Unveiling the Colors of North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Continent’s Geographic Diversity
Related Articles: Unveiling the Colors of North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Continent’s Geographic Diversity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Colors of North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Continent’s Geographic Diversity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Colors of North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Continent’s Geographic Diversity

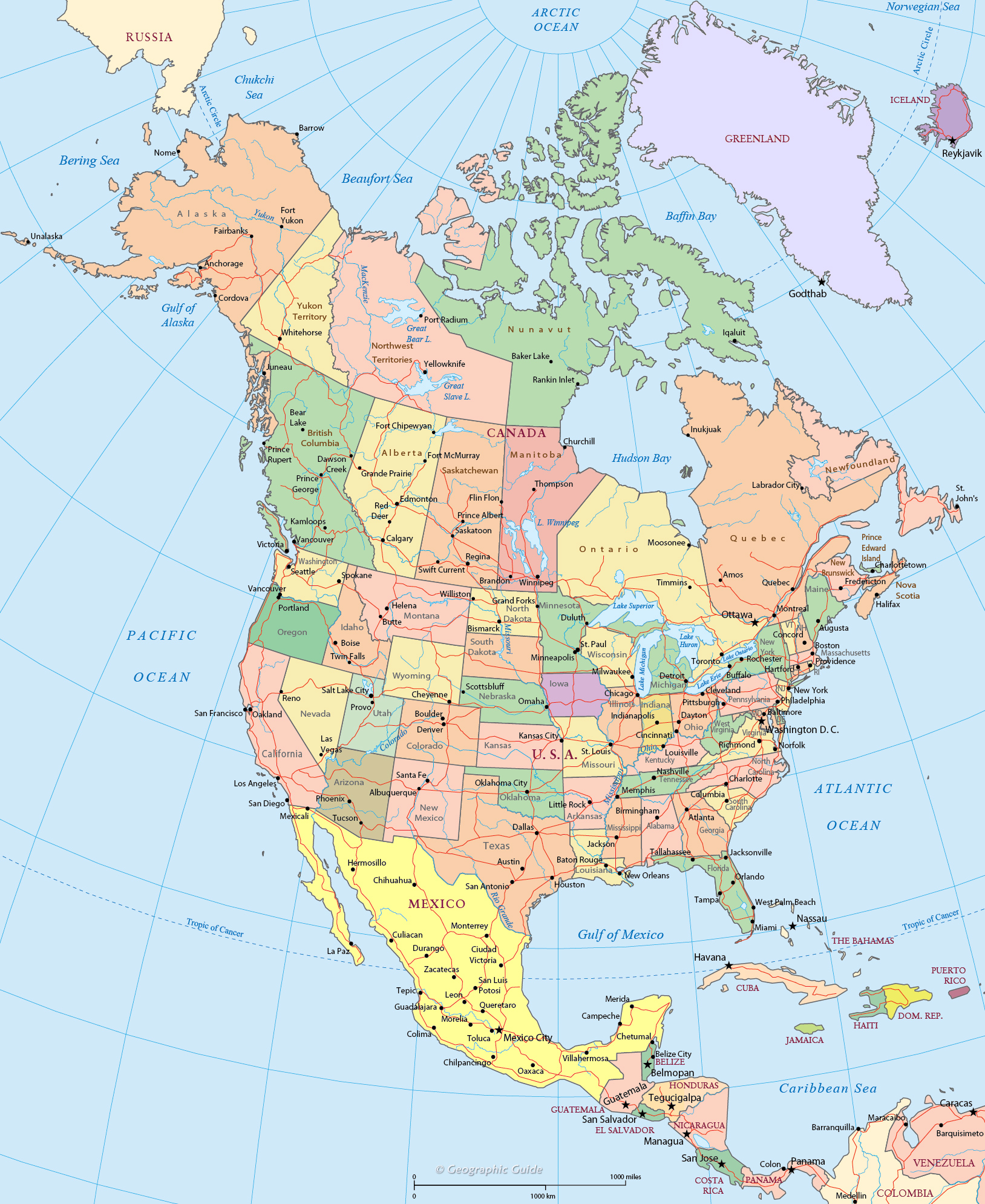
North America, a vast and diverse continent, is a tapestry of landscapes, climates, and cultures. Understanding its geographic makeup is crucial for appreciating its rich history, its present-day challenges, and its future potential. A North American color map, a visual representation of the continent’s diverse geographical features, serves as a powerful tool for navigating this complexity. This article delves into the intricacies of North American color maps, exploring their significance, applications, and the insights they provide.
The Power of Visual Representation
Color maps are not merely aesthetic representations; they are powerful tools for conveying complex information in a readily digestible format. By employing color as a visual cue, they allow us to quickly grasp spatial relationships, identify patterns, and understand the distribution of various geographical elements. This visual clarity is especially valuable when studying a continent as vast and diverse as North America.
