Unveiling the Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Vegetation Map of the United States
Related Articles: Unveiling the Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Vegetation Map of the United States
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Vegetation Map of the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Vegetation Map of the United States
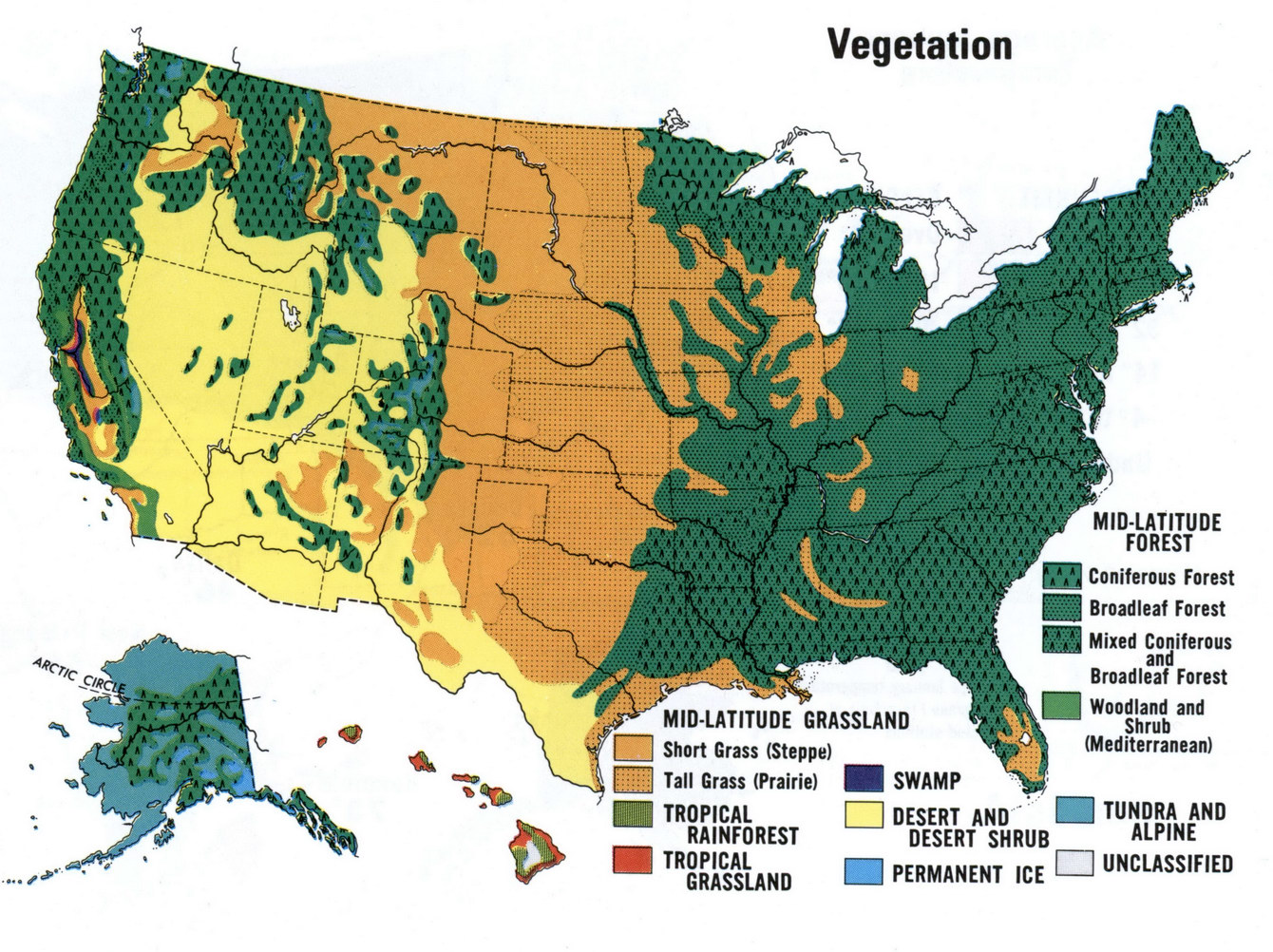
The United States, a vast and diverse landmass, boasts an equally diverse array of plant life. From the towering redwoods of the Pacific Northwest to the sun-baked deserts of the Southwest, a tapestry of vegetation patterns stretches across the country. Understanding this intricate mosaic is crucial for various disciplines, including environmental management, resource planning, and ecological research. This article delves into the intricacies of the vegetation map of the United States, highlighting its significance and exploring its multifaceted applications.
A Visual Representation of Nature’s Diversity
The vegetation map of the United States is a cartographic representation of the dominant plant communities across the country. It serves as a visual guide to the distribution of different vegetation types, providing valuable insights into the ecological characteristics and biogeographic patterns of the nation. This map, often presented as a series of colors and symbols, allows researchers and policymakers to quickly grasp the spatial distribution of various plant communities.
The Building Blocks of the Map: Vegetation Types
The vegetation map of the United States classifies plant communities into various categories, each representing a distinct ecological unit. These categories are based on factors such as:
- Climate: Temperature, precipitation, and seasonality significantly influence plant growth and distribution. For example, the arid Southwest supports desert vegetation, while the humid Southeast harbors lush forests.
- Soil: Soil type, fertility, and drainage patterns determine the suitability of a site for specific plant communities.
