A: The best time to visit Nevada mountains depends on your interests and desired activities. Summer offers ideal conditions for hiking and camping, while winter is perfect for skiing and snowshoeing.
Conclusion:
Nevada’s mountains are a testament to the state’s natural beauty and ecological diversity. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these ranges through comprehensive maps and resources is crucial for appreciating their significance and navigating their challenges. Whether seeking outdoor adventure, cultural immersion, or simply a connection with nature, Nevada’s mountains offer a unique and rewarding experience. By respecting these natural wonders and practicing responsible recreation, we can ensure their preservation for generations to come.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Nevada’s Majestic Peaks: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Mountainous Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!