Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps
- 3.1 What are Topography Maps?
- 3.2 Key Elements of Topography Maps
- 3.3 Types of Topography Maps
- 3.4 Benefits of Using Topography Maps
- 3.5 Reading and Interpreting Topography Maps
- 3.6 The Role of Technology in Topography Mapping
- 3.7 FAQs about Topography Maps
- 3.8 Tips for Using Topography Maps
- 3.9 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps

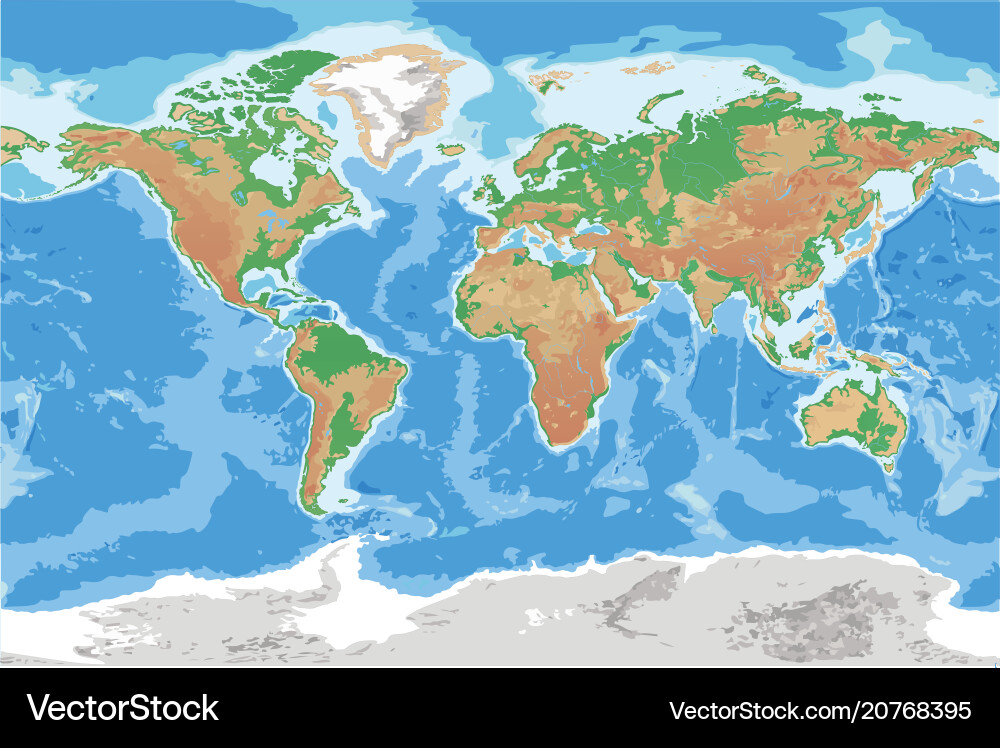
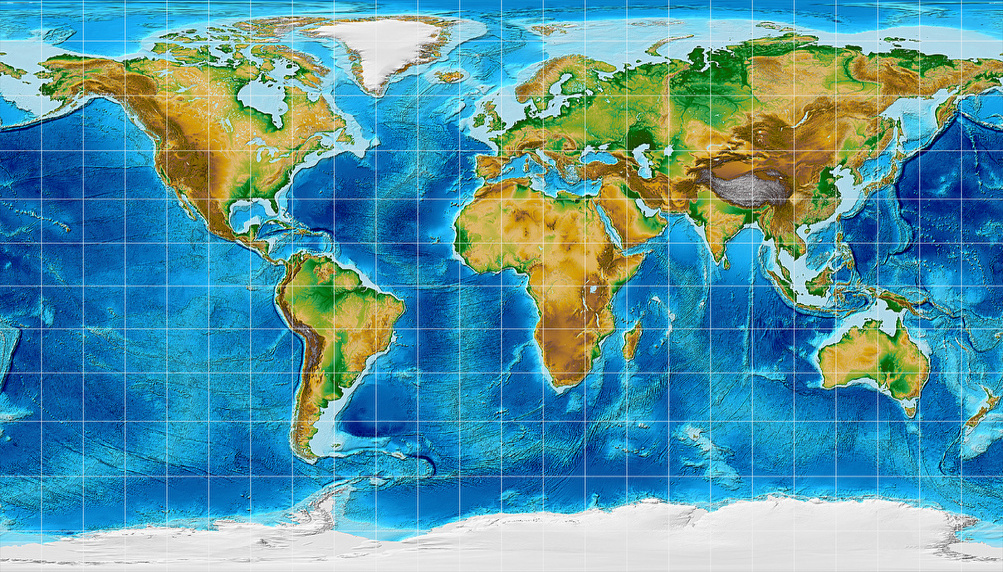
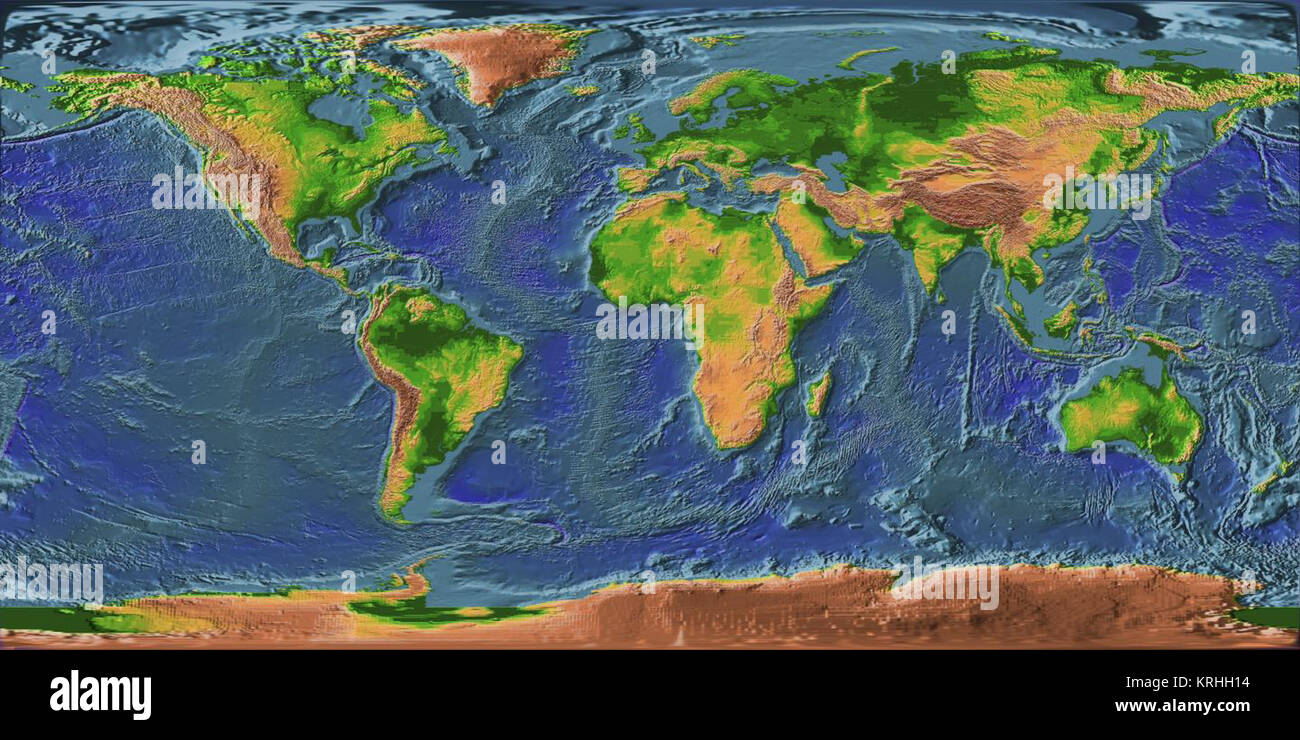
The Earth, a planet teeming with life and diverse landscapes, presents a complex and fascinating surface. Understanding its physical features, from towering mountains to vast oceans, is crucial for various disciplines, including geography, geology, environmental science, and even urban planning. This is where topography maps come into play, providing a visual representation of the Earth’s surface, revealing its intricate contours and elevations.
What are Topography Maps?
Topography maps, also known as topographic maps, are specialized maps that depict the Earth’s surface relief, showcasing the elevation changes and features of the land. They are essential tools for visualizing the landscape, understanding its characteristics, and planning activities ranging from hiking and exploring to infrastructure development and disaster preparedness.
Key Elements of Topography Maps
Topography maps employ a unique set of symbols and conventions to represent the landscape accurately. These elements include:
- Contour Lines: These are the most prominent feature of topography maps. They connect points of equal elevation, forming a series of closed curves that trace the shape of the terrain. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope.