- Topography: Elevation, slope, and aspect influence microclimates and, consequently, vegetation patterns.
- Human Influence: Land use practices, such as agriculture and urbanization, can significantly alter natural vegetation patterns.
Major Vegetation Zones of the United States
The vegetation map of the United States identifies several major vegetation zones, each characterized by specific plant communities and ecological characteristics:
- Forests: Dominated by trees, forests cover a significant portion of the United States. These can be further classified into various subtypes, including deciduous forests, coniferous forests, and mixed forests.
- Grasslands: Characterized by grasses and herbaceous plants, grasslands occur in regions with moderate rainfall and seasonal droughts. They are further divided into prairies, steppes, and savannas.
- Deserts: Sparsely vegetated areas with low rainfall and extreme temperatures, deserts are found primarily in the Southwest.
- Tundra: Cold and treeless regions, tundras are located in Alaska and the high elevations of the Rocky Mountains.
- Wetlands: Areas saturated with water for at least part of the year, wetlands include marshes, swamps, and bogs.
Importance and Applications of the Vegetation Map
The vegetation map of the United States serves as a critical tool for various purposes:
- Resource Management: It helps in understanding the distribution of valuable resources, such as timber, forage, and medicinal plants. This information aids in sustainable resource management and conservation efforts.
- Environmental Monitoring: The map provides a baseline for monitoring changes in vegetation patterns over time, allowing researchers to identify trends related to climate change, habitat fragmentation, and invasive species.
- Wildlife Conservation: Understanding the distribution of vegetation types is crucial for wildlife conservation. It helps identify critical habitats for endangered species and informs conservation strategies.
- Land Use Planning: The map assists in land use planning by providing information on the suitability of different areas for various activities, such as agriculture, forestry, and urban development.
- Climate Change Research: The map plays a vital role in understanding the impacts of climate change on vegetation patterns. It helps track changes in vegetation distribution and assess the vulnerability of different ecosystems.
Data Sources and Development
The vegetation map of the United States is a collaborative effort involving various institutions and researchers. Data sources for this map include:
- Satellite Imagery: Remote sensing technologies, such as Landsat and MODIS, provide valuable data for mapping vegetation types across large areas.
- Aerial Photography: Aerial photographs offer high-resolution imagery, enabling detailed mapping of vegetation patterns.
- Ground Surveys: Field surveys provide accurate data on vegetation composition and structure at specific locations.
- Existing Datasets: Existing vegetation maps and databases, such as the National Vegetation Classification (NVC), provide valuable information for developing and updating the map.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the significant progress in developing the vegetation map of the United States, several challenges remain:
- Maintaining Accuracy: Keeping the map updated with changing vegetation patterns, due to factors such as climate change and human activities, is a continuous challenge.
- Standardization: Ensuring consistency in data collection and classification methods across different regions is crucial for accurate mapping.
- Integration of Data: Integrating data from various sources, such as satellite imagery, aerial photography, and field surveys, is essential for creating a comprehensive and accurate map.
- Accessibility: Making the map readily accessible to researchers, policymakers, and the public is crucial for its effective use.
Future directions in vegetation mapping include:
- Developing High-Resolution Maps: Utilizing advanced remote sensing technologies to create more detailed and accurate maps.
- Integrating Climate Change Data: Incorporating climate change projections into vegetation mapping to predict future changes in vegetation distribution.
- Developing Interactive Maps: Creating interactive maps that allow users to explore vegetation patterns and access related information.
FAQs on Vegetation Map of the United States
1. What is the purpose of the vegetation map of the United States?
The vegetation map serves as a comprehensive representation of the distribution of plant communities across the country, providing insights into ecological characteristics, biogeographic patterns, and resource management.
2. How is the vegetation map created?
The map is developed using a combination of data sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, ground surveys, and existing datasets.
3. What are the major vegetation zones identified on the map?
The map identifies several major vegetation zones, including forests, grasslands, deserts, tundras, and wetlands.
4. How is the vegetation map used in environmental management?
The map helps in understanding the distribution of resources, monitoring changes in vegetation patterns, and informing conservation strategies.
5. What are the challenges in developing and maintaining the vegetation map?
Challenges include maintaining accuracy, ensuring standardization, integrating data from various sources, and ensuring accessibility.
6. What are the future directions in vegetation mapping?
Future directions include developing high-resolution maps, integrating climate change data, and creating interactive maps.
Tips for Using the Vegetation Map
- Understand the map legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and colors used to represent different vegetation types.
- Consider the scale: The map’s scale determines the level of detail it provides.
- Consult additional resources: Use the map in conjunction with other sources of information, such as field guides and ecological databases.
- Interpret data with caution: Recognize that the map represents a snapshot in time and may not reflect the full complexity of vegetation patterns.
Conclusion
The vegetation map of the United States serves as a vital tool for understanding the intricate tapestry of plant life across the country. It provides valuable insights into ecological characteristics, resource distribution, and the impacts of human activities. By leveraging this map, researchers, policymakers, and the public can gain a deeper understanding of the nation’s natural heritage and contribute to its sustainable management. As technology advances and our understanding of vegetation dynamics evolves, the vegetation map will continue to play a crucial role in informing environmental decisions and shaping the future of the United States’ ecosystems.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Vegetation Map of the United States. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!