Unveiling the Landscape of Vermont: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographical Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Vermont: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographical Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape of Vermont: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographical Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Vermont: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographical Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Landscape of Vermont: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographical Maps
- 3.1 Understanding Topographical Maps: A Visual Language of Terrain
- 3.2 Navigating Vermont’s Topography: A Journey Through Contour Lines
- 3.3 Beyond Recreation: The Broader Significance of Topographical Maps
- 3.4 Understanding Vermont’s Unique Topography: A Closer Look
- 3.5 Exploring Topographical Maps: Resources and Tools
- 3.6 FAQs: Navigating the World of Topographical Maps
- 3.7 Tips for Utilizing Topographical Maps: A Guide for Exploration
- 3.8 Conclusion: A Window into Vermont’s Natural Beauty
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Landscape of Vermont: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographical Maps
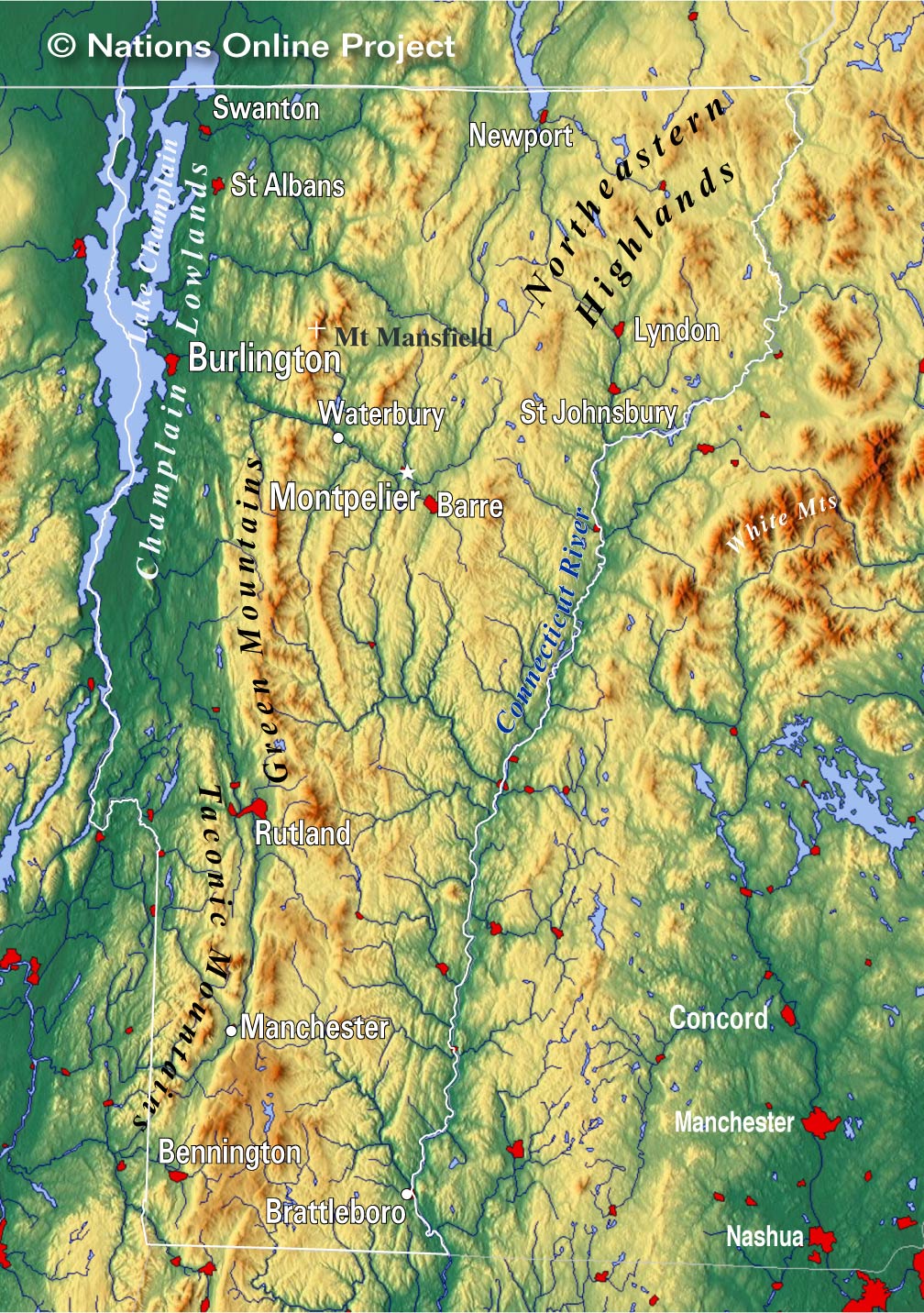
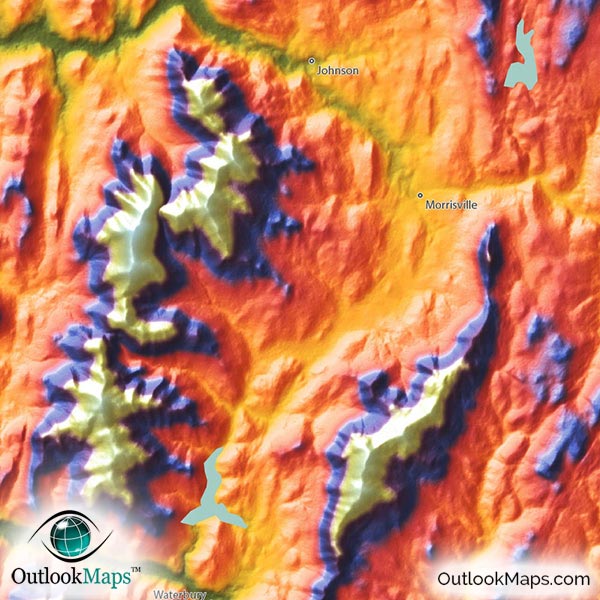
Vermont, known for its picturesque landscapes, rolling hills, and verdant valleys, offers a unique and captivating natural environment. Understanding the intricate topography of this New England state is crucial for various purposes, from outdoor recreation and land management to scientific research and historical exploration. Topographical maps, with their detailed representations of elevation, terrain, and features, serve as invaluable tools for navigating and comprehending Vermont’s diverse landscape.
Understanding Topographical Maps: A Visual Language of Terrain
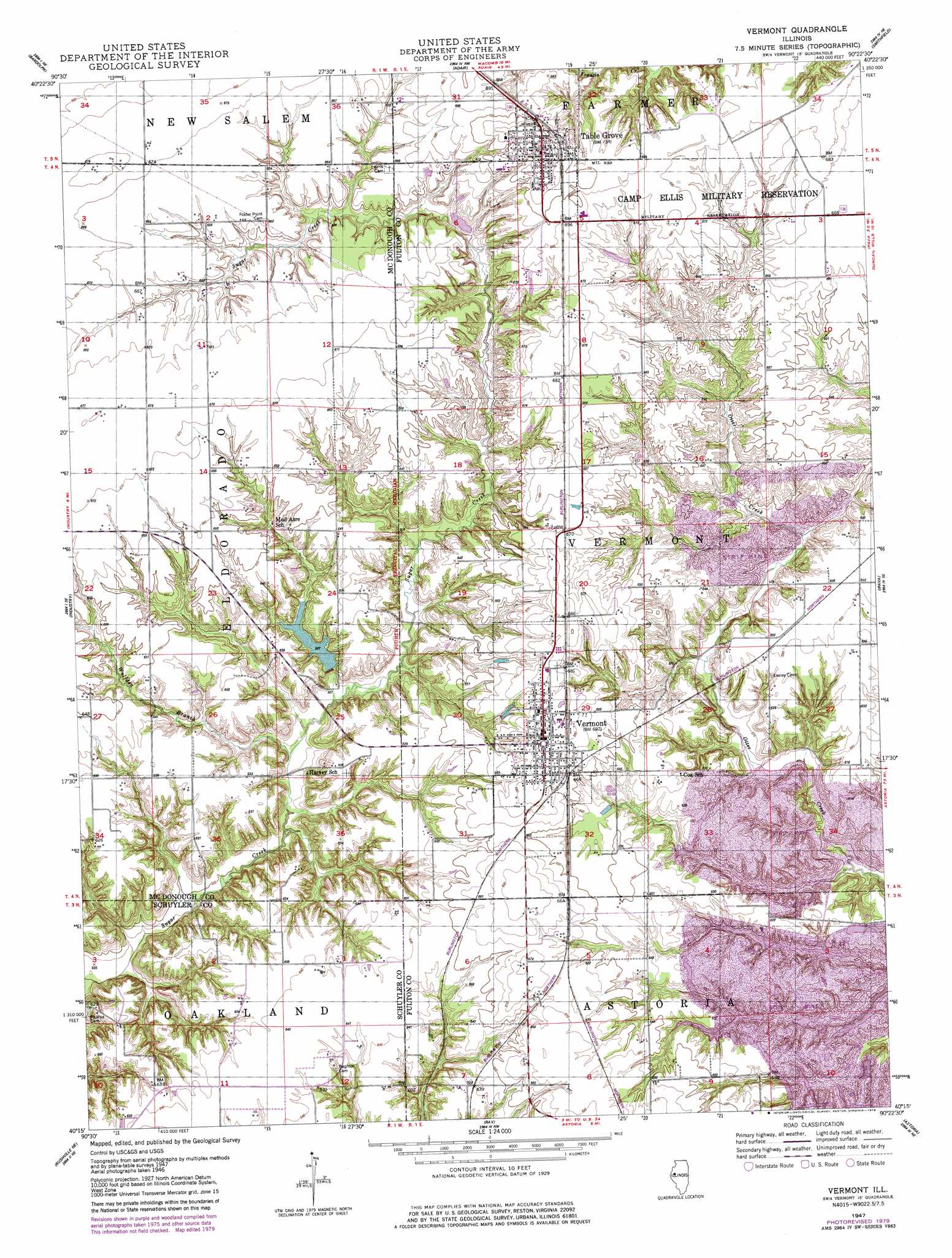
Topographical maps are specialized maps that depict the shape and elevation of the Earth’s surface. Unlike traditional maps, which primarily focus on political boundaries and geographical locations, topographical maps employ contour lines to represent elevation changes. These lines connect points of equal elevation, creating a visual representation of the landscape’s undulations and slopes.
Key Elements of a Topographical Map:
- Contour Lines: These lines represent points of equal elevation, with a specific interval (e.g., 10 feet or 20 meters) between each line. Closer contour lines indicate steeper slopes, while widely spaced lines suggest gentler terrain.
- Elevation Points: Numbers are often placed on contour lines or within enclosed areas to indicate specific elevations.
- Relief Shading: This technique uses shading to create a three-dimensional effect, highlighting areas of higher and lower elevation.
- Symbols and Legends: Topographical maps utilize symbols to represent various features such as rivers, lakes, forests, roads, and buildings. A legend explains the meaning of these symbols.
Navigating Vermont’s Topography: A Journey Through Contour Lines
Topographical maps are essential tools for navigating Vermont’s diverse terrain. They provide a visual representation of the landscape, enabling hikers, bikers, skiers, and outdoor enthusiasts to plan routes, identify potential hazards, and appreciate the intricacies of the environment.