- Elevation Points: These are marked with numbers indicating the precise elevation of a specific point on the map.
- Spot Elevations: These are points of known elevation marked with a small circle and the corresponding elevation value.
- Relief Shading: This technique uses shading to create a three-dimensional effect, highlighting areas of high and low elevation.
- Symbols: Topography maps use a variety of symbols to represent different features, such as roads, buildings, water bodies, vegetation, and cultural landmarks.
Types of Topography Maps
Topography maps are available in various formats and scales, each tailored to specific purposes:
- Large-Scale Maps: These maps cover smaller areas with greater detail, often used for local planning, engineering projects, and recreational activities.
- Small-Scale Maps: These maps cover larger areas with less detail, suitable for regional planning, geological studies, and global analyses.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): These are digital representations of elevation data, often used for creating 3D models of the terrain and conducting spatial analysis.
Benefits of Using Topography Maps
Topography maps offer a wealth of information, making them indispensable tools for a wide range of applications:
- Land Use Planning: Understanding the terrain’s characteristics allows for informed decision-making regarding land use, infrastructure development, and resource management.
- Environmental Studies: Topography maps are crucial for analyzing environmental factors such as water flow patterns, soil erosion, and vegetation distribution.
- Disaster Preparedness: By understanding the terrain, emergency responders can better assess risks, plan evacuation routes, and manage disaster relief efforts.
- Military Operations: Topography maps are essential for navigating challenging terrain, planning troop movements, and understanding the battlefield environment.
- Recreation and Exploration: Topography maps enable hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts to plan their routes, assess risks, and navigate unfamiliar terrain.
Reading and Interpreting Topography Maps
Understanding the conventions used in topography maps is crucial for extracting valuable information. Here’s a breakdown of key aspects:
- Contour Lines: The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope. Widely spaced contour lines indicate gentle slopes, while closely spaced lines represent steep slopes.
- Elevation Points and Spot Elevations: These points provide precise elevation data, allowing for accurate assessment of the terrain’s height.
- Relief Shading: Areas with darker shading represent higher elevations, while lighter shading indicates lower elevations.
- Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used on topography maps to identify different features and landmarks.
The Role of Technology in Topography Mapping
Technological advancements have revolutionized topography mapping, offering new tools and methods:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software allows for the creation, analysis, and visualization of spatial data, including topography maps.
- Remote Sensing: Techniques like satellite imagery and aerial photography provide high-resolution data for creating detailed topographic maps.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology uses laser pulses to measure distances and create precise elevation models, capturing even minute details of the terrain.
FAQs about Topography Maps
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a regular map?
A: A regular map focuses on general features like roads, cities, and political boundaries, while a topography map emphasizes the terrain’s elevation and shape.
Q: How are contour lines created?
A: Contour lines are created by connecting points of equal elevation, forming a series of closed curves that depict the terrain’s shape.
Q: What is the significance of the contour interval?
A: The contour interval represents the difference in elevation between adjacent contour lines. A smaller interval indicates greater detail and precision in depicting the terrain.
Q: Can topography maps be used for navigation?
A: Yes, topography maps can be used for navigation, especially in areas with limited or no GPS coverage.
Q: What are some applications of topography maps in different fields?
A: Topography maps are used in land use planning, environmental studies, disaster preparedness, military operations, recreation, and infrastructure development.
Tips for Using Topography Maps
- Study the Map Legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and conventions used on the map to interpret the information accurately.
- Pay Attention to Contour Lines: Analyze the spacing of contour lines to understand the slope and terrain features.
- Use a Compass and Altimeter: These tools are helpful for navigating and determining your location and elevation.
- Consider the Map Scale: Choose a map with an appropriate scale for your needs and the area you are exploring.
- Plan Your Route Carefully: Study the topography map before embarking on any outdoor activity to identify potential hazards and plan your route accordingly.
Conclusion
Topography maps provide a powerful visual representation of the Earth’s surface, revealing its intricate contours and elevations. They are essential tools for understanding the landscape, planning activities, and making informed decisions in various fields. As technology continues to evolve, topography mapping will continue to play a crucial role in our understanding and management of the Earth’s environment. By embracing the information provided by these maps, we can better navigate the complexities of our planet and make informed decisions for its future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Guide to Topography Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!