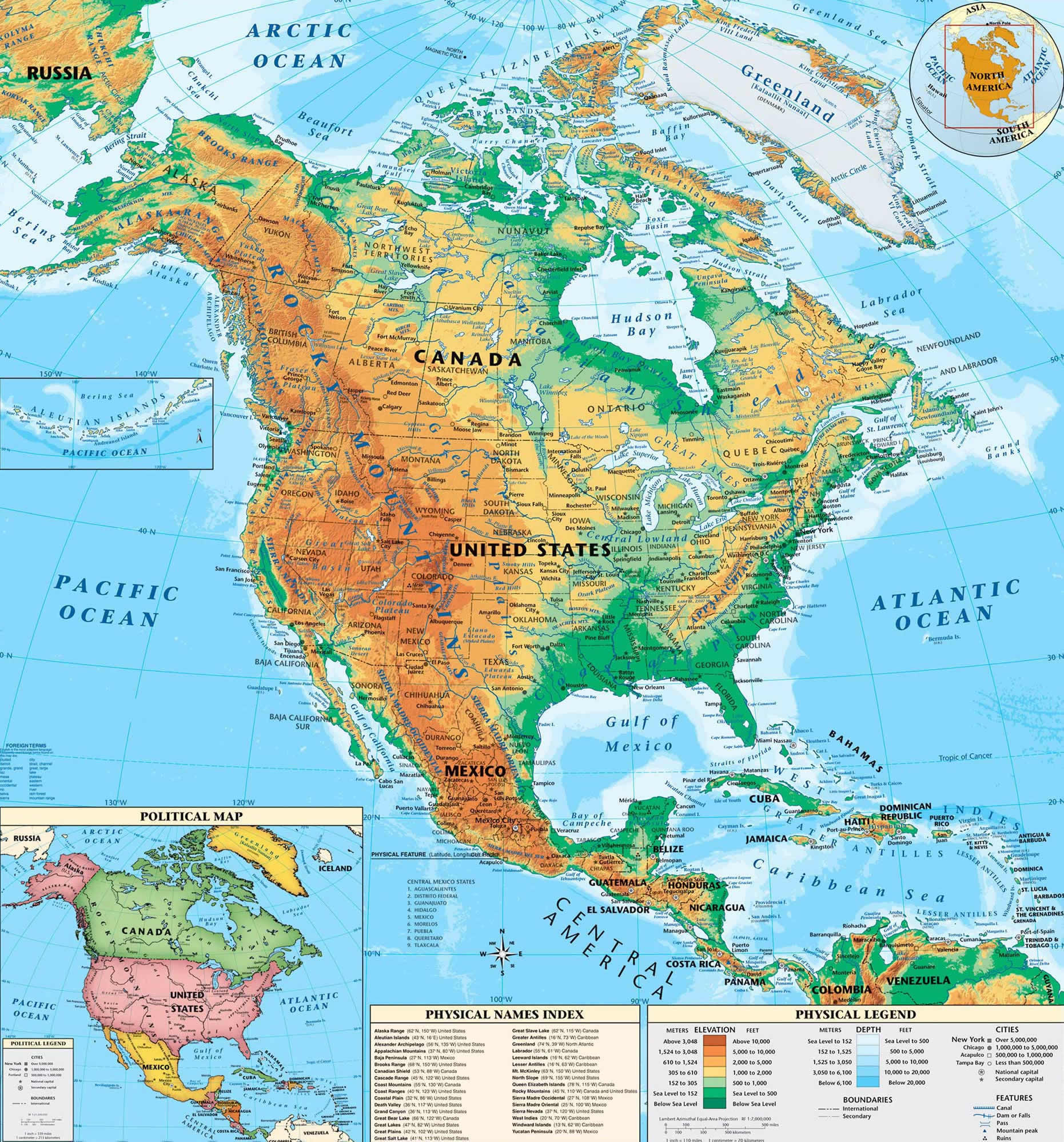
Decoding the Colors: A Geographical Palette
A typical North American color map utilizes a spectrum of colors to represent different geographical features, including:
- Elevation: Shades of green typically depict low-lying areas, transitioning to yellow, orange, and finally red or brown for higher elevations, representing mountains and plateaus. This color scheme helps visualize the continent’s diverse topography, from the coastal plains to the towering peaks of the Rockies.
- Vegetation: Green hues represent forests, with darker shades signifying dense woodlands and lighter shades indicating sparse vegetation. This allows us to see the distribution of various forest types, including the vast boreal forests of Canada, the deciduous forests of the eastern United States, and the desert scrublands of the southwestern United States and Mexico.
- Water Bodies: Blue shades are used to represent oceans, lakes, and rivers. Different shades of blue can indicate varying depths, with darker blues representing deeper waters. This visual representation helps highlight the importance of water bodies in shaping the continent’s climate, biodiversity, and human settlements.