Key Applications of Topographical Maps in Vermont:
- Hiking and Backpacking: Maps help hikers determine trail elevation changes, identify challenging sections, and locate water sources, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
- Mountain Biking: By understanding the terrain, bikers can choose routes that match their skill level and avoid steep descents or challenging climbs.
- Skiing and Snowboarding: Maps are crucial for navigating ski resorts, identifying slopes, and assessing avalanche risks, ensuring safety and maximizing enjoyment.
- Wildlife Observation: Topographical maps can help identify areas with specific vegetation types, which attract different wildlife species, aiding in wildlife observation and photography.
Beyond Recreation: The Broader Significance of Topographical Maps
Topographical maps play a vital role in various sectors beyond recreation, contributing to sustainable land management, scientific research, and historical understanding.
Applications of Topographical Maps in Various Fields:
- Land Management: Maps are used to assess land suitability for different purposes, such as agriculture, forestry, and development, ensuring sustainable land use practices.
- Resource Management: Topographical data helps identify water resources, manage watersheds, and monitor environmental changes, contributing to responsible resource utilization.
- Infrastructure Planning: Maps provide essential information for road construction, pipeline routing, and other infrastructure projects, ensuring efficient and environmentally sound development.
- Historical Research: Topographical maps can reveal historical land use patterns, settlement locations, and infrastructure development, offering insights into past societies and their interactions with the environment.