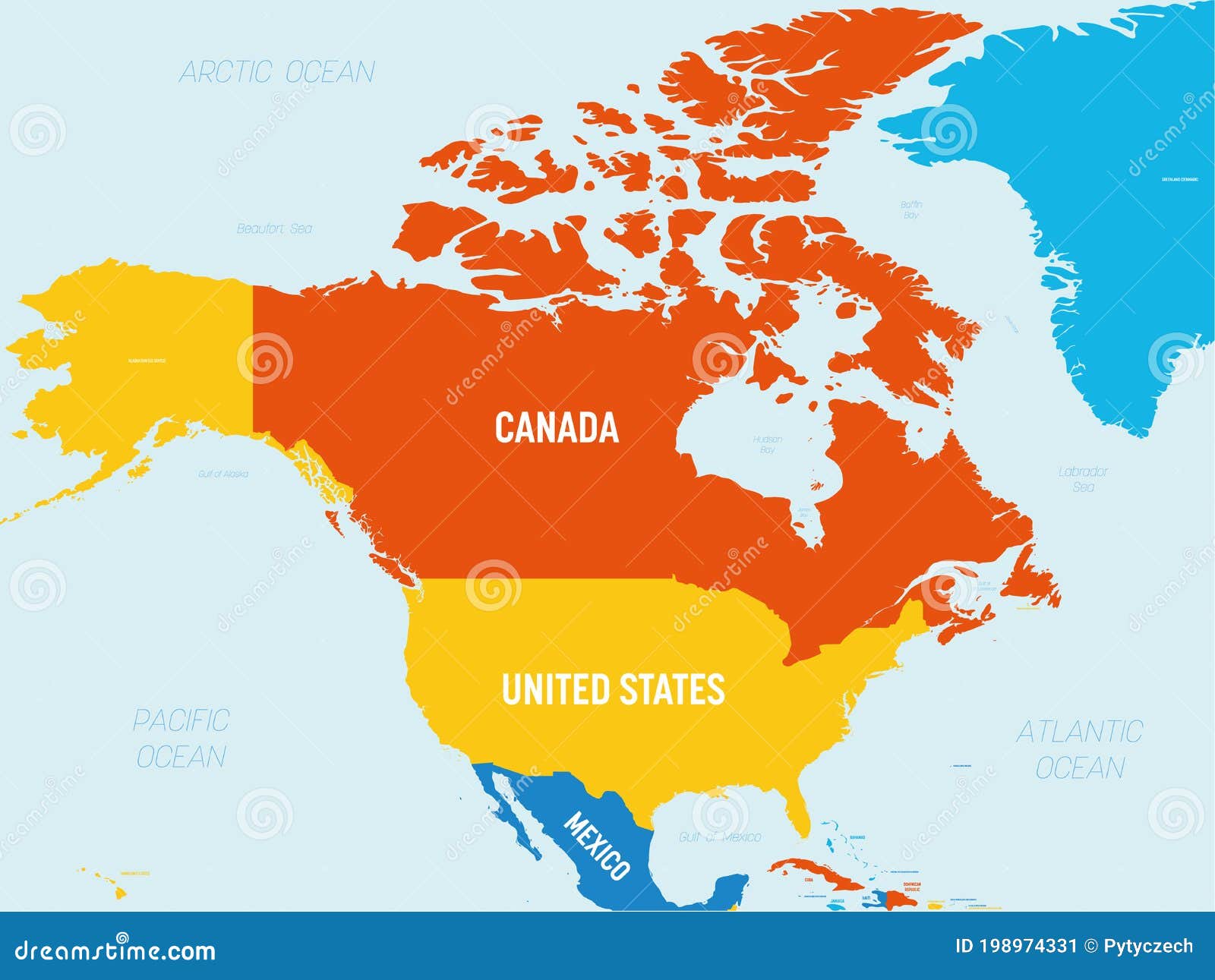
- Political Boundaries: Different colors may be used to distinguish between countries and states, providing a visual representation of the continent’s political landscape. This allows for easy identification of the borders of the United States, Canada, and Mexico, as well as the various states and provinces within these countries.
- Climate Zones: Color maps can also depict climate zones, using different colors to represent distinct temperature and precipitation patterns. This visual representation helps understand the distribution of different climate types, from the frigid Arctic to the subtropical climates of the southern United States and Mexico.
Applications of North American Color Maps
North American color maps find diverse applications in various fields:
- Education: They are invaluable tools in classrooms, providing students with a visual understanding of the continent’s geography, its diverse landscapes, and the distribution of natural resources.
- Research: Scientists and researchers utilize color maps to analyze spatial patterns, identify trends, and understand the relationships between different geographical features. For example, climate scientists can use color maps to study the impact of climate change on different regions of North America.
- Planning and Development: Urban planners, environmental agencies, and policymakers rely on color maps to assess the suitability of land for different purposes, identify areas prone to natural disasters, and develop strategies for sustainable development.
- Tourism and Recreation: Color maps can help travelers plan their trips, identifying scenic areas, national parks, and points of interest. They provide a visual guide to the continent’s diverse landscapes and attractions.
- Historical Studies: Color maps can be used to visualize historical events, such as the westward expansion of the United States, the migration patterns of indigenous populations, and the impact of colonization on the continent’s geography.
Beyond the Surface: Understanding the Underlying Dynamics
While a North American color map provides a valuable visual overview, it is crucial to remember that it represents a snapshot in time. The continent is constantly evolving, influenced by factors such as:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events are altering the continent’s landscapes and ecosystems.
- Human Activities: Population growth, urbanization, deforestation, and agricultural practices are shaping the continent’s environment and impacting its biodiversity.
- Natural Processes: Geological processes like plate tectonics, volcanic activity, and erosion continue to reshape the continent’s landscape.
Engaging with the Data: Exploring the Nuances
To fully appreciate the complexities of North America, it is essential to engage with the data beyond the visual representation. This involves:
- Understanding the Scale: Color maps often represent large areas, and it is important to consider the scale at which they are presented. A map of the entire continent will provide a different perspective than a map of a specific region.
- Interpreting the Symbols: Each color on a map represents a specific geographical feature or data point. It is crucial to understand the legend or key accompanying the map to correctly interpret the information presented.
- Considering Multiple Data Sets: Combining different types of data, such as elevation, vegetation, and population density, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the continent’s complexities.
- Exploring Interactive Maps: Digital maps offer interactive features that allow users to zoom in and out, select specific data layers, and access additional information.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What are the most significant geographical features of North America?
North America is characterized by a diverse range of geographical features, including:
- The Rocky Mountains: A vast mountain range stretching from Canada to Mexico, forming the continental divide and shaping the climate and biodiversity of the western United States and Canada.
- The Great Plains: A vast expanse of flat grasslands stretching from the Rocky Mountains to the Mississippi River, historically important for agriculture and cattle ranching.
- The Mississippi River: The longest river in North America, flowing from Minnesota to the Gulf of Mexico, playing a crucial role in transportation, agriculture, and the continent’s history.
- The Great Lakes: A system of five interconnected lakes, the largest freshwater system in the world, vital for transportation, recreation, and the economy of the region.
- The Appalachian Mountains: An ancient mountain range stretching from Canada to Alabama, influencing the climate and biodiversity of the eastern United States.
2. How has human activity shaped the landscape of North America?
Human activity has significantly impacted the landscape of North America, leading to:
- Deforestation: Large-scale clearing of forests for agriculture, urban development, and resource extraction has resulted in habitat loss and biodiversity decline.
- Pollution: Industrial activities, agriculture, and urban development have led to air, water, and soil pollution, impacting human health and ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have contributed to global warming, leading to changes in precipitation patterns, rising sea levels, and more frequent extreme weather events.
- Urbanization: The growth of cities has resulted in habitat fragmentation, increased pollution, and changes in land use patterns.
3. How can North American color maps be used to promote sustainability?
North American color maps can be used to:
- Identify areas prone to natural disasters: By visualizing areas susceptible to floods, earthquakes, wildfires, and other hazards, maps can help prioritize mitigation efforts and guide development decisions.
- Assess the distribution of natural resources: Maps can highlight areas rich in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, facilitating the development of sustainable energy infrastructure.
- Monitor environmental changes: Color maps can track deforestation, pollution levels, and other environmental changes, providing data for informed decision-making and conservation efforts.
- Promote responsible land use: Maps can help identify areas suitable for agriculture, forestry, urban development, and other land uses, ensuring sustainable practices and minimizing environmental impact.
Tips for Using North American Color Maps Effectively
- Pay attention to the scale: Consider the area covered by the map and the level of detail it provides.
- Understand the legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and colors used on the map to correctly interpret the information.
- Compare different maps: Combine data from multiple maps to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the continent’s complexities.
- Use interactive maps: Explore digital maps to zoom in and out, select specific data layers, and access additional information.
- Consider the context: Understand the historical, cultural, and social factors that have shaped the continent’s geography.
Conclusion
North American color maps are powerful tools for visualizing and understanding the continent’s diverse geography. They provide a visual representation of its landscapes, climates, and political boundaries, offering insights into its history, its present-day challenges, and its future potential. By understanding the colors, the underlying data, and the context in which these maps are presented, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of North America and the interconnectedness of its various geographical features. As the continent continues to evolve, North American color maps will remain valuable tools for navigating its complexities and shaping its future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Colors of North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Continent’s Geographic Diversity. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!