Understanding Vermont’s Unique Topography: A Closer Look
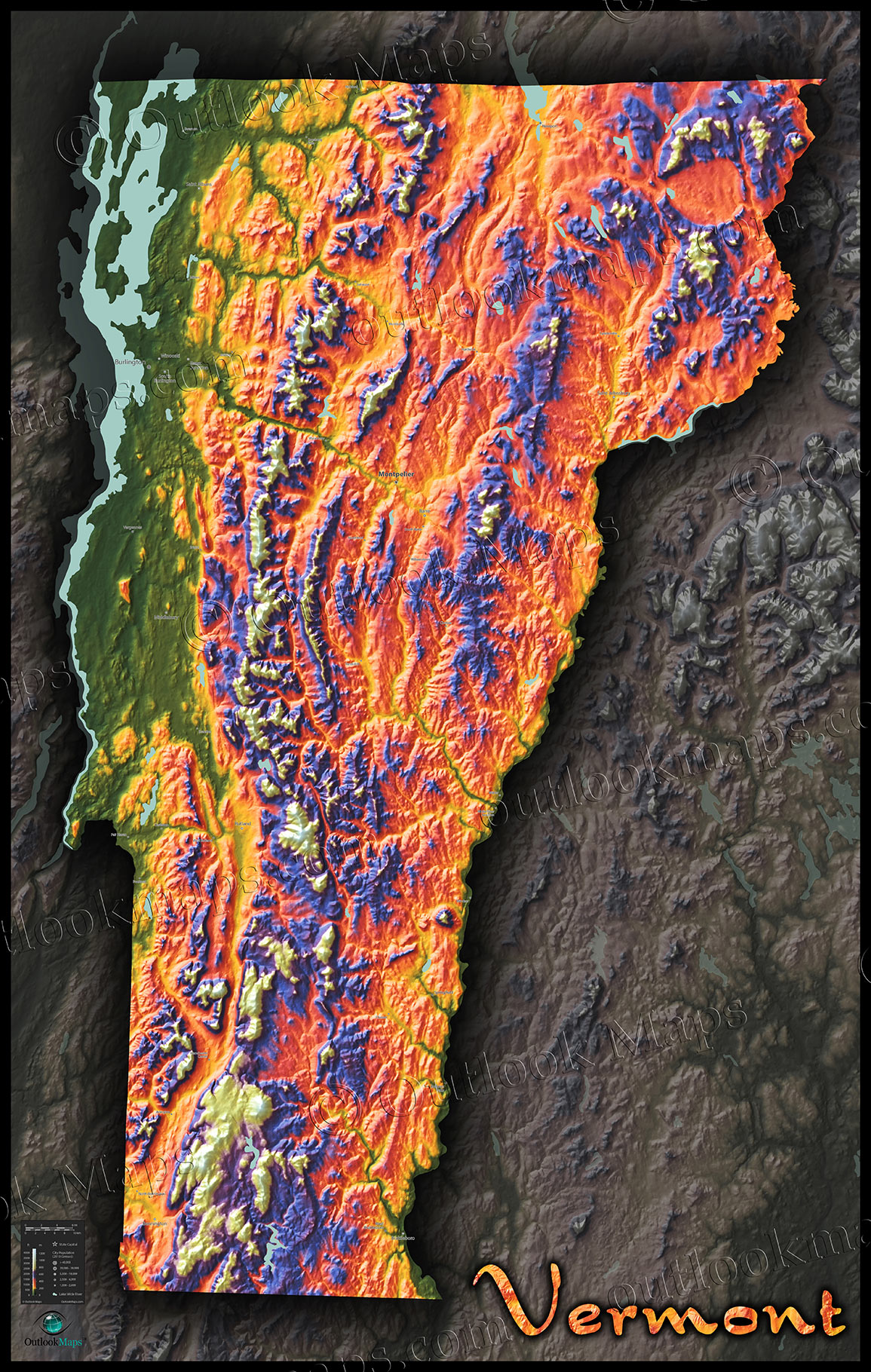
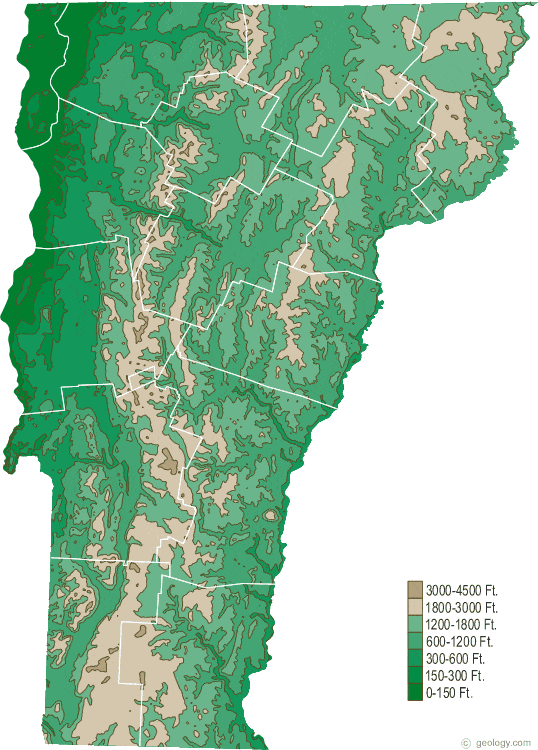
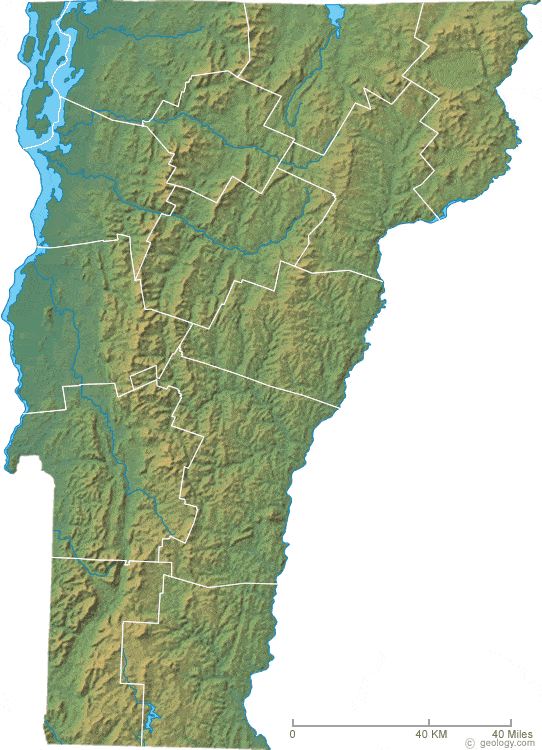
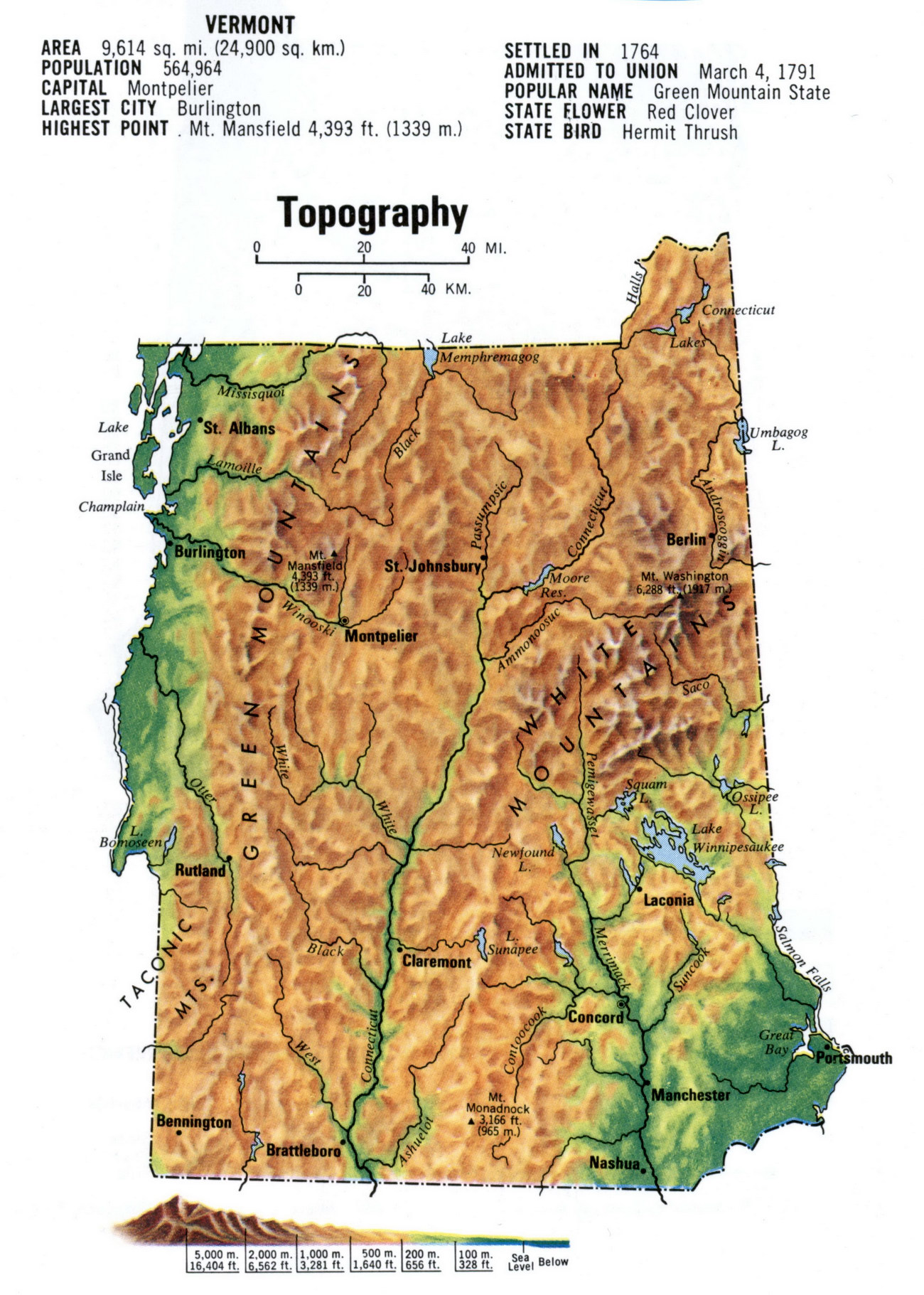
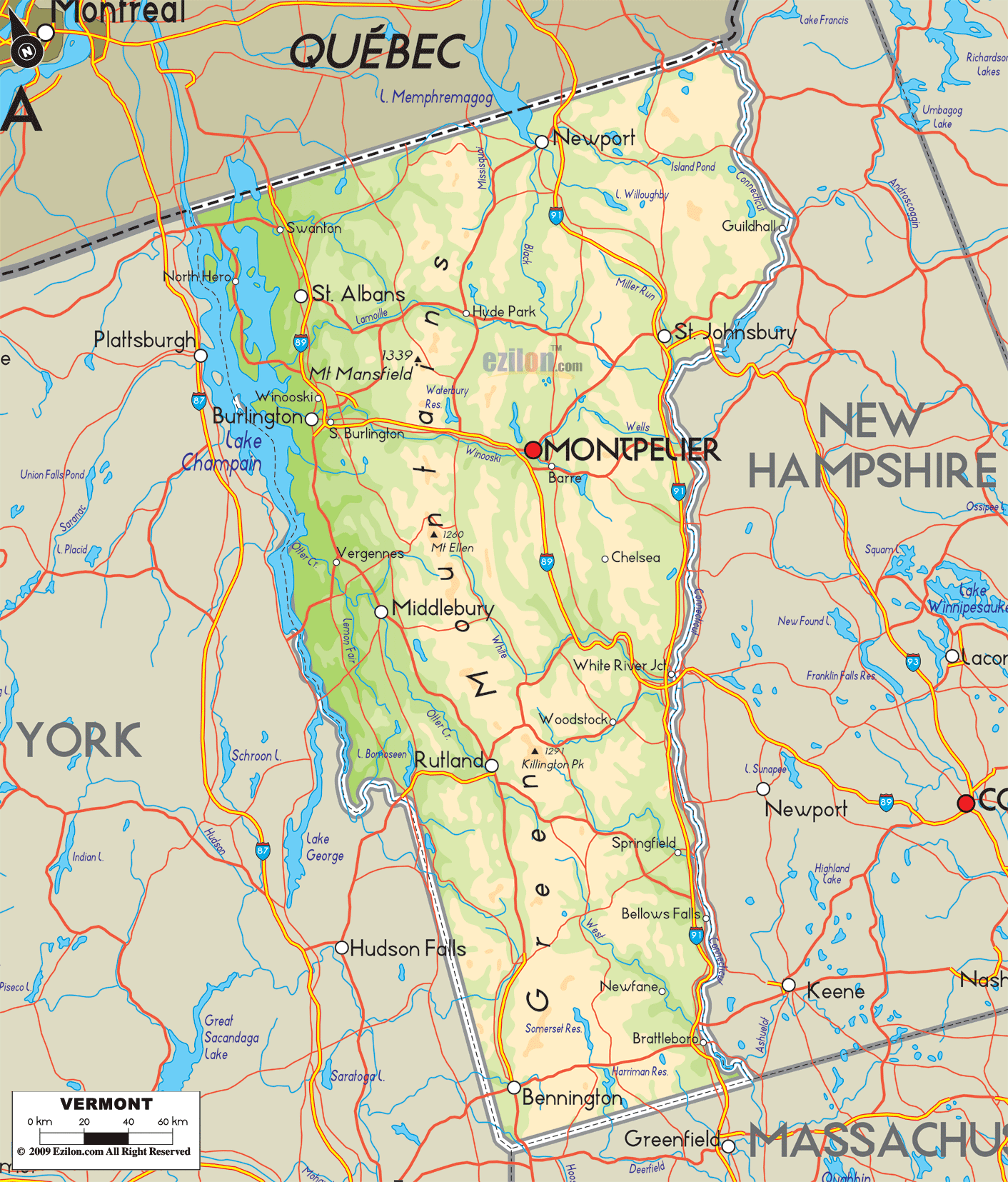
Vermont’s landscape is characterized by a distinct topography shaped by geological processes and glacial activity. The Green Mountains, a prominent mountain range running north-south through the state, form the backbone of Vermont’s topography. The mountains are dissected by valleys and rivers, creating a diverse landscape of hills, plateaus, and riverine lowlands.
Key Topographical Features of Vermont:
- The Green Mountains: This range, known for its forested slopes and scenic vistas, reaches its highest point at Mount Mansfield, the highest peak in Vermont.
- The Champlain Valley: This fertile valley, located along the western border of Vermont, is characterized by low elevation and rich agricultural land.
- The Connecticut River Valley: This valley runs along the eastern border of Vermont, featuring a gently sloping landscape and fertile soils suitable for agriculture.
- The Taconic Mountains: Located in western Vermont, these mountains are smaller than the Green Mountains, offering picturesque views and challenging hiking trails.
Exploring Topographical Maps: Resources and Tools
Numerous resources are available for accessing and utilizing topographical maps of Vermont, both online and in print format.
Online Resources:
- USGS TopoView: This website offers free access to USGS topographic maps, allowing users to view, download, and print maps for specific areas.
- CalTopo: This online mapping platform provides a comprehensive suite of tools for creating custom maps, analyzing terrain, and planning outdoor activities.
- Google Earth: This platform allows users to explore Vermont’s topography in a 3D environment, providing a visual understanding of the landscape.
Printed Resources:
- USGS Topographic Maps: These maps are available for purchase from the USGS store or from local retailers specializing in outdoor equipment.
- Trail Maps: Many hiking trails and outdoor recreation areas in Vermont provide detailed topographical maps for navigation and planning.
FAQs: Navigating the World of Topographical Maps
Q: What is the difference between a topographical map and a regular map?
A: A topographical map focuses on representing elevation and terrain features using contour lines, while a regular map emphasizes political boundaries, cities, and roads.
Q: How do I read a topographical map?
A: Familiarize yourself with contour lines, elevation points, and symbols. Closer contour lines indicate steeper slopes, while widely spaced lines suggest gentler terrain.
Q: What are the best resources for finding topographical maps of Vermont?
A: Online resources like USGS TopoView and CalTopo offer free access to maps, while printed maps are available from the USGS store or outdoor retailers.
Q: Can I use a topographical map for navigation on my phone?
A: Yes, several apps like Gaia GPS and Avenza Maps allow you to download and use topographical maps on your mobile device.
Tips for Utilizing Topographical Maps: A Guide for Exploration
- Identify the Map’s Scale: The scale indicates the ratio between the map’s distance and the actual distance on the ground, crucial for accurate distance calculations.
- Understand Contour Intervals: The interval between contour lines determines the elevation difference represented by each line, aiding in understanding slope gradients.
- Utilize Symbols and Legends: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used to represent features such as rivers, roads, and vegetation, ensuring accurate interpretation.
- Consider the Map’s Date: Maps can become outdated, so check the publication date to ensure accuracy, especially for areas with dynamic environments.
- Use a Compass and Altimeter: These tools, combined with a topographical map, provide accurate navigation and elevation measurements.
Conclusion: A Window into Vermont’s Natural Beauty
Topographical maps provide a powerful tool for understanding and appreciating Vermont’s diverse and captivating landscape. From navigating hiking trails to planning land management strategies, these maps offer a visual language that unlocks the secrets of the terrain. By utilizing these resources, individuals can explore Vermont’s natural beauty, engage in responsible outdoor recreation, and contribute to the sustainable management of this unique and treasured landscape.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape of Vermont: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographical Